Dynamic Routing protocol that uses up to 15 hops to determine the shortest path between routers on a network
What is RIP?
This protocol is responsible for obscuring your private IP address when you are navigating the internet
What is Network Address Translation/NAT?

What is a firewall?
Reasons why we use plenum wiring
Plenum wiring refers to cables with a flame-retardant, low-smoke jacket designed for use in a plenum space, which is a building area used for air circulation, like the space above a dropped ceiling. These cables are required by fire codes to prevent the rapid spread of toxic smoke and fire through HVAC systems, ensuring greater safety for building occupants. Plenum-rated cables (CMP) are made with special materials like FEP or low-smoke PVC and are designed to be self-extinguishing.
The process DHCP goes through to assign an IP address (all steps)
What is Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge?
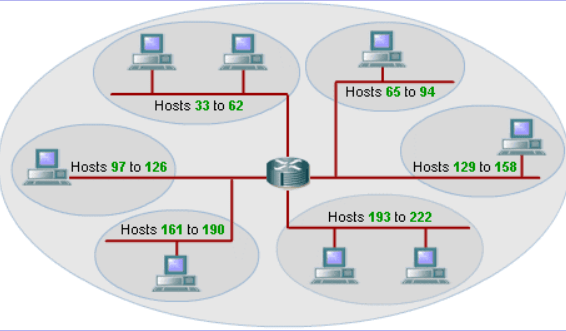
The subnet mask of this network (assume 192.168.1.x)
What is 255.255.255.224 or /27?
Dynamic routing protocol that efficiently exchanges routing information within an autonomous system using the Shortest Path First algorithm
What is OSPF/Open Shortest Path First?
This kind of NAT allows for a large number of devices to share the same external IP address
What is a Dynamic NAT?
This type of device includes a firewall as well as many other security focused appliances in one device
What is a Unified Threat Management/UTM?
Purpose of a patch panel
Patch panels are used to organize, simplify, and centralize network and audio/video cabling. They serve as a central point for all cables, making it easier to move, add, or change connections without having to run new wires directly to the equipment. This organization also reduces cable clutter, improves airflow, simplifies troubleshooting, and protects the jacks on more expensive devices from wear and tear.
Type of autoconfiguration for IPv6 networks that does not require a central server.
What is Stateless Address Autoconfiguration/SLAAC?
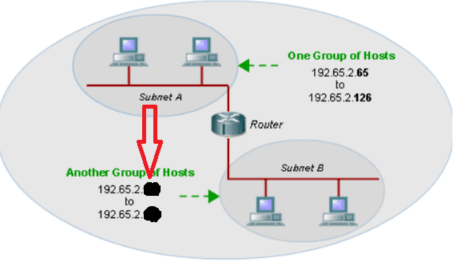
The first available HOST IP in the bottom network
What is 192.65.2.129?
What is port 443 HTTPS
This type of NAT allows inbound connections to start from outside the network
What is a Static NAT?
Description of a NGFW
NGFWs combine traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features like deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and application awareness.
Administrative Distance is this
The purpose of administrative distance (AD) is to help a router choose the best route to a destination when it has learned about the same destination from multiple routing sources, such as different routing protocols. It is a measure of the trustworthiness of the source, with a lower AD value indicating a more reliable and preferred source. Routers use AD to rank the reliability of different routes and install the one with the lowest AD in its routing table.
Type of IPv6 autoconfiguration, uses a central server but gives a lot more control over how your network is configured
What is DHCPv6?
The broadcast IP for the network that host 192.168.0.35 is on when there are 64 possible hosts on the subnet
What is 192.168.0.63?
/26 network, 192.168.0.0 network address
Explain what a routing protocol is and/or does
Routing protocols are rules that routers use to communicate and determine the best path for data to travel across a network. They help ensure efficient, reliable delivery of packets between devices.
What Are Routing Protocols?
Routing protocols enable routers to dynamically discover and share information about network paths. They help routers build and maintain routing tables, which are used to decide where to forward packets. Without routing protocols, routers would need manual configuration for every possible route — a nightmare in large networks.
Key Functions of Routing Protocols
- Discover network paths
- Share routing information with neighboring routers
- Calculate the best route based on metrics like hop count, bandwidth, or delay
- Update routes when network topology changes
- Provide fault tolerance by rerouting traffic if a path fails
Types of Routing Protocols
Routing protocols are typically classified into three main categories:
Type Description Example Distance Vector Chooses path based on hop count; routers share entire routing tables periodically. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) Link-State Builds a complete map of the network; routers share only topology changes. OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Hybrid Combines features of both distance vector and link-state. EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
Interior vs Exterior Routing Protocols
- Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs): Used within a single organization or autonomous system.
