She Moves
26 year old man evaluated for "episodes":
He has no memory of the episodes, family reports he suddenly stops talking and sometimes has twitching of the right arm. He will not look at them, will not speak, and does not follow verbal commands. Family members also report stiffness and clenching of his right hand toward the end of an episode, which typically lasts 30 to 90 seconds. After he regains speech and the twitching stops, he usually has slurred speech, right-arm weakness, and mild confusion for up to 30 minutes.
What type of seizure is the patient experiencing?
Focal seizure with impaired awareness
66 year old man is evaluated for abnormal behavior during sleep. Wife reports a prolonged history of nocturnal flailing and jerking movements and of shouting, punching, and jumping out of bed. The patient does not recall these movements and reports no discomfort. He also has a history of urinary incontinence and falls. He takes no medications.
On exam, vital signs are normal. He has reduced facial expression and bilateral rigidity. His gait is unsteady, with postural imbalance during turns, and he cannot walk in tandem. Other neurologic examination findings are unremarkable.
A polysomnogram reveals complex movements associated with preserved muscle tone during rapid-eye-movement sleep.
What is the diagnosis?
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder
54-year-old woman presents to ED with severe, nonpulsatile, bilateral occipital headache accompanied by photophobia and vomiting that suddenly began 3 hours ago. She describes the headache as being “different” from her usual migraine. Whereas rizatriptan typically is effective in resolving the migraine, neither rizatriptan nor ibuprofen has relieved her current symptoms.
All vital signs within normal limits. She appears uncomfortable and prefers a dark room; remainder of exam is unremarkable. Labs are within normal limits.
What is your next step in evaluating this patient?
Head CT
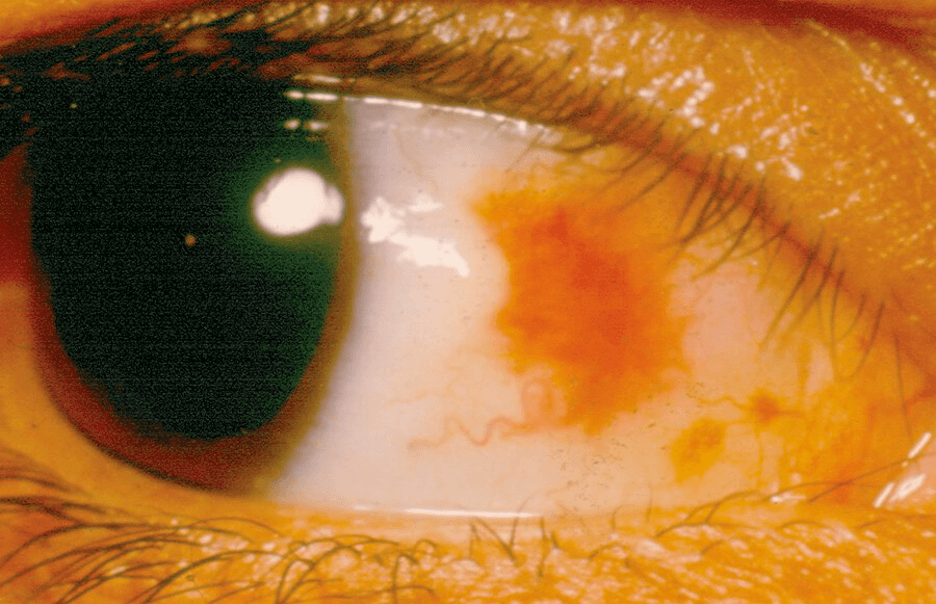
What is the diagnosis?
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
67 year old woman is admitted to the MICU for ARDS 2/2 CAP. She has been intubated and mechanically ventilated for 3 days. Prior to intubation, neuro exam was normal. Antibiotics and propofol were initiated. 12 hrs ago, the propofol was discontinued, but the patient remains unresponsive.
On exam, vital are normal. The patient does not respond to verbal stimuli and does not open her eyes or move her limbs when asked, but there is intermittent twitching of the left upper and lower extremities. She withdraws all extremities to noxious stimuli.
Labs are normal, head CT shows evidence of remote hemispheric stroke but no additional findings.
What is your next step in evaluation?
Continuous EEG
56-year-old woman presents for changes in her voice. Over the past year her voice has become strained and strangled, and she has had problems with expressing certain consonants. She reports no pain or shortness of breath but has intermittent tightness in her throat.
