ID this structure.

Internal acoustic meatus
ID this region of the brain
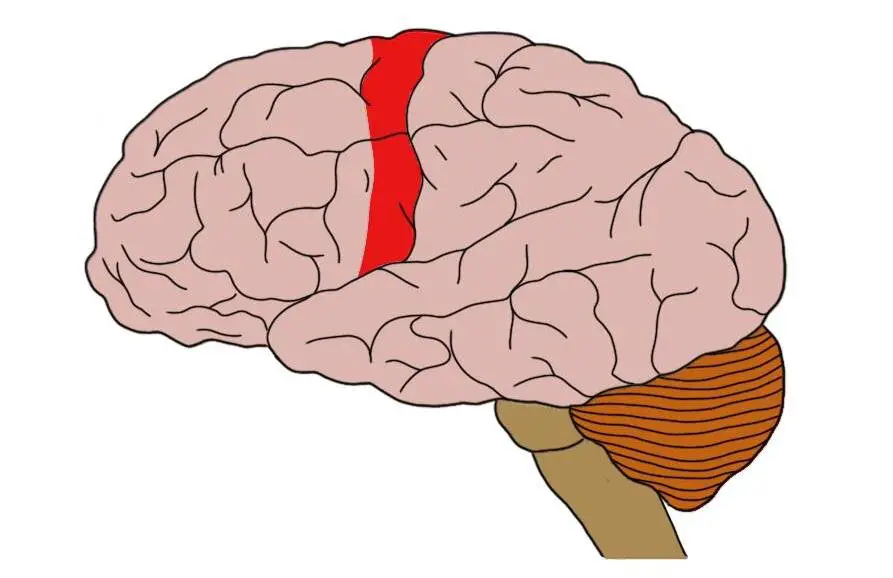
Primary motor cortex
ID this brainstem level

Caudal medulla
ID this CN
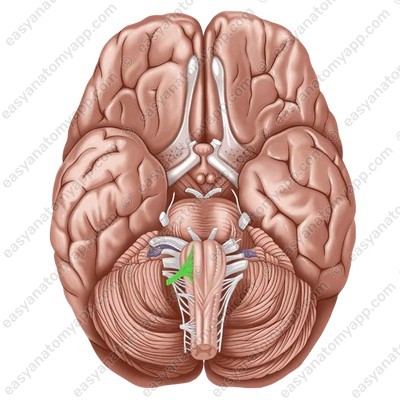
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
ID this blood vessel
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/arteria-cerebelli-anterior-inferior/thRyBCrBHtmNAGM4Etd2Q_A._inferior_anterior_cerebelli_01.png)
Name the cranial nerves that pass through this opening

CNIII, IV, V1, VI
What happens if this region of the brain is lesioned?
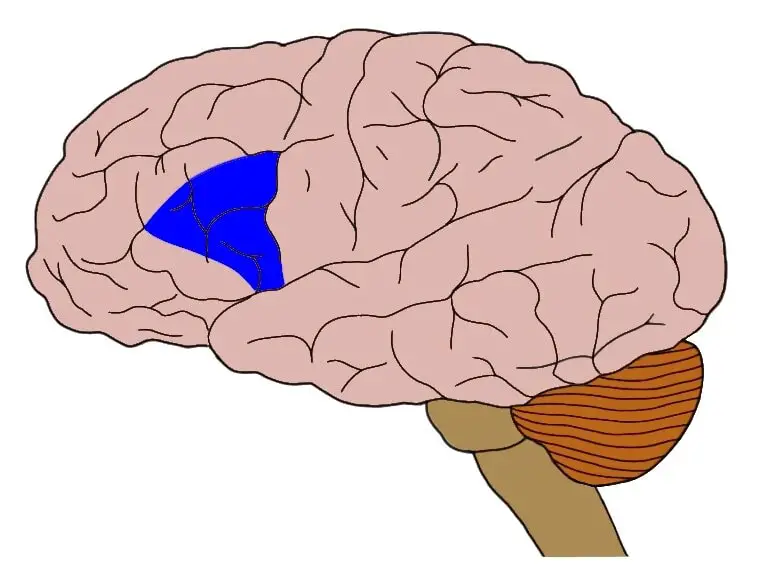
Broca’s aphasia (nonfluent speech + good comprehension + poor repetition)
Explain what happens if this region is lesioned
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/anterior-limb-of-internal-capsule/x3GjVESPfIgCf2dfSNaHOg_Anterior_crus_of_internal_capsule.png)
A large internal capsule lesion → contralateral severe UMN weakness + sensory loss (face/arm/leg) with facial involvement and possible dysarthria.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/internal-capsule/1cvCJe7bKI0gp2ZXOG0A_hqAgcc1Ntox2dpaMZbd8A_Internal_capsule.png)
What types of nerve fibers are contained in CN IX? (motor, sensory, special sensory, parasympathetic)
motor, sensory, special sensory, parasympathetic
What artery supplies the occipital lobe?
Posterior cerebral artery
What can happen when this area of the skull is lesioned?
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/foramen-ovale-3/fAu4C3pdGHxXQyynO1Rfw_Foramen_ovale_02.png)
Foramen ovale lesion → V3 sensory loss + weakness of mastication with jaw deviation toward lesion
What are the functions of this region of the brain?
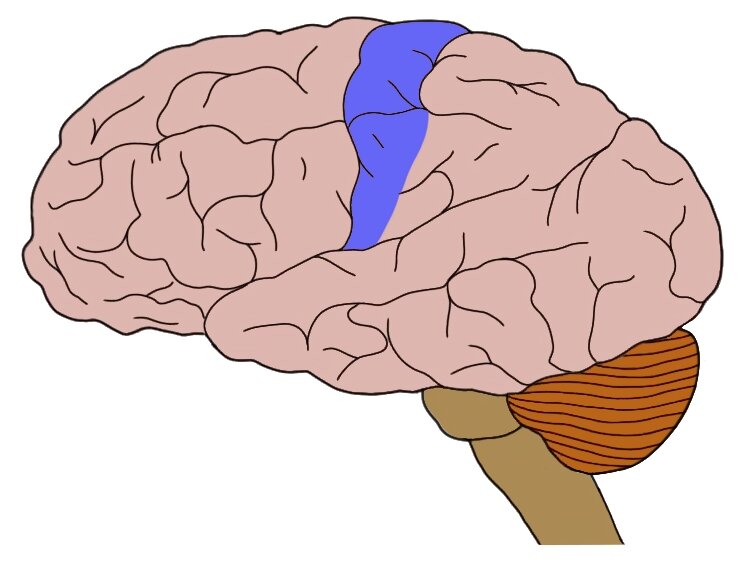
Primary somatosensory cortex – processes conscious touch, proprioception, pain, and temperature from the opposite side of the body
What is the name of the area circled and what is that area responsible for (be specific)?

