Functions
Miscellaneous
part of the limbic system; influences emotion such as aggression
amygdala
what is the center for processing sensory information
forebrain
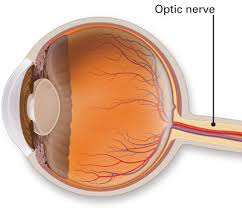
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
smell
olfactory
subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities
somatic nervous system
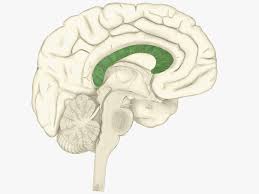
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
bridge to transmit signals from hindbrain and forebrain
midbrain
the first pair of cranial nerves
olfactory nerves
sight
optic
subdivision of nervous system composed of cranial and spinal nerves
peripheral nervous system
located in left frontal lobe; controls production of speech
broca's area
control center for visceral functions
hindbrain
the second pair of cranial nerves lead from the eyes to the occipital lobes of the brain
optic nerve
face sensation
trigeminal
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
wrinkled outer portion of the brain
cerebral cortex
regulation of voluntary movement
cortex
third pair of cranial nerves arise from the midbrain and pass into the orbits of the eyes where one component of each nerve connects to voluntary muscles that raise the eyelids
oculomotor nerves
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
cells that support, insulate, and protect neurons
neuroglia
part of the brain that coordinates balance, movement, reflexes
cerebellum
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
smallest cranial nerves
trochlear nerve
moves tongue
hypoglossal
end of neuron that releases neurotransmitters away from the cell body
axon