On examination, vital signs are normal. Her voice is hoarse, and she speaks with a strained and pressured voice disrupted by sudden pauses, but she can sing without any problems. The remainder of the neurologic examination is normal.
Video laryngoscopy reveals slow, sustained, and nonrhythmic pulling of vocal cords toward midline with intermittent relaxations.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Dystonia
48 year old man presents for 25 year hx of headaches that have become increasingly frequent. They previously occurred 4-5x per month but now occur 16-20x per month and last 12-24 hrs. The headaches are bilateral, throbbing, moderate in intensity, aggravated by physical activity, and accompanied by photophobia and phonophobia. The patient takes amitriptyline and sumatriptan for the headaches and has been taking sumatriptan four to five times weekly for the past 3 months.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are all normal.
What is the next step in treatment?
Stop sumatriptan
A 38 year old woman presents with a severe, unrelenting headache. What are these funduscopic findings?
Papilledema: elevated optic disc and indistinct disc margins
47 year old man presents to ED with prolonged seizure. According to family, the initial seizure lasted for 3 minutes and stopped, but the patient did not regain consciousness and a second generalized tonic-clonic seizure started within 5 minutes and has continued. The patient received 4 mg intravenous lorazepam in the ambulance. In the ED, the seizure continues and he receives an additional 4 mg of intravenous lorazepam followed by another 2 mg 10 minutes later without benefit. The patient has a history of generalized tonic-clonic seizures treated with levetiracetam.
On exam, BP is 147/92, HR 122, RR 18, saturating 90% on RA. Pupils are reactive. Clonic seizure activity persists.
20 minutes later, patient is intubated, access obtained, labs collected. POC glucose is 126.
What is the next step in therapy?
IV fosphenytoin
A 45-year-old woman is evaluated for sleeping difficulties. Her main symptom is an uncomfortable urge to move her legs when she is at rest or in bed at night. This may result in difficulty falling asleep or sometimes in maintaining sleep. She may wake up 3-5x a night and then walk around the house for a few minutes to relieve her symptoms before attempting to go back to sleep. Her husband reports no snoring or witnessed apneic episodes or daytime sleepiness.
On physical examination, vital signs and the remainder of the physical examination are normal.
What lab test should you order next?
Ferritin
25 year old woman presents with 3 month hx of headaches that previously occurred weekly but now occur daily. The headaches are holocranial, dull, and vice-like, and worsened by the Valsalva maneuver. The patient reports associated neck stiffness, intermittent visual blurring without diplopia, and nocturnal pulsatile tinnitus. She also has a history of acne and vitamin D deficiency. Medications are topical benzoyl peroxide, oral doxycycline, and vitamin D.
Vital signs and BMI are within normal limits. Neurologic examination reveals bilateral papilledema. LP shows opening pressure of 280 mm H2O. Other labs are within normal limits. MRI with contrast shows partially empty sella and widened optic nerve sheaths. MRV is within normal limits.
What is the next step in therapy?
Discontinue doxycycline
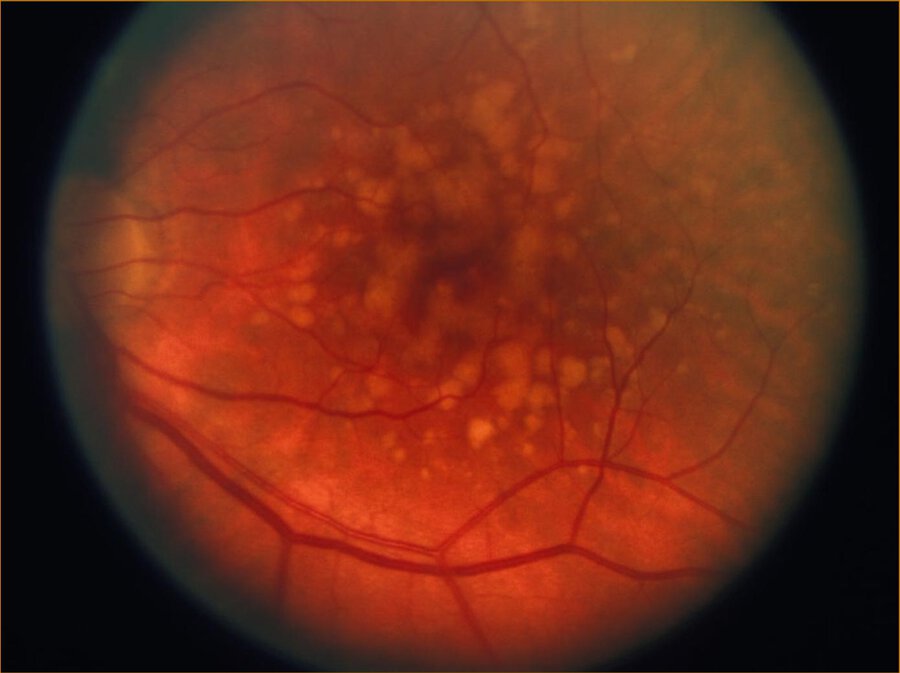
71 year old male presents with progressive vision loss over many years.
