This anatomical term is used to describe position of the brainstem to the cerebellum.
What is anterior?
There are three major regions of the adult brain. This region is necessary for conscious awareness and is connected by the corpus callosum.
What are the cerebral hemispheres?
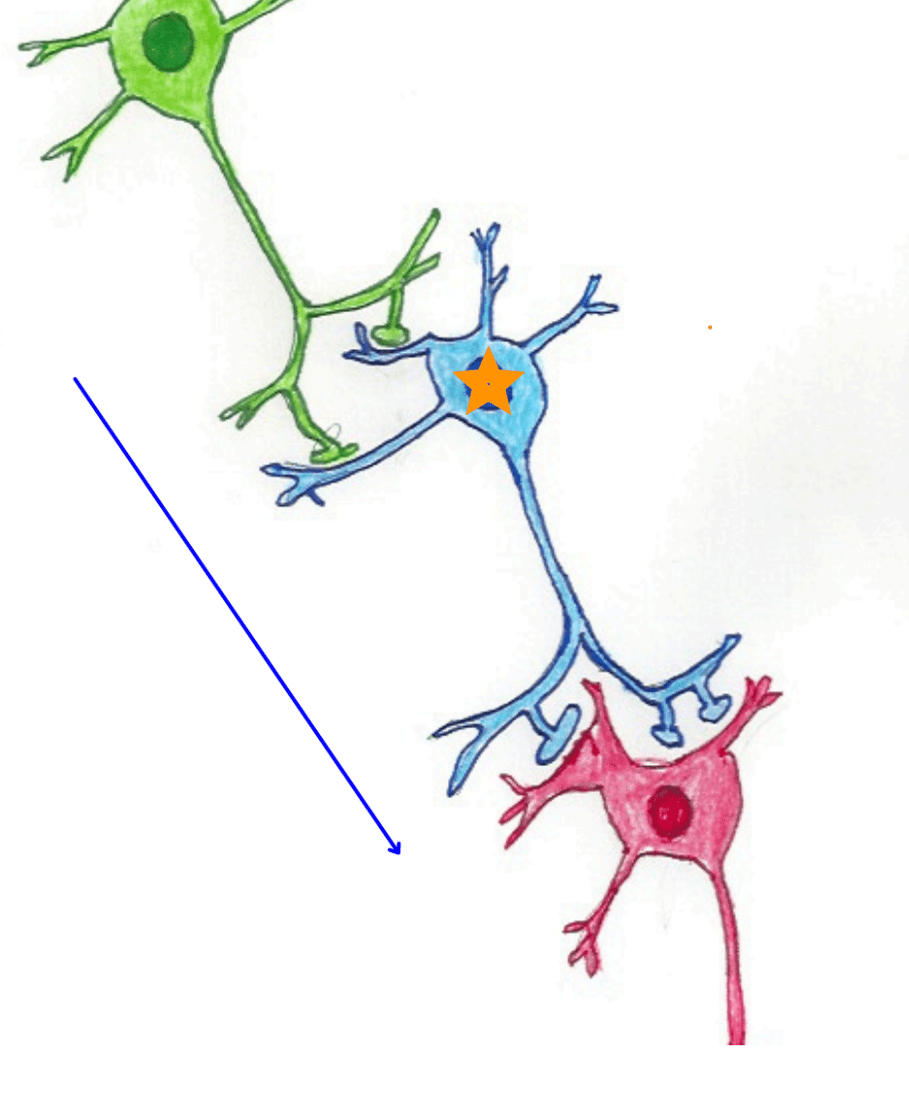 This structure, indicated by the star, functions as the metabolic center of the neuron.
This structure, indicated by the star, functions as the metabolic center of the neuron.
What is the cell body (soma)?
