What is evolution?
Change over time or descent with modification.
What are trephinations?
What is phrenology?
trephinations - holes drilled into the skull that were though to possibly treat conditions like headaches, seizures, or brain injuries - also possibly treating madness or evil spirits
phrenology - phrenologists believed that the bumps on the skull represented different mental strengths (pseudoscience)
What are the two types of fatty acids?
saturated - straight hydrocarbon chain with the max. number of hydrogens bind to the carbon with single bonds
unsaturated - bent hydrocarbon chains with less than the max. number of hydrogens bonded to carbon with some double bonds.
cis - hydrogen on same side of double bond, trans - hydrogen on opposite side of double bond
Draw and label a diagram of a General Prokaryotic Cell and what structures are contained in the cytoplasm?
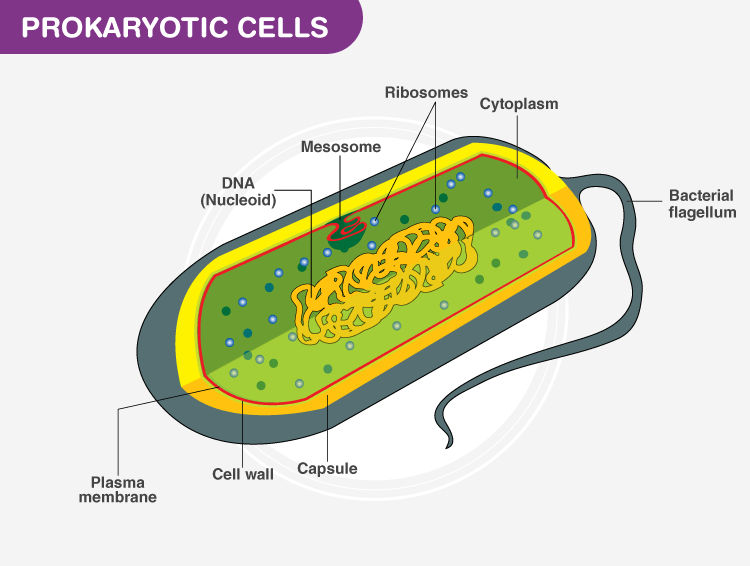
Nucleoid region, ribosomes, thylakoid
Who stated that human populations tend to increase much faster than resources?
The ideas of paleontology, gradualism, and economics affected two individuals, who were the first to apply these ideas to organisms?
Thomas Malthus
Charles Darwin - natural selection and Jean Baptiste de LaMarck - inheritance of acquired characteristics.
What is cell theory? What are the two types of cells found on Earth?
1.) all organisms are made of cells
2.) all cells come from pre-existing cells
Eukaryotic - nucleus, more complex structure found in all plants, animals, and fungi
Prokaryotic - no nucleus, much more simple structure found in bacteria and archaea
What are the two main ideas about the brain developed during 1700 CE to 1900 CE? What idea brought these two ideas together and what is it defined as?
localizationist- believed that certain areas of the brain controlled a function and only that function
holists - believed the entire brain was involved in mental function - no specialized areas
connectionism - areas of the brain responsible for certain functions, but these areas are connected and work together.
What are the characteristics of DNA and RNA?
DNA - double stranded that form a double helix, deoxyribose sugar in nucleotides, A,G,T, or C for nitrogen bases.
RNA - single stranded structure, ribose sugar in the nucleotides, A,G,U, or C for nitrogen bases.
Draw and label a diagram of a General Animal and Plant cell.