What is the diagnosis?
Age related macular degeneration
A 25 year old woman is diagnosed with epilepsy. She and her partner are thinking of starting a family within the next year. Which medication should you start?
Lamotrigine or levetiracetam
64 year old man is evaluated for recent emergence of involuntary twisting movements of his neck and extremities. Parkinson disease was diagnosed 8 years ago. Mobility and fatigue improve after each dose of carbidopa-levodopa. A few months ago, he started to feel excessive slowness and anxiety 1 hour before each dose of medication and was treated with an increased dose of his carbidopa-levodopa. Now, he has developed involuntary nonrhythmic movements that peak after each dose. Current medication is carbidopa-levodopa.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. He is examined half an hour after taking a dose of levodopa. He exhibits cogwheel rigidity, shuffling of gait, and large-amplitude ballistic and flowing movements of the neck and extremities. Other examination findings are unremarkable.
What is the next step in treatment?
Amantadine
30 year old man presents with 1 hour hx of a severe headache. He has had similar headaches for the past 2 weeks that start in the evening, last 2 to 3 hours, and are characterized by intense left-sided pain that is periorbital and piercing. Associated features are photophobia, nausea, and ipsilateral tearing. Nasal sumatriptan, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen have not relieved the pain. He has a 7-pack-year smoking history.
Vital are within normal limits. Left ptosis and miosis are noted on exam. Labs and MRI brain with contrast are within normal limits.
Oxygen therapy is started, what additional treatment is recommended?
Subcutaneous sumatriptan
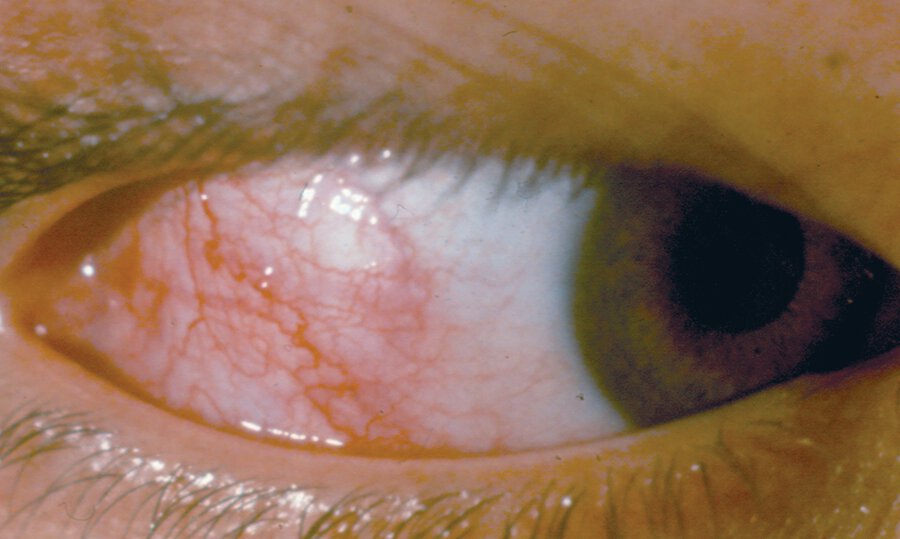
Patient presents with 1 day of redness, tearing, and irritation of R eye. Denies eye pain, photophobia, or change in vision. Her left eye is uninvolved. She has no other symptoms. Visual acuity is 20/20 in both eyes. Pupils are equally round and reactive to light and accommodation.
What is the diagnosis?