Identify the structure indicated by the blue star.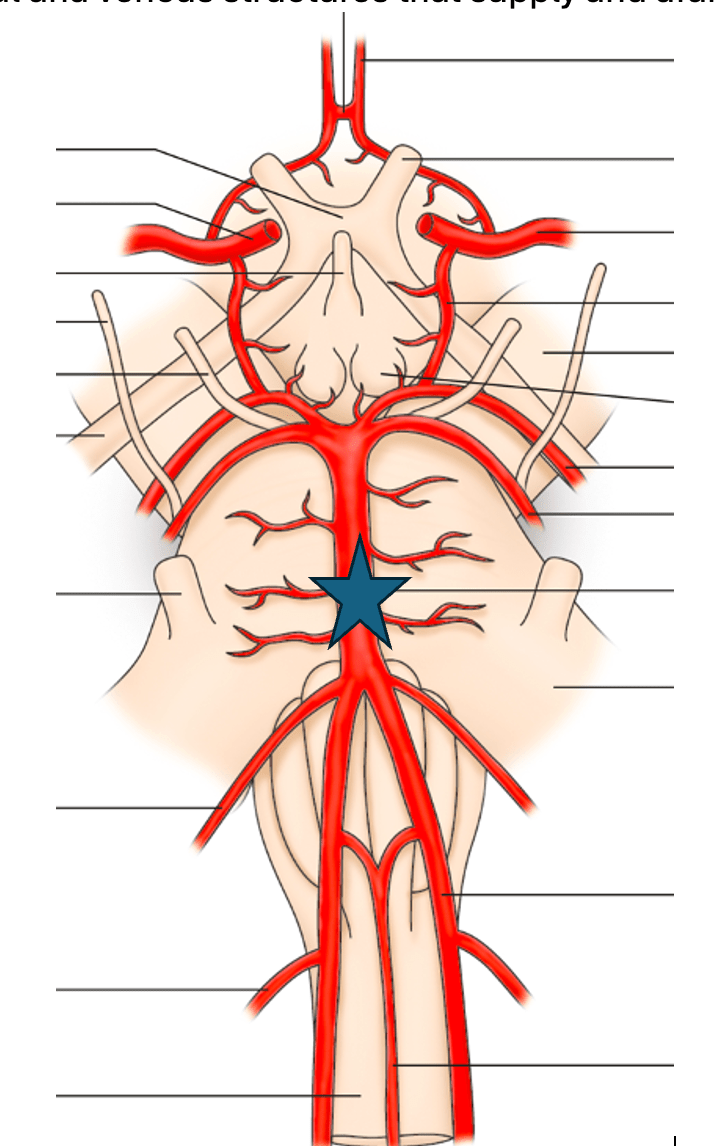
What is the Basilar artery?
The inner, meningeal layer of the dura forms three main septa. This septum separates the two cerebellar hemispheres.
What is falx cerebelli?
The spinal cord is the caudal most part of the central nervous system. These structures are housed within its gray matter.
What are cell bodies of neurons?
This structure separates the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
What is the central sulcus?
This type of neuron is classified by a single process that extends from a round cell body that divides into a peripheral and central process.
What is Pseudounipolar neuron?
This artery supplies the medial portion of the cerebral hemispheres within the longitudinal fissure.
What is the anterior cerebral artery?
This nerve provides innervation to the dura of the anterior and middle cranial fossae.
What is the Trigeminal nerve (CN V)?
These axons carry sensory information into the CNS.
What are afferent axons?
Identify the structure indicated by the red and white checks.
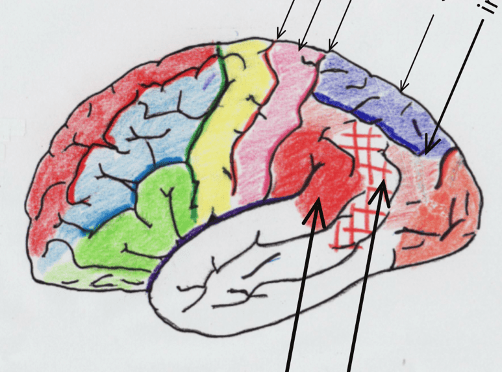
What is the angular gyrus?
