A ______ is defined as an episode of new or worsened neurologic sxs, lasting more than 24 hours, not due to fever or infection.
Relapse. AKA attack, bout, or exacerbation
Taste anterior two- thirds of tongue
Facial nerve
Syndrome. Right hemiparesis, RHH, and aphasia
Left MCA syndrome
Acetazolamide inhibits this enzyme
Carbonic anhydrase
Presynaptic P/Q type voltage gate calcium channel antibodies are seen in this syndrome
Lambert- Eaton myasthenic syndrome
Immature defense mechanism involving the misattribution of one's unacceptable feelings or impulses to another person who does not have them
Projection
Wrote the book "The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat"; describes a man with visual agnosia
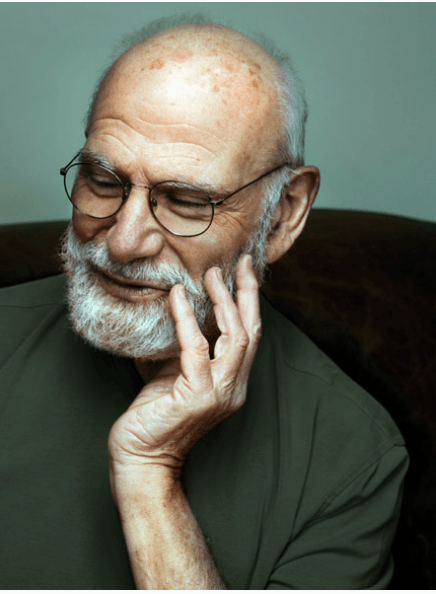

Sjogren syndrome; sensory neuronopathy
Direct pathway: excitatory or inhibitory to cortex?
Excitatory- increases thalamic excitation of cortex
INO: disorder of _____
Medial longitudinal fasciculus
Ex: with a R INO, on left gaze- cannot ADDuct R eye. Have L eye abduction nystagmus
Corneal reflex: afferent and efferent
Structure (mostly) affected in pure sensory lacunar syndrome. Presents as c/l hemisensory loss
Thalamus
Name some headache red flags
Systemic symptoms (fever, chills, wt loss)
Hx of prior cancer. Immunodeficiency
FND
Thunderclap HA
New onset HA after age 50
Precipitation by exertion, strain, or position changes
Increasing HA frequency and severity
New onset seizures
Inheritance: X- linked recessive
Dystrophin
Pathologic impulses to set fire
Pyromania
Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies in the psyche through dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst. 
Sigmund Freud
Headache, oral, and genital ulcers in patient of Eastern Mediterranean descent
Phenomenon that dystonias can be diminished by sensory tricks like touch in affected body part
Geste-Antagoniste
Your 34 yo AA female pt with relapsing neurologic symptoms has CSF testing. Which of the following findings would prompt you to consider diagnoses other than MS?
a. Elevated kappa chains
b. WBC count of 22
c. Neutrophilic pleocytosis
d. Elevated IgG synthesis rate
e. Normal CSF immunologic parameters
Elevated kappa chains indicate Ab formation in CNS- can be seen in NS
WBC can be elevated (no more than 50 cells) and are usually lymphocytic predominant
IgG synthesis rate elevation is measure of increased intrathecal elaboration of Ab and can be seen in MS
Some pts have normal CSF- does not r/o MS
Closure of eye when smiling (reverse may also occur). When some axons from motor neurons to labial muscles involved in smiling may regenerate and misdirect to the orbicularis oculi
Synkinesis
Structure affected in pure motor lacunar syndrome
Posterior limb of internal capsule. Presents as c/l motor deficits
New name for basilar migraine
Migraine with brainstem aura. Reflects the fact that migraine is now viewed as primarily neurologic disorder rather than vascular disorder.