Episcleritis
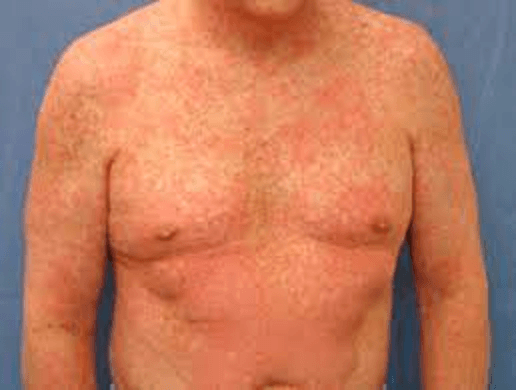
A patient develops this rash after starting lamotrigine. Which AED should you switch them to?
Gabapentin
27 year old woman presents with 10 days of involuntary movements involving the face, arms, and trunk. Symptoms began as occasional twitching of the limbs and then became more generalized and persistent to the point that now she has difficulty sitting still. She cannot suppress the movements voluntarily. The patient has no personal or family medical history of involuntary movements. She is otherwise well and takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Variable and random movements that flow from one body part to another are noted; the movements are not distractible. Gait has a prancing quality with flailing arms. Cognition is intact and motor strength and deep tendon reflexes are normal.
A complete blood count and comprehensive metabolic profile are normal.
What is the next diagnostic test to run?
Pregnancy Test
51 year old woman presents with 5 year hx of increasingly frequent and disabling migraine episodes. Whereas she previously had migraine on the first 2 days of menses, migraine episodes now have increased to 10 days monthly; once monthly, she experiences a scotoma lasting 20 minutes before migraine onset. Oral and subcutaneous sumatriptan have been effective in controlling symptoms, but because of the increased frequency of her headaches she sometimes runs out of medication during the month. Preventive trials of propranolol, amitriptyline, and topiramate over the past 2 years have been unsuccessful.
All physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal. Results of laboratory studies are within normal limits.
What is the next step in therapy?
Beta blocker (propranolol, timolol, metoprolol)
AED (topiramate, divalproex sodium)
Monoclonal antibody / Biologic
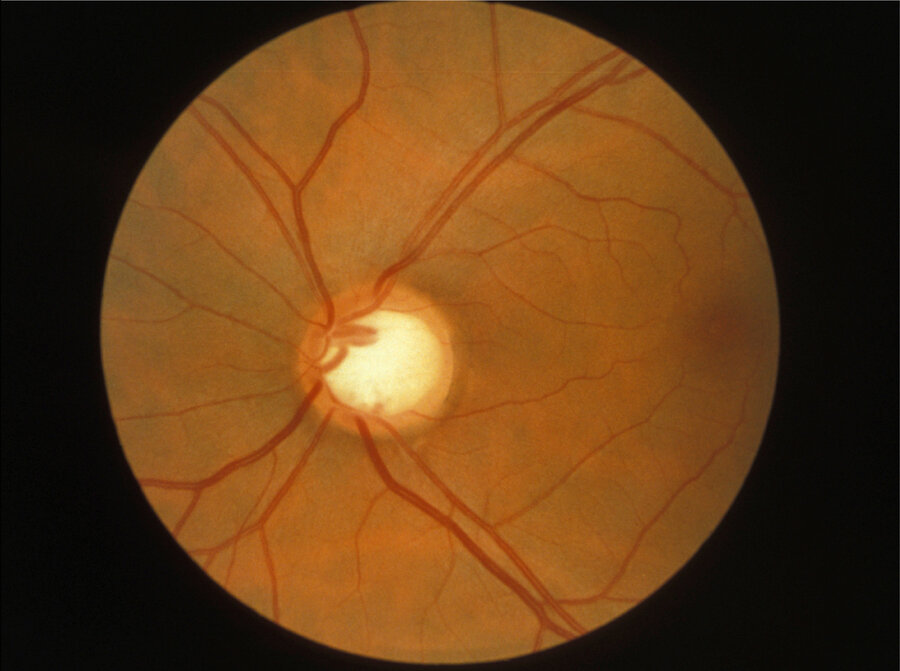
35-year-old man is evaluated for loss of peripheral vision discovered during a comprehensive ophthalmologic examination. The patient is asymptomatic and has 20/20 visual acuity in both eyes.
What is the diagnosis?
Glaucoma