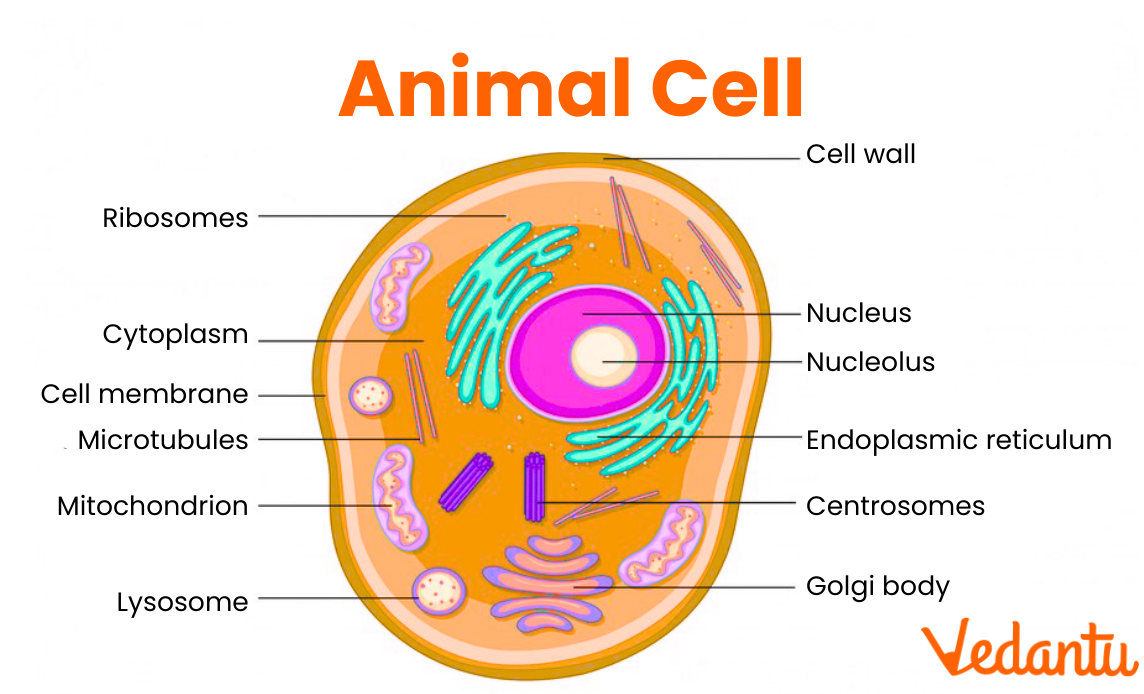
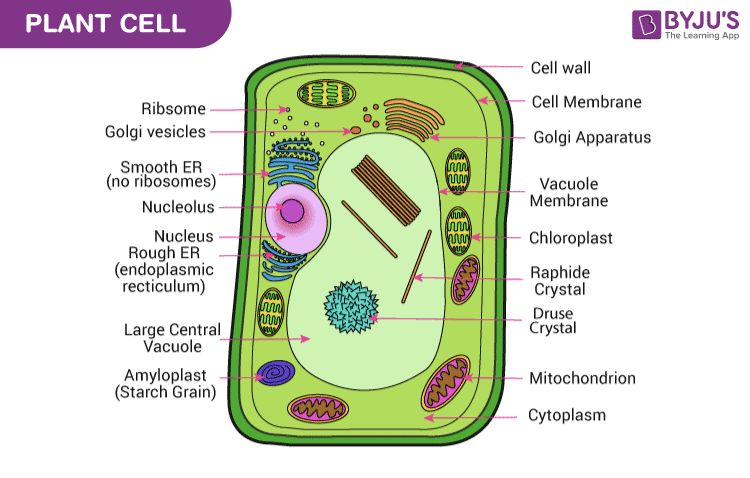
What is paleontology and who is the father of it?
What is gradualism and who developed it?
Paleontology- defined as the study of fossils - remains or traces of organisms from the past. Georges Cuvier
Gradualism- the idea that profound changes could take place through the accumulation of slow changes over time. Developed by geologists James Hutton and Charles Lyell
Define the following:
Neuroscience
Anatomy
Physiology
Pathology
Nervous System
Neuroscience- The study of the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the nervous system
Anatomy- the study of structures
Physiology- the study of function
Pathology- the study of diseases and disorders
Nervous System- body system that allows us to communicate with the environment - sensing things and responding to them
What did the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans believe was the center of mental functions
Egyptians and Greeks believed the heart was the center of mental function. Romans were first to associate the brain with mental processes.
