Functions
Miscellaneous
Meaning of Rostral and Caudal
Rostral - toward the forehead
Caudal - toward the spinal cord
Pineal Gland secretes
Melatonin
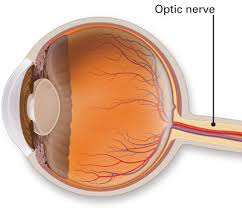
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
Olfactory Nerve
Smell
Wernicke’s area function
Reading, writing, speaking, and understanding words
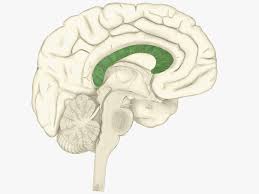
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
Diencephalon contains
Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus (pineal gland)
Optic nerve is #
II
Abducens nerve
Movement of eyeball
What tract connects left and right cerebral hemispheres?
Corpus callosum
Meninges in order for superficial to deep
Dura Mater, Arachnoid Mater, Pia Mater
Function of cerebrospinal fluid
Buoyancy, protection, and chemical stability
Vestibulocochlear nerve is #
VIII
Movement of the eye is sensory or motor or both
Motor
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
Dura Mater attached to which bone and bone surface?
Cerebrospinal fluid is reabsorbed by
Arachnoid villi
All ascending and descending fibers connecting brain and spinal cord pass through the
Medulla
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
Limbic system location
In each cerebral hemisphere
Blood brain barrier is for what?
Regulates what substances can get from bloodstream into tissue fluid of the brain
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
Cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII are located where
The Pons
Hypoglossal nerve
Movement of tongue during speech and swallowing
Lesions of cerebellum can cause
Ataxia