(Outdated vascular theory is basis for ongoing contraindication to triptan and DHE in migraine with BS aura and hemiplegic migraine- deemed to be safe)
This medication inhibits glutamate release, which slows disease progression (prolongs survival by approx 3 months) in patient with ALS
Riluzole
This medication is an agonist at GABAb receptors. Used often as muscle relaxer
Baclofen
French Neurologist. Has many associated eponyms including a pathological reflex where the great toe extends in presence of an injury to the pyramidal tract. Suffered from PD in his last years.

Joseph Babinski
Recurrent sinusitis, renal disease, multiple cranial neuropathies, see granulomas
Wegener granulomatosis
Check c-ANCA
Name 3 synucleinopathies
PD
LBD
MSA
This phenomenon, is when transient symptoms of demyelination are elicited by heat or exercise
Uthoff's phenomenon
Manifests as blurry vision with exercise d/t impaired conduction in an optic nerve that has had demyelinating injury
Name for type of afferent pupillary defect: no response to direct light, but response to consensual light in contralateral eye present
Marcus Gunn pupil
This artery forms the vascular supply to both medial thalami
Artery of Percheron
DDx for bilateral trigeminal neuralgia or trigeminal neuralgia in a young pt
MS, sarcoidosis, Lyme disease
GQ1b
Duration of symptoms distinguishing acute stress reaction from PTSD
<1 month: ASR
>/1month: PTSD
Father of modern Neurology
Named and was the first to describe multiple sclerosis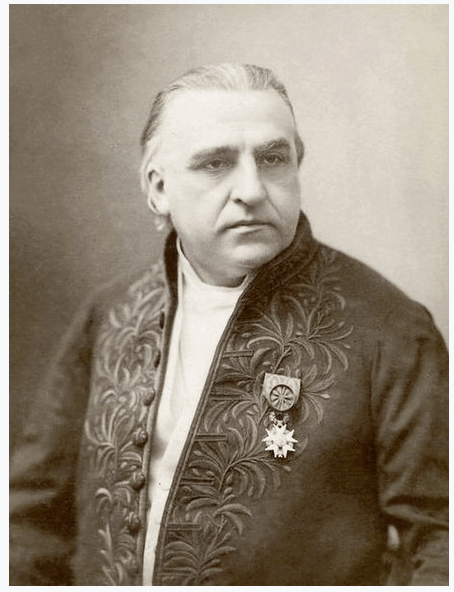
Jean- Martin Charcot
Fever, abdominal pain, headache, mononeuritis multiplex in patient with Hep B
Polyarteritis nodosa; check p-ANCA
PD Med: COMT inhibitor
Entacapone
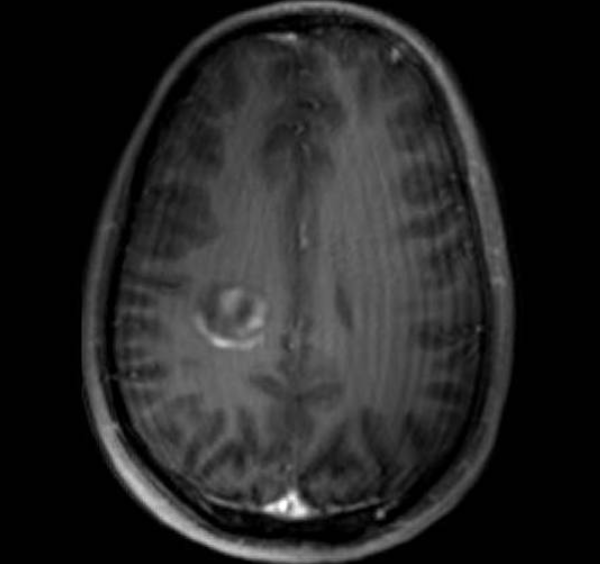
Tumefactive MS
Subform of RRMS with large, mass like lesions
Incomplete peripheral enhancement- "open ring sign"
Tx: IV steroids but may need PLEX or IVIG
V3, mandibular nerve aka 3rd division of trigeminal nerve passes through which skull foramina?