Identify the function of the cell indicated in the image. 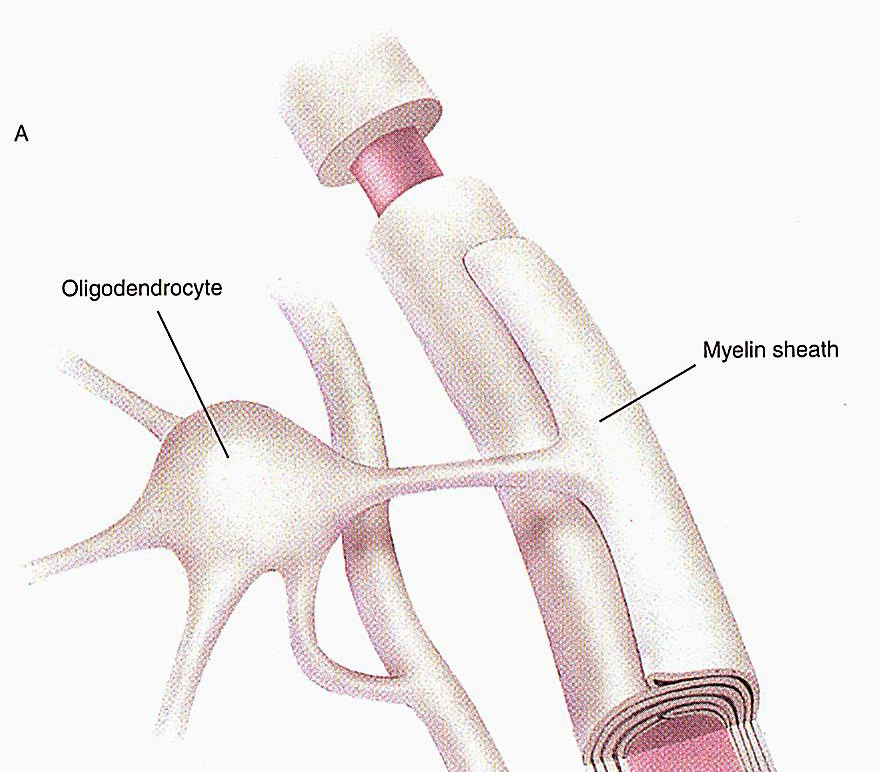
What is increase the conduction speed of neurons in the CNS?
The cerebral arterial circle serves as the interconnection between these two arterial systems.
What are the Internal carotid and vertebrobasilar systems?
The structure indicated by the star performs this specific function.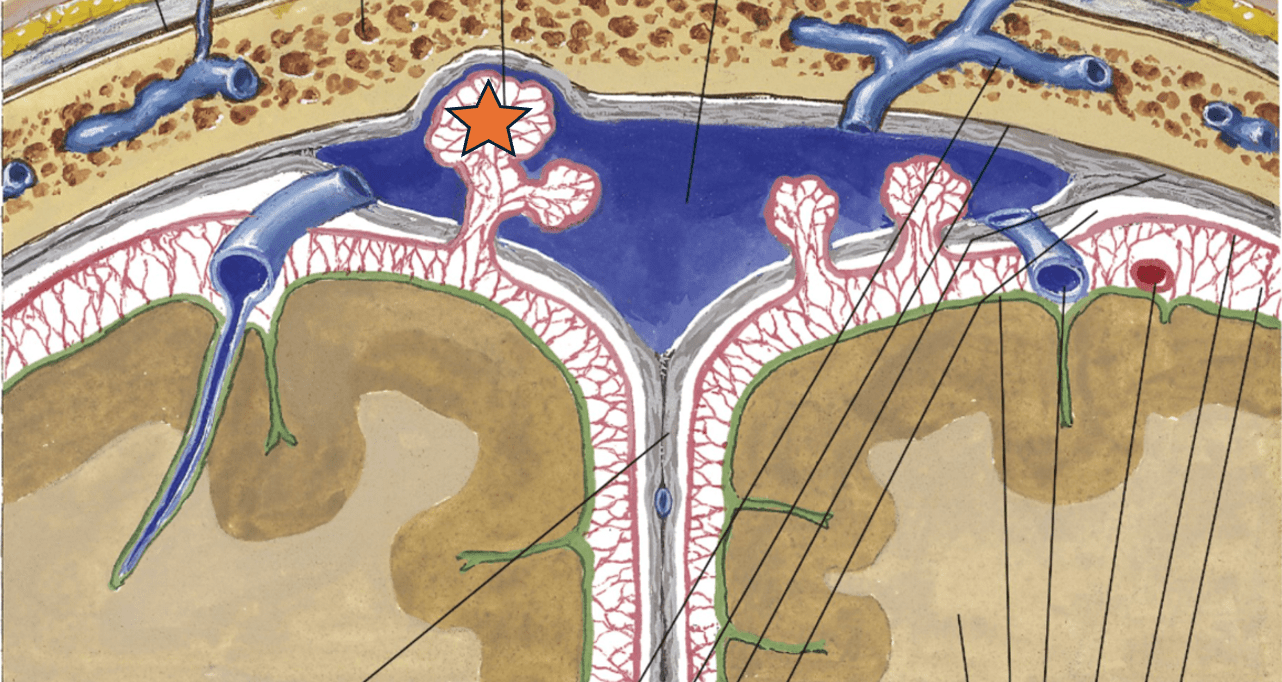
What is the reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the subarachnoid space?
