What does the Application Protocol do?
An application protocol is a messaging protocol that defines the language network applications use to fulfill user requests.
Application layer protocols are the topmost layer of the protocol hierarchy, where actual communication begins. It governs the way the client and server communicate.
What are the characteristics of an Ethernet cable?
In twisted-pair cables, wires are grouped in pairs and twisted together to reduce interference.
The pairs of wires are colored so that the same wire at each end can be easily identified.
What does a switch use to send data?
IP Address or Mac Address?
Mac Address. Layer 2 Addressing!
What is Encapsulation?
The process of placing one message format inside another message format.
Russian Nesting Dolls

What does the Internet Protocol do?
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a protocol, or set of rules, for routing and addressing packets of data so that they can travel across networks and arrive at the correct destination.
Data is taken from the transport protocol, encapsulated into smaller pieces called packets and addressed so they can reach their intended destination across networks.
What are the criteria for choosing a network medium?
Criteria for choosing a network medium are the distance across which the selected medium can successfully carry a signal, the environment in which the selected medium is to be installed, the amount of data and the speed at which the data must be transmitted, and the cost of the medium and its installation.
What does a Switch use to build it Mac Address Table?
The Source Mac address of a packet.
What do all communication methods include?
All communication methods include a message source, destination, and a transmission medium.
What are the min and maximum sizes that can be sent by an Ethernet frame?
According to the Ethernet standards, each Ethernet frame can carry 46 to 1500 bytes of user data. During the encapsulation process, other fields are added, such as destination MAC address, source MAC address, and FCS.
The size of Ethernet frames is normally limited to a maximum of 1518 bytes and a minimum of 64 bytes.
What does the Network Access Protocol do?
Network access protocols are a set of rules that govern how connected devices communicate across a network.
They are similar to a common language for devices to communicate with each other, regardless of differences in software, hardware, or internal processes.
What type of network cable is the backbone of most networks?
Fiber-Optic
Disadvantages of using Fiber Optic Cables?
Cost
Which statement describes a MAC address?
It is a physical address assigned to an Ethernet NIC by the manufacturer.
What does a switch do if it get a frame/packet who's destination Mac address is not in it's Mac Address Table?
It floods the frame out all ports on the switch , excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
What does the Transport Protocol do?
Transport protocols are responsible for point-to-point communication between networked devices.
They are located on top of the IP protocol and allow applications to communicate with each other without directly interacting with the IP layer.
Name the different types of ethernet cables.
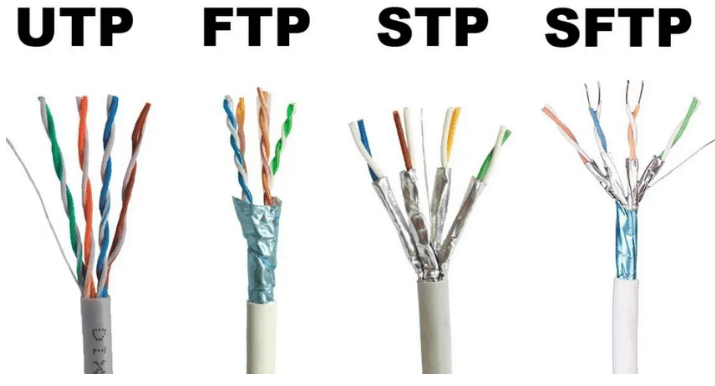
U/UTP - Unshielded cable, unshielded twisted pairs
F/UTP - Foil shielded cable, unshielded twisted pairs
U/FTP - Unshielded cable, foil shielded twisted pairs
S/FTP - braided shielded cable, foil shielded twisted pairs
Where: TP = twisted pair, U = unshielded, F = foil shielded, S = braided shielding.
Advantages of using Fiber Optic Cables?
Go farther before needing to be repeated
Fastest data transmission
Not susceptible to EMI or RFI
Name as many Standards Organizations as you can.

Which layers of the TCP/IP model match which layers of the OSI model map?

What does data communications protocol do?
A data communications protocol is a set of rules that govern how devices communicate and exchange information.
What does a Switch do if it get's a packet who's source Mac Address is not in it's Mac Address Table?
It adds it to the Mac Address Table.
Copper Cables:
Fiber Optics:
WiFi:
Copper Cables: Electric Pulses
Fiber Optics: Light Pulses
WiFi: Radio Waves