Lateral spinothalamic tract. Pain & temperature.
A 35 y/o female presents with a severe recurring pain lasting <1 minute that she describes as “electric shock-like” affecting her jaw. What is the specific cranial nerve, branch, and name of this pathology?
CN V3, mandibular branch, trigeminal neuralgia
What artery supplies the midbrain and can cause an ipsilateral blown pupil when it impinges on CNIII (ex. Berry aneurysm)?
Posterior cerebral artery
What type of intracranial bleed would be caused by damage to the vessels that run in these grooves?

Epidural hematoma
A 45 y/o male presents to the ED after a motorcycle accident. He is alert and has normal sensation (normal two-point discrimination); however, when you ask him to close his eyes and use his hands to feel familiar objects (like a pen) he is unable to identify the object. 1) Which functional brain region is damaged and 2) What lobe is the lesion in?
Unimodal association cortex. Parietal lobe
Explain what neurologic signs/symptoms would occur if there was a lesion in the circled area. What side of the body would this affect?

L sided upper motor neuron symptoms (weakness, babinski sign, hyperreflexia, no muscle atrophy), lesion to L lateral cortical spinal tract in spinal cord
List all the functions of CN VII
Motor: muscles of facial expression, stapedius, (also to stylohyoid and posterior belly of digastric)
Sensory: small area of external auditory canal (behind the ear), part of tympanic membrane
Special sensory: taste to anterior ⅔ of tongue
Parasympathetic: lacrimal glands for tear production, submandibular and sublingual glands for saliva production (also to nasal and palatine glands)
An 80 y/o male presents with momentary blindness in his R eye caused by atherosclerosis of an artery in the optic canal. What this artery is a branch of what larger artery?
Internal carotid artery
A patient presents to your ED at 2AM following a barfight, they have craniofacial disjunction and the facial skeleton appears to be detached from the base of the skull. Name the fracture (be specific)?

Le Fort III fracture
A 35 y/o female with a history of intractable epilepsy underwent a surgery to treat her seizures. Her neurosurgeon states that the surgery went well, but she may experience a variety of symptoms such as: an inability to verbally identify objects presented in her left visual field or difficulty performing tasks requiring coordinated use of both hands. One week later she finds that she is able to paint with her left hand while solving calculus with her right. Explain what the surgical procedure was and why this explains her strange symptoms, identify the relevant area on this hemisection.

Cut the corpus callosum, resulting in split-brain syndrome AKA left & right hemispheres can’t communicate
What is the name of the circled structure?

Globus pallidus (output/motor of basal ganglia)
A 23 y/o female presents with numerous ecchymoses, stating that she falls every time she sees blood, hears Dr. Ahmed’s voice, or smells formaldehyde. What is the area of the brain responsible for this response and what cranial nerve provides the innervation?
vasovagal -> NTS -> CNX
A 70 y/o female presents with language deficits and R sided weakness/paralysis. What artery is most likely occluded?