Identify the structure indicated by the blue star.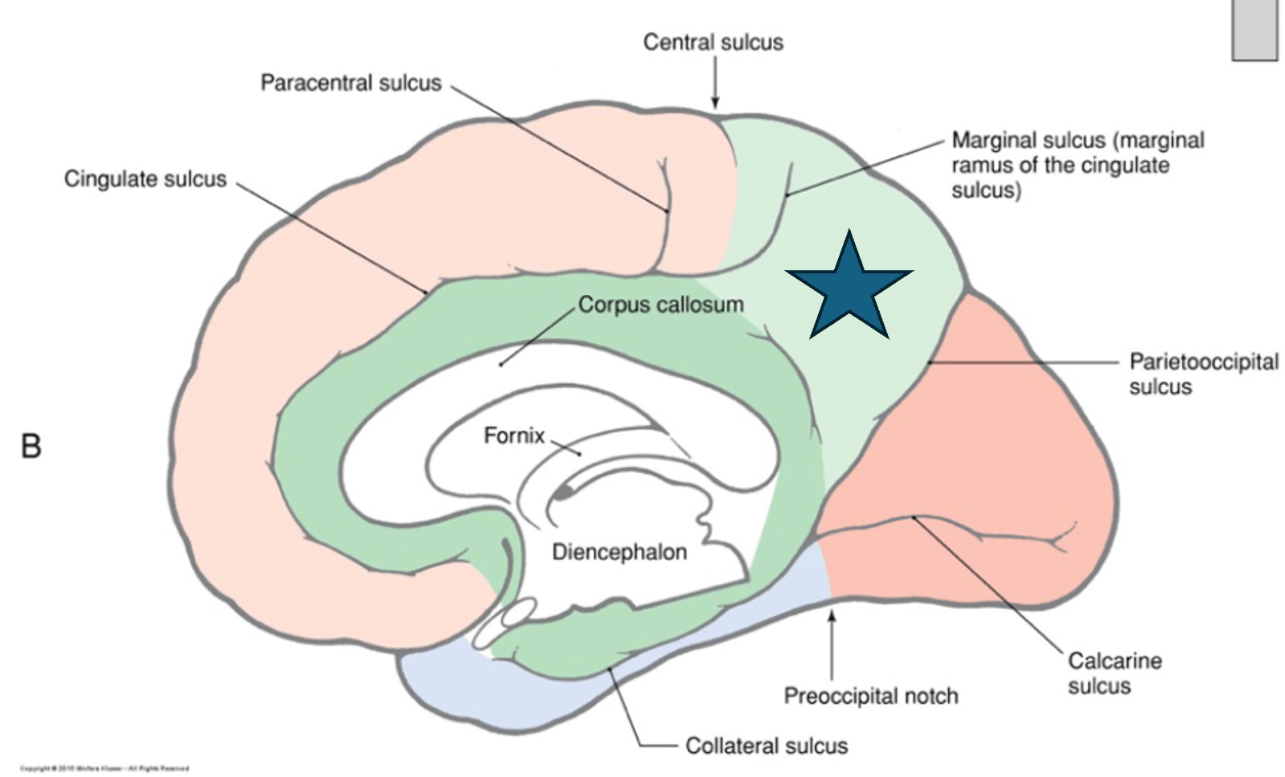
What is the parietal lobe?