What are the three types of carbohydrates and what are examples of each?
Monosaccharide - glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharide - sucrose, lactose, maltose
Polysaccharide - starch, glycogen, cellulose
Draw diagram of diffusion, facilitated transport, and active transport.

What are the four steps to Darwin's model of evolution?
*Look at peppered moths in England example*
Variation - individuals in a population are different - they each have unique characteristics or traits
Competition - individuals in a population must fight for a small and limited supply of resources needed to survive
Differing Reproduction - individuals in a population will reproduce at different rates and will have varying numbers of offspring
Adaptations - traits that will help organisms survive or compete for resources.
What are the two families of molecules on Earth?
What are the four families of organic molecules that build life?
Organic - building blocks of life made of a skeleton of carbon and hydrogen atoms to make big molecules
Inorganic - everything else which is usually very small molecules, some still essential to life
Four families are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids
Who began to conduct more careful studies in anatomy and made detailed drawings of the brain? Tell me about them
Leonardo da Vinci was one of the first people to make detailed anatomical drawings of the brain
Rene Descartes proposed the idea of daulism - humans have a material mind and a non-material soul
What are some examples of proteins?
Keratin - hair/nails
Collagen - Skin/tendons
Enzymes - speed up chemical reactions
Antibodies - part of the immune system to fight off foreign substances
What are the three types of solutions cells can be placed in based on tonicity and how may the cells change in practicable ways?
Isotonic - equal solute/water concentration inside and outside the cell. No change in cell.
Hypertonic - higher solute/lower water concentration outside of the cell compared to inside. Cell shrivels.
Hypotonic - lower solute/higher water concentration outside of cell compared to inside. Cell swells, possible bursts.
Darwin vs. LaMarck:
Why do modern day giraffes have long necks?
LaMarck:
1.)Early giraffes had short necks
2.)Giraffes stretch their necks to reach leaves on trees
3.)Offspring of those giraffes had slightly longer necks from the parents stretching
4.)Each generation got longer and longer until they didn't need to stretch
Darwin:
1.)Early giraffes had necks of varies lengths
2.)Longer necked giraffes had access to more resources
3.)Longer necked giraffes reproduced more
4.)Eventually only the ones with longest necks survived
What is the model used to describe the cell membrane?
Tell me about it.
Fluid-Mosaic model - a combination of phospholipids, steroids, and proteins that move positions and can change composition from the cell membrane.
What advancements has the modern era of neuroscience been dominated by?
Imaging technology has allowed modern neuroscientists to see the brain and its activity in living individuals
Molecular techniques have allowed modern neuroscientists to see the locations of proteins and other molecules in the brain
Surgical techniques have allowed modern neuroscientists to manipulate brain tissue and study behaviors
What are the different levels of structure that proteins are organized into?
Primary - linear sequence of amino acids
Secondary - when the linear sequence folds into commons shapes
Tertiary - when the shapes fold to form the final 3D protein structure
Quaternary - only occurs in proteins with multiple subunits - when multiple tertiary structures come together
Draw the five different types of membrane proteins found in cell membranes.



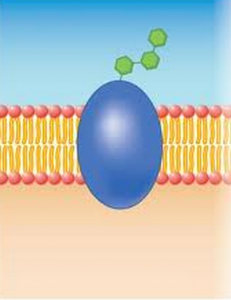
What are several good pieces of evidence for evolution?
Fossils - show that past life was different from present life
Anatomy - shows that the same structures are found in body parts with very different functions
Biochemistry - all organisms on earth have DNA, RNA and the same genetic code for proteins
Observable Evolution - sometimes, evolution can be observed in real time