Which of the following best describes the dark-stained basophilic structures within the cytoplasm of the neuronal cell bodies?
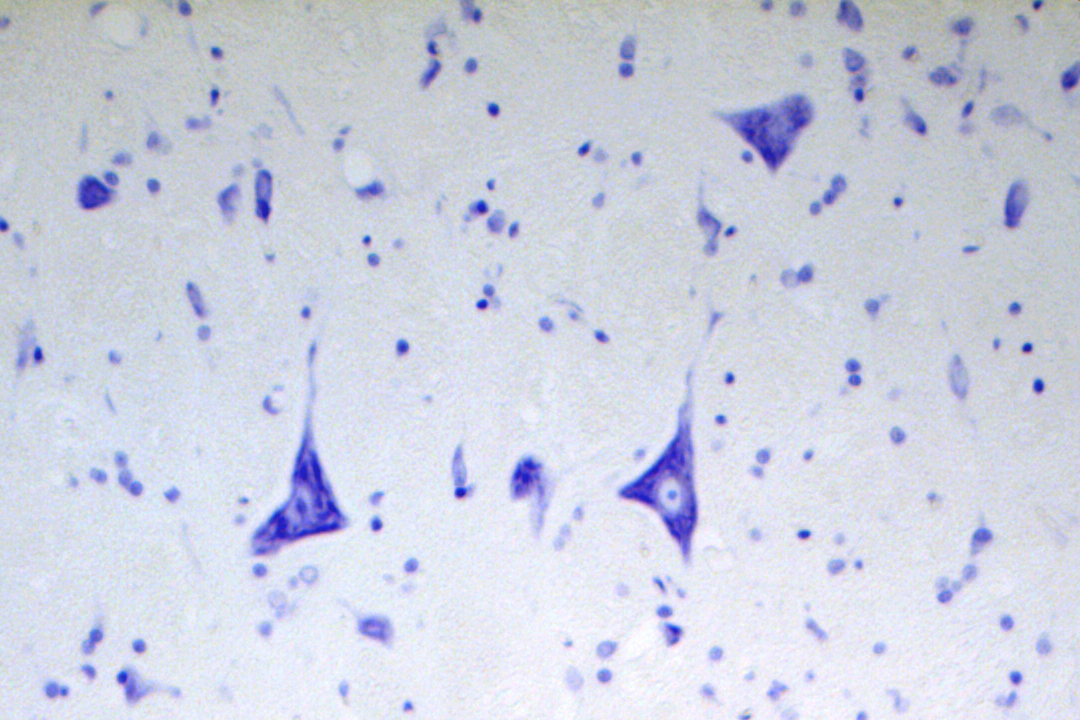
(A) Heterochromatin
(B) Lysosomes
(C) Nissl bodies
(D) Peroxisomes
(E) Segmented nuclei
(C) Nissl bodies
35-year-old woman injures her common fibular nerve in a motorcycle accident. Which of the following best describes the primary function of neuronal axons ?
(A) Convey signals to dendrites
(B) Receive signals from other neurons
(C) Synthesize structural proteins
(D) Transmit signals to other cells
(E) Uptake of neurotransmitters
(D) Transmit signals to other cells
Which of the following glial cells contributes to the formation of the blood–brain barrier in the central nervous system?
(A) Astrocytes
(B) Ependymal cells
(C) Microglial cells
(D) Oligodendrocytes
(E) Schwann cells
(A) Astrocytes
•The structure labeled by the arrow is which of the following?
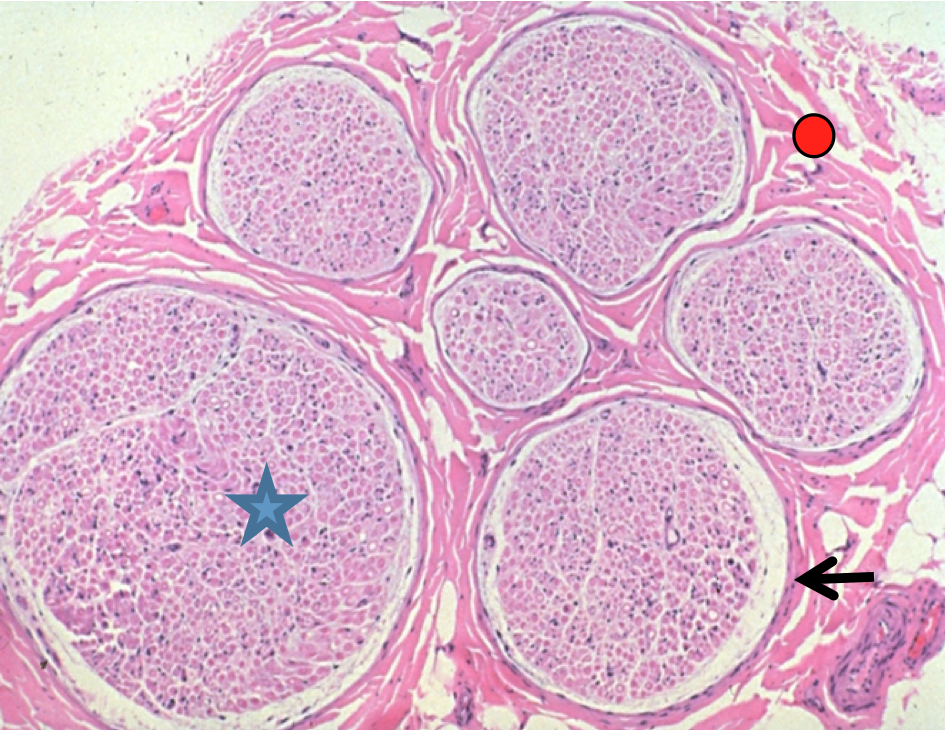
a. Perineurium
b. Epineurium
c. Endomysium
d. Perimysium
e. Tunica media
a. Perineurium
For the nerve specimen provided in this photo, the nucleus shown is of which of the following glial cells?
(A) Astrocyte
(B) Fibroblast
(C) Oligodendrocyte
(D) Satellite cell
(E) Schwann cell
(E) Schwann cell
Which of the following cellular structures lacks Nissl granules?
(A) Axon hillock
(B) Centromere
(C) Centrosome
(D) Kinetochore
(E) Dendrites
(A) Axon hillock
An 80-year-old woman with a history of diabetic neuropathy suffers a stroke and died. At autopsy, a peripheral nerve is examined by electron microscopy (shown in the image). Which of the following best describes the structures that are darkly stained?