Identify the midbrain structures indicated by the blue stars that are specialized for vision.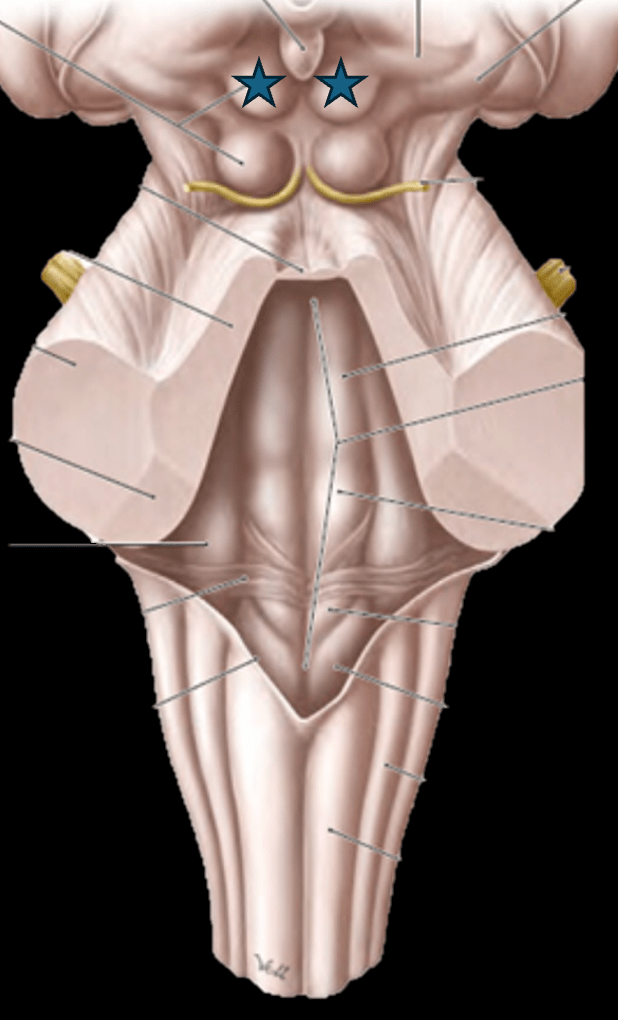
What are the superior colliculi?
The Middle cranial fossa is composed of the sphenoid and temporal bones and holds these lobes of the brain.
What are temporal lobes?
The sigmoid sinus is the continuation of this sinus that follows along the lateral border of the tentorium cerebelli.
What is the transverse sinus?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates within the subarachnoid space through a specific path. CSF drains from the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle by way of this structure.
What is the cerebral aqueduct?
Glial cells have various functions, one of which is to produce myelin and increase the conduction speed of neurons. These supportive cells produce myelin in the PNS.
What are Schwann cells?
A patient comes into your clinic. Looking at their chart you see they have had a stroke that affected their occipital lobe.
You expect this primary function to be impaired.
What is vision?
A patient complains of numbness in his distal lower extremities and weakness in his gait that has gotten progressively worse in the last two weeks. The doctor suspects Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Identify the region that will be affected by this diagnosis.
What is the Peripheral nervous system?
A patient presents in the emergency department with confusion, inability to control their bladder, and frequent episodes of wandering. MRI confirms a stroke involving the Anterior cerebral artery with multiple surrounding infarctions.
Identify the most likely diagnosis.
What is Multi-infarct dementia?
A two-week-old baby is brought into the emergency department after experiencing what the parents called a seizure. MRI confirms excess cerebrospinal fluid within the CNS.
Identify the most likely diagnosis.
What is hydrocephalus?