What parts of the body are included in the central nervous system (CNS)?
Brain & spinal cord
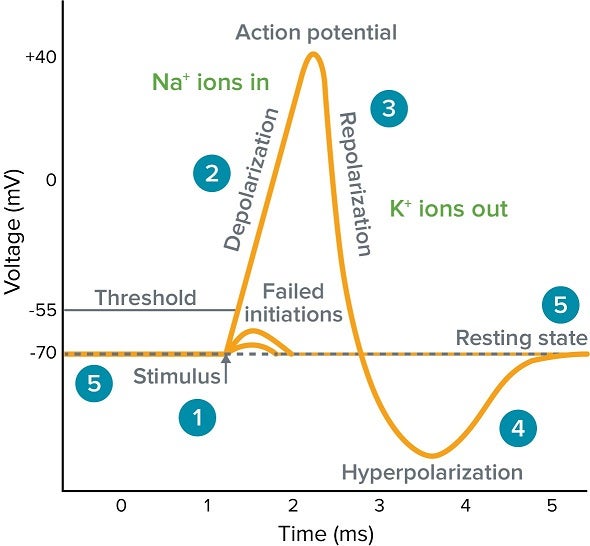
During action potential, the -70mV value on the neuron cell membrane is the value of:
Resting Membrane Potential
Which part of the neuron is the receptor and receives the signal?
Dendrites
The meninges are best described as:
Protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord - cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the spaces to bathe them, absorb shock, and exchange nutrients/wastes between blood and nervous tissue
Explain what a "knee jerk reaction" is?
An involuntary reaction to a stimulus
The sympathetic nervous system controls all _________ responses of the body.
The parasympathetic nervous system ___________ the body.
fight or flight (emergency situations)
calms
Repolarization
What is the space between two neurons at a synapse called?
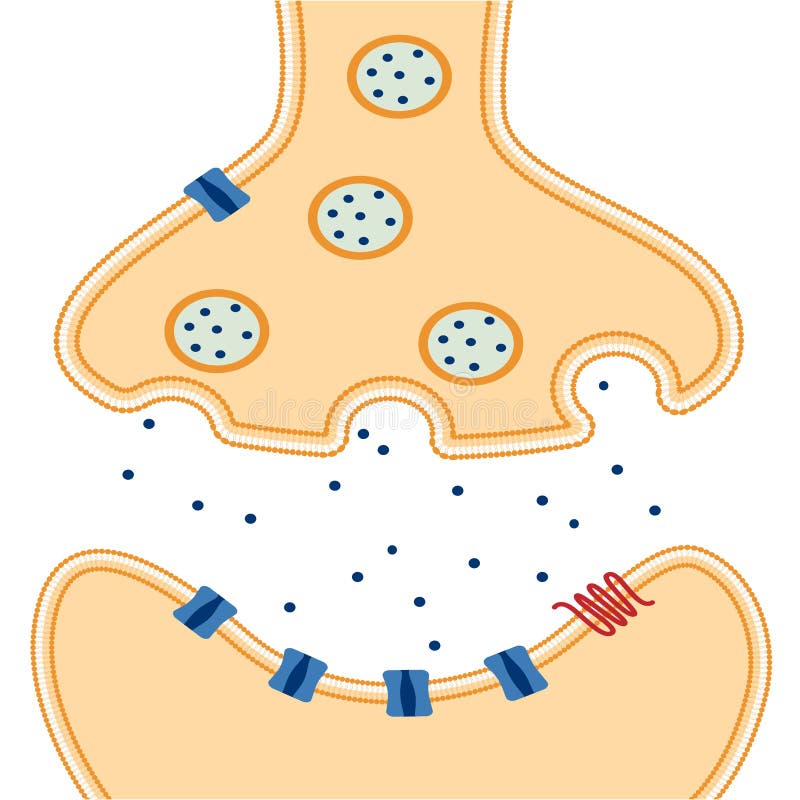
Synaptic cleft
What is the green portion and what is its function?
Cerebellum - responsible for balance and coordination
What are the neurons called in the gray matter of the spinal cord that connects and translates from sensory neurons to motor neurons?
Interneurons
Describe function the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Central nervous system (CNS) - control center of the body (interprets information from the PNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) - receives information from the environment and relays commands from the CNS to organs and glands
During an action potential the neuron cell membrane opens sodium gates and sodium rushes into the cell, what is this called?
Depolarization
________________ are structural and functional units of the nervous system , whereas _______________ are accessory cells in nerve tissue.
Neurons & neuroglial cells
What is the blue portion of the brain and what is its function?
Cerebrum - largest part of the brain that controls senses, thoughts, emotions, and imagination
Afferent neurons communicate to the spinal cord through the
C (afferent root)
Describe the function of the sensory division and the motor division within the peripheral nervous system.
Sensory division - transmit impulses from sense organ to the CNS
Motor division - transmits impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands
Explain what resting membrane potential is.
•When a neuron is “at rest,” it is constantly pumping sodium ions out and potassium ions in to maintain a potential across the membrane of about –70 millivolts.
•The outside of the neuron has a slightly positive charge, the inside a slightly negative charge.
•Membrane potential is a potential gradient that forces ions to passively move in one direction: positive ions are attracted by the 'negative' side of the membrane and negative ions by the 'positive' one.

Label the neuron.
A - dendrite
B - cell body
C - axon
D - myelin sheath
E - node
F - axon terminal
The medulla oblongata is colored orange at the inferior portion of the brain stem. What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
Regulates breathing & heart rate
Afferent nerves are called____________
Efferent nerves are called____________
sensory nerves
motor nerves
Describe the function of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system.
Autonomic nervous system - regulates activities that are involuntary (heart rate, glands, digestion)
Somatic nervous system - regulates activities under voluntary control (skeletal muscle movement, reflexes)
Draw an action potential graph and label the graph with resting potential, threshold, hyperpolarization, depolarization, repolarization, and stimulus.
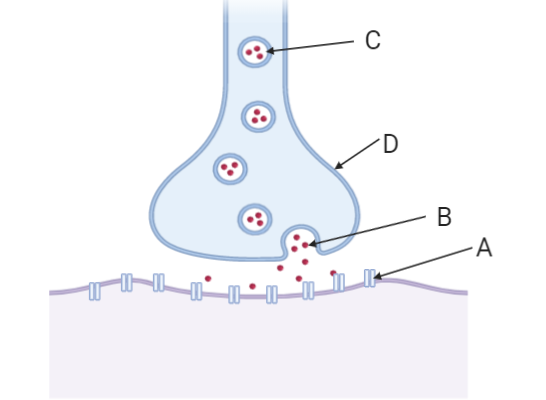 Label A, B, C, D
Label A, B, C, D
A - receptor
B - neurotransmitters
C- synaptic vesicle
D - presynaptic neuron
What is the primary function of the hypothalamus?
Temperature regulation and hunger
What are the four steps for a reflex arc?
5 (receptor), 4 (afferent root), 9 (efferent root), 8 (effector)