This autonomic nervous system branch, when overactivated, can contribute to Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (aka “broken heart syndrome”), often seen in aSAH
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System
A swollen vein that's plain to see means the right heart’s in misery.
What is the Jugular Vein or Jugular Venous Distension?
This antiplatelet agent, given immediately in ACS, irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 to reduce thrombus formation.
What is aspirin?
This common and highly emergent condition is a double misnomer
What is a ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction?
ST elevation - actually, everything else is depressed except for the ST segment
Infarction? - May just represent severe ischemia (i.e. can be reversible - which is why it is an emergency)
An enlarged inferior vena cava (IVC) with minimal respiratory collapse suggests this volume status issue.
What is fluid overload or increased Right Atrial Pressure?
The recommended dose of epinephrine during cardiac arrest, given every 3–5 minutes.
What is 1mg?
A stroke in this brain region can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias due to its role in autonomic regulation.
What is the insular cortex
A 35-year-old woman with a history of pulmonary hypertension becomes hypotensive after receiving 1 liter of normal saline. What is the likely cause?
What is worsening right ventricular failure?
The class of drugs including clopidogrel and ticagrelor prevents platelet activation by blocking this receptor
P2Y12
This high-risk STEMI equivalent presents with deep ST depression in V1-V3 and requires posterior ECG leads to confirm infarction
What is a posterior wall MI?
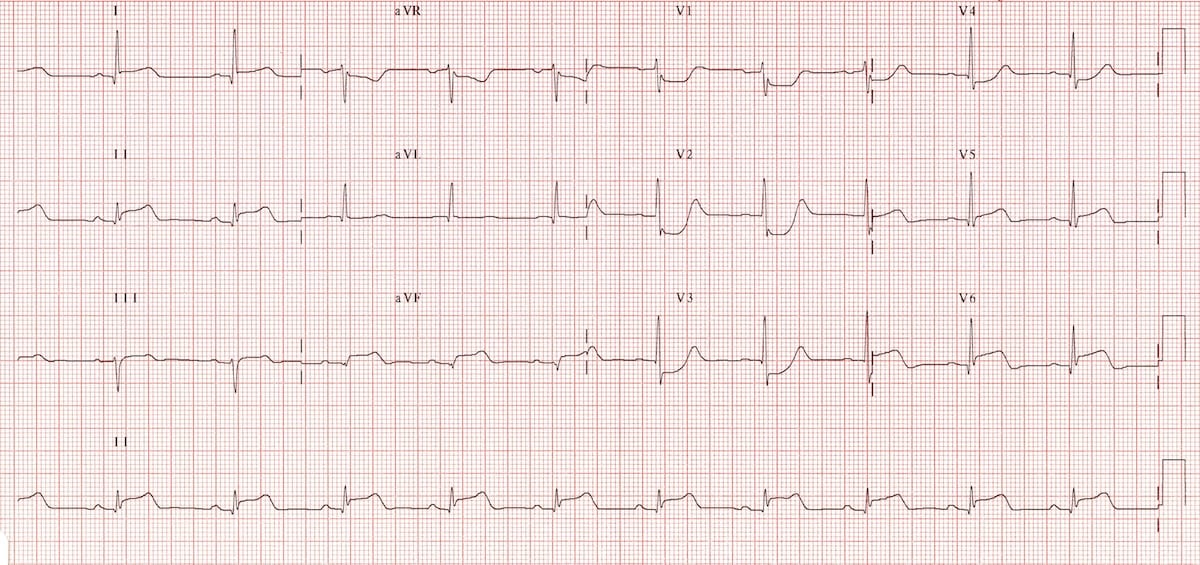
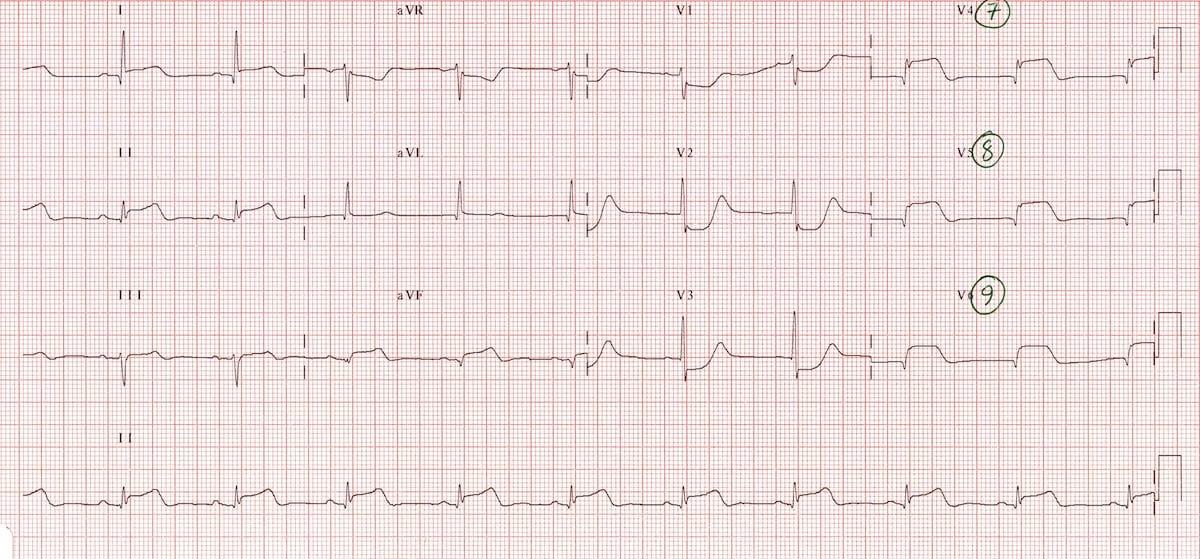
In a patient with acute myocardial infarction, severe hypokinesis of the anterior wall suggests an occlusion in this coronary artery.
What is the left anterior descending artery?