- Examples: RIP, OSPF, EIGRP
- Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs): Used between different organizations or autonomous systems.
- Example: BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
Routing Metrics
Routing protocols use metrics to evaluate the best path:
- Hop count (RIP)
- Bandwidth (EIGRP)
- Delay
- Cost (OSPF)
Static vs Dynamic Routing
- Static Routing: Manually configured routes; no protocol involved.
- Dynamic Routing: Routes are learned and updated automatically using routing protocols.
This protocol maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address using different port numbers
What is Port Address Translation/PAT?
Describe the difference between stateful and stateless packet inspection firewalls
Stateful firewalls track active connections and make decisions based on context, while stateless firewalls treat each packet independently without memory of past traffic.
Stateless Firewalls
- How they work:
Stateless firewalls inspect each packet individually, without considering previous packets or connection state. - Filtering method:
They rely solely on static rules based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols. - Pros:
- Faster performance due to simpler processing
- Easier to configure for basic traffic filtering
- Lower resource usage
- Cons:
- No awareness of connection state
- Vulnerable to spoofing and certain types of attacks
- Less effective for complex traffic patterns
- Use case:
Often used in simple or high-speed environments where minimal filtering is needed.
Stateful Firewalls
- How they work:
Stateful firewalls monitor the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of traffic flow. - Filtering method:
They track TCP sessions and other connection details, allowing them to understand whether a packet is part of a valid, established session. - Pros:
- More secure and intelligent filtering
- Can detect abnormal behavior and block suspicious traffic
- Better suited for dynamic environments
- Cons:
- Higher resource consumption
- Slightly more complex configuration
- May introduce latency in high-throughput networks
- Use case:
Ideal for enterprise networks and environments requiring robust security and traffic analysis.
A load balancer does this (don't just say it balances loads)
A load balancer is a device or software that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, improving performance, reliability, and availability.
Here’s a deeper dive into how load balancers work and why they’re essential:
What Does a Load Balancer Do?
A load balancer acts like a traffic director for your network or application. When multiple users try to access a website or service, the load balancer ensures that the requests are evenly distributed across a group of servers — known as a server pool or server farm — so that no single server bears too much load.
Without a load balancer, one server might get overwhelmed while others sit idle, leading to slow performance or even outages.
How Load Balancing Works
- Traffic Distribution: The load balancer receives incoming requests and forwards them to one of the available servers based on a specific algorithm.
- Health Monitoring: It continuously checks the health of servers. If a server goes down, the load balancer stops sending traffic to it.
- Failover Support: If one server fails, traffic is rerouted to healthy servers, ensuring high availability.
- Session Persistence: Some load balancers can keep a user connected to the same server during a session, which is important for applications that store session data locally.
Common Load Balancing Algorithms
- Round Robin: Distributes requests sequentially across servers.
- Least Connections: Sends traffic to the server with the fewest active connections.
- IP Hash: Uses the client’s IP address to determine which server will handle the request.
Types of Load Balancers
Real-World Use Cases
- Web Applications: Distribute user traffic to multiple web servers.
- Cloud Services: Balance workloads across cloud instances.
- Data Centers: Ensure uptime and scalability for enterprise applications.
Benefits of Load Balancers
- High Availability: Prevents downtime by rerouting traffic during failures.
- Scalability: Easily add or remove servers without disrupting service.
- Improved Performance: Reduces latency and speeds up response times.
- Security: Can help mitigate DDoS attacks by absorbing and distributing traffic.
Give me an valid host IP w/ CIDR that will give you 8 class C subnets
Something that ends with /27, isn't a multiple of .32 or .31
Alvin is planning 3 sequential networks and needs help figuring out the subnet masks. 192.168.0.27 and 192.168.0.62 are on the same subnet, 192.168.0.70 is on the following network, and 192.168.0.81 is on the last network, which should be assigned this CIDR value to minimize wasted IP addresses
What is /30?
Network 1 is a /26 from .1-.62, network 2 is a /28 from .65-.78
This happens when a static route fails but has OSPF enabled
When a static route fails and the router also has OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) enabled, the router can automatically fall back to a dynamic route learned via OSPF — but only if the OSPF route has a lower administrative distance than the failed static route or if the static route is removed from the routing table.
Routing Decision Logic
Routers choose routes based on administrative distance (AD) — a value that ranks the trustworthiness of a route source. Lower AD means higher priority.
So normally, a static route is preferred over OSPF.
What Happens When the Static Route Fails?