(A) Endoneurium
(B) Epineurium
(C) Glycocalyx
(D) Myelin sheath
(E) Perineurium
(D) Myelin sheath
A 27-year-old man suffers a gunshot wound to the thorax and died. A dorsal root ganglion near the bullet track is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). The green labelled nuclei identify which of the following types of cells?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2398/bp1maeDiYMY94Pm9Dd3eQ_Satellite_cells.png)
(A) Astrocytes
(B) Neurons
(C) Oligodendrocytes
(D) Satellite cells
(E) Schwann cells
(D) Satellite cells
Which of the following intercellular junctions is essential for maintaining the integrity of the blood–brain barrier?
(A) Gap junctions
(B) Hemidesmosomes
(C) Macula adherens
(D) Zonula occludens
(E) Zonula adherens
(D) Zonula occludens
The mechanochemical enzyme that can be found on the surfaces of cellular organelles where it mediates movement toward the minus end of microtubules is which of the following?
a. Myosin (myosin II)
b. Minimyosin (myosin I)
c. Dynein
d. Kinesin
e. Filamin
c. Dynein
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the cells ( multiple small nuclei in the provided diagram)?

(A) Defense against pathogens and neoplastic cells
(B) Generation of cerebrospinal fluid
(C) Myelination of neuronal axons
(D) Phagocytosis of senescent neurons
(E) Support and nourishment of neurons
(E) Support and nourishment of neurons
A 70-year-old woman presents with a history of memory loss and occasionally becoming lost and disoriented in her own home. At autopsy, Which of the following is a key histological finding to the pathology underlying this patient’s disease?
a. Melanin
b. Lewy body
c. Dynein
d. Kinesin
e. Tau protein
e. Tau protein
A 35-year-old woman complains of blurred vision. Two months later, she develops double vision and numbness in the fingers. MRI shows scattered plaques in the brain and spinal cord suggestive of multiple sclerosis. This plaques represent selective loss of which of the following?
(A) Acetylcholine receptors
(B) Alpha-synuclein
(C) Beta-amyloid protein
(D) Myelin
(E) Tubulin
(D) Myelin
The cells in the accompanying photomicrograph, labeled with anti-GFAP, function to do which of the following?

A. Form synaptic contacts with neurons
b. Present antigen
c. Phagocytose dying neurons
d. Form a glial scar following damage
e. Form myelin in the CNS
d. Form a glial scar following damage
A 32-year-old man recently recovered from an infection and is now complaining of symmetrical weakness in the distal lower extremities. The patient is suffering from Guillain-Barre syndrome. Which cell type has been damaged?
a. Motor Neurons
b. Microglia
c. Schwann Cells
d. Astrocytes
e. Ependymal Cells
c. Schwann Cells
Which of the following are abundant in axons and are involved in anterograde bulk cytoplasmic transport?
A- synaptic vesicles
B- neurotubules
C- neurofilamintes
D- nissel graules
E- GFAP
B- neurotubules
Mutations in genes coding for proteins responsible for transporting neurotransmitter synthesized in the cell body to the axons terminals has been identified as the reason for motor neuron disease. Which of the following proteins might be a target for this mutation?
a- kinesin
b- dynein
c- actin
d- tau protein
e-myosin
a- kinesin
A nerve conduction velocity test performed on the ulnar nerve confirms markedly reduced conduction velocity. Which of the following cells synthesizing the defective protein in this patient ?
a. oligodendrocytes
b. microglia
c. Schwann Cells
d. astrocytes
e. Ependymal Cells
Schwann Cells
The micrograph shown in the image obtained from the brain of a 75-year-old man suffering from Parkinson's disease, at autopsy. Which of the following best describes the pathology underlying this patient’s disease process?
(A) Nerve cell body atrophy
(B) Defective transport along microtubules
(C) Loss of neural fibers
(D) Loss of pigmented neurons
(E) Malignant tumor cells derived from the nerve fibers
(D) Loss of pigmented neurons
44-year-old man after surgical amputation of the left leg, encounter severe pain. CT scan showed a neuroma at the stump of the left sciatic nerve. Which of the following contributed to this neuroma?
(A) Disintegration of Nissl granules
(B) Disintegration of microtubules
(C) Absence of Schwann Cells endoneural tube
(D) Loss of nerve cell processes
(E) Malignant Schwann cell tumor
(C) Absence of Schwann Cells endoneural tube