This shockable rhythm requires immediate defibrillation and is often described as a chaotic, disorganized electrical activity in the heart
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Increased intracranial pressure can trigger this reflex, leading to bradycardia, hypertension, and irregular breathing.
What is the Cushing Reflex?
A patient with massive pulmonary embolism has a dilated right ventricle on bedside ultrasound and a septum that bows into the left ventricle. What is this sign called?
What is intraventricular septal shift (D-sign)?
This intravenous anticoagulant, often used in PCI, works by potentiating antithrombin III to inhibit clot formation.
What is heparin?
Widespread ST depression with ST elevation in aVR suggests a severe blockage in this major coronary artery.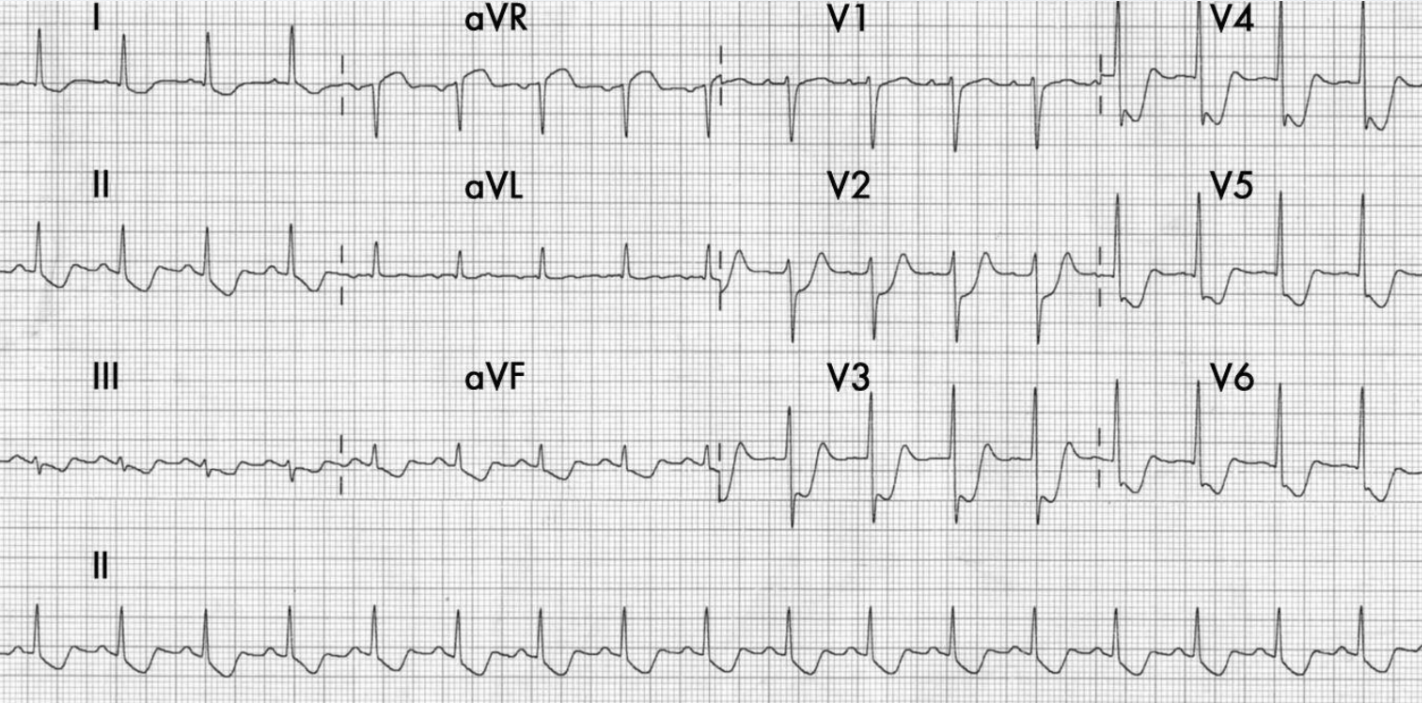
What is the Left Main Coronary Artery?
A hyperdynamic left ventricle with small chamber size suggests this hemodynamic state, commonly seen in sepsis
What is hypovolemia or distributive shock?
This medication is the first-line antiarrhythmic given after the second shock in a shockable cardiac arrest.
What is amiodarone?
Diffuse T wave inversions can be caused by this classic mechanism of causing secondary injury to the brain
What is elevated intracranial pressure?

The right heart’s weak, it needs a squeeze! This pressor is often used to support the right heart in acute failure
What is dobutamine?
This medication class, often initiated within 24 hours of an MI, improves survival by reducing ventricular remodeling and afterload.
What is an ACE inhibitor?
This coronary syndrome presents with persistent ST elevation after reperfusion and is associated with poor outcomes due to microvascular obstruction
What is the no-reflow phenomenon?
Early collapse of this chamber is seen on an echo due to elevated pericardial pressure during cardiac tamponade
What is Right Atrial Collapse
The H's and T's are used in ACLS to identify reversible causes of cardiac arrest. This "H" represents a severe loss of blood.