- If the static route becomes unreachable (e.g., the next-hop IP is down or the interface goes down), the router removes it from the routing table.
- OSPF steps in: If OSPF has a valid route to the same destination, it will be installed in the routing table.
- Traffic reroutes: Packets destined for that network will now follow the OSPF-learned path.
Example Scenario
- You have a static route:
ip route 192.168.50.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 - OSPF also advertises 192.168.50.0 via a different path.
- If 10.1.1.1 becomes unreachable:
- The static route is removed.
- The OSPF route (AD 110) is installed.
- Traffic flows through the OSPF path.
Pro Tip for Network+ N10-009
This behavior is part of route failover and redundancy planning. You can also configure floating static routes with a higher AD (e.g., 120) so they act as backups to OSPF — the reverse of the default behavior.
The purpose of port forwarding
Port forwarding allows external devices to access services on a private network by directing traffic from a specific port on a public IP to a designated device and port inside the network. It’s essential for enabling remote access to internal resources like web servers, gaming consoles, or surveillance systems.
Why Use Port Forwarding?
Here’s why port forwarding is useful:
- Remote Access:
Access internal services (e.g., a home web server or security camera) from outside your network. - Online Gaming:
Improves connectivity and reduces lag by allowing game servers to communicate directly with your console or PC. - Hosting Services:
Lets you run a website, FTP server, or other service from your home or office network. - Peer-to-Peer Applications:
Enables apps like BitTorrent to connect more efficiently with other peers.
How Port Forwarding Works
- Incoming Request:
A device on the internet sends a request to your public IP address on a specific port (e.g., port 80 for HTTP). - Router Rule:
Your router checks its port forwarding rules and sees that traffic on port 80 should go to 192.168.1.10 (your internal web server). - Forwarding:
The router forwards the request to the internal device, which responds as if it were directly connected to the internet.
Port forwarding is often used with NAT (Network Address Translation). Since NAT hides internal IPs, port forwarding tells the router how to handle specific incoming traffic
A VPN does this
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet, protecting your data and masking your IP address. It enhances privacy, security, and can bypass geographic restrictions.
Here’s a breakdown of how VPNs work and why they matter:
What Is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a service that routes your internet traffic through a secure tunnel to a remote server operated by the VPN provider. This masks your real IP address and encrypts your data, making your online activity private and secure — even on public Wi-Fi.
️ How Does a VPN Work?
Encryption:
Your data is encrypted before it leaves your device, making it unreadable to hackers, ISPs, or anyone else trying to snoop.Tunneling:
The encrypted data travels through a secure “tunnel” to a VPN server, which then forwards it to the internet.IP Masking:
The websites and services you access see the VPN server’s IP address, not yours — hiding your location and identity.Decryption:
Once the data reaches the VPN server, it’s decrypted and sent to its final destination.
Key Benefits of Using a VPN
- Privacy Protection: Hides your IP address and browsing activity from ISPs and third parties.
- Security on Public Wi-Fi: Shields your data from hackers on unsecured networks like coffee shops or airports.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: Access content and websites that may be blocked in your region (e.g., streaming services).
- Avoid Censorship: Useful in countries with restricted internet access.
- Remote Access: Enables secure access to corporate networks for remote workers.
Common VPN Protocols
Protocol Description OpenVPN Highly secure and widely used; open-source. IKEv2/IPSec Fast and stable, especially on mobile. WireGuard Newer, lightweight, and very fast. L2TP/IPSec Older, less efficient, but still used.
️ What a VPN Can’t Do
- Complete Anonymity: VPNs hide your IP, but websites can still track you via cookies or browser fingerprinting.
- Protection from Malware: VPNs don’t replace antivirus software.
- Illegal Activity: VPNs don’t make illegal actions legal.
Choosing a VPN
When selecting a VPN, look for:
- No-log policy
- Strong encryption
- Fast speeds
- Wide server network
- Multi-device support
Explain STP (not the ethernet one)
Describe STP
Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 network protocol that prevents broadcast storms and network loops by creating a single, active, loop-free logical path between switches, while simultaneously maintaining redundant links for failover. It works by electing a root bridge and then blocking redundant paths that would cause a loop, putting them in a standby state. When a primary path fails, STP unblocks a redundant path to restore connectivity.
The broadcast address of 192.168.0.157/23
What is 192.168.1.255?
Katharin went to Starbucks with her laptop and got on the wifi, a week later she noticed unexpected charges on a credit card she did not use to purchase anything with at Starbucks, but did order a cute little hat for her dog while she was there with it, because this happened to her
What is an on path or man in the middle attack? I will also accept social engineering but need you to know this is what they expect as an answer to this.