Functions
Miscellaneous
Major components of brain
Diencephalon, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Functions of CSF (cerebral spinal fluid)
Buoyancy, Protection, Chemical stability
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
Olfactory nerve
Smell
Wernicke Area
Permits recognition of spoken and written language
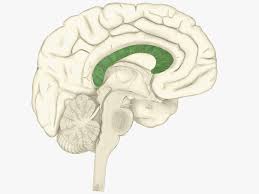
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
Frontal Lobe
Reasoning, planning, speech
What is cranial nerve #4
Trochlea nerve, motor nerve that innervates the superior oblique muscle of eye
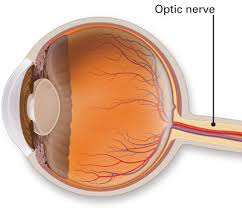
Optic nerve
Vision processing
Left hemisphere
Usually the categorical hemisphere
Gyri
Thick folds
Hypothalamus
Hormone secretion, autonomic effects
What is cranial nerve #7
Facial nerve, emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression
Oculomotor nerve
Eye movements
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
Sulci
Shallow grooves
Parietal lobe function
Receives sensory input for touch and body position
What is cranial nerve #9
The glossopharyngeal nerve, mixed nerve that carries both afferent sensory and efferent motor information. Exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
Right hemisphere
Usually the representational hemisphere
brainstem
What remains of the brain if the cerebrum and cerebellum are removed
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
What is cranial nerve #11
The accessory nerve supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
Controls movement of lateral rectus muscle, responsile for outward glaze
Sensory & Motor fibers
motor fibers begin in nuclei of brainstem and lead to the glands and muscles.
snesory fiber begin in receptors located mainly in head and neck and lead mainly to the brainstem