What is hypovolemia?
H's (5)
- Hypoxia – Lack of oxygen leading to cardiac arrest.
- Hypovolemia – Severe fluid or blood loss causing shock and cardiac arrest.
- Hydrogen ion (Acidosis) – Severe metabolic or respiratory acidosis affecting cardiac function.
- Hyperkalemia/Hypokalemia – High or low potassium levels causing lethal arrhythmias.
- Hypothermia – Body temperature too low, leading to bradycardia and arrest.
T's (5)
- Tension pneumothorax – Air trapped in the pleural space causing pressure on the heart.
- Tamponade (Cardiac) – Fluid buildup around the heart, preventing proper filling and contraction.
- Toxins – Drug overdoses or poisoning causing cardiovascular collapse.
- Thrombosis (Pulmonary) – Massive pulmonary embolism blocking blood flow to the lungs.
- Thrombosis (Coronary) – Myocardial infarction (heart attack) leading to cardiac arrest.
This phenomenon, common in brain-injured patients, leads to episodes of excessive sympathetic outflow, hypertension, tachycardia, and cardiac dysfunction.
What is paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity (or storming)?
A patient with decompensated right heart failure is started on inhaled nitric oxide which works via this mechanism
What is pulmonary vasodilation to reduce RV afterload
Used cautiously in acute MI, this drug class lowers myocardial oxygen demand by reducing heart rate and contractility but should be avoided in acute heart failure.
What is a beta blocker?
The presence of ST elevation in V1-V2 with a rightward axis suggests proximal occlusion of this artery, often missed in standard STEMI criteria.
What is the LAD?
McConnell’s sign, or akinesia of the RV free wall with apical sparing, is a classic ultrasound finding in this diagnosis.
What is an acute Pulmonary Embolism?
The recommended joules for initial biphasic defibrillation when treating ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
What is 120 -200J?