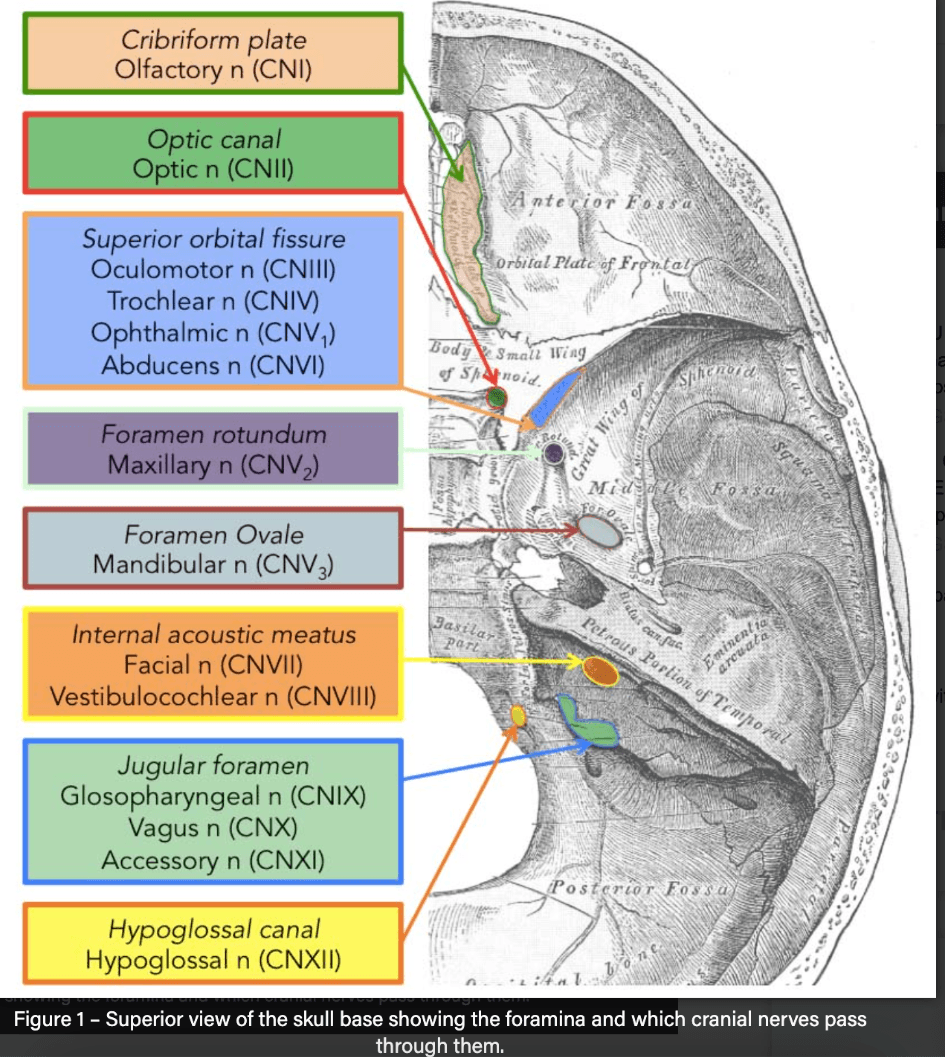
Standing Room Only (V1, V2, V3): Superior orbital fissure, foramen Rotundum, foramen Ovale
Limited upward gaze, convergence retraction nystagmus, light- near dissociation, lid retraction, and skew deviation of eyes
Parinaud's syndrome
Lesion affecting quadrigeminal plate (constituted by superior and inferior colliculi). AKA tectum- dorsal portion of midbrain. Located posteriorly to cerebral aqueduct
Is there an association b/w women who have migraine with aura and increased stroke risk?
YES
In women <45yo, who have migraine WITH aura, there is two-fold increased risk of stroke (migraine w/o aura does not have same increased risk)
Risk increases to six- fold with OCP use and nine- fold with smoking+OCP
_____ is an inflammatory demyelinating disorder of childhood in which there is monophasic immunologic reaction to a viral illness. Present with encephalopathy, see confluent white matter changes on MRI and inflammatory markers in CSF. SC may be affected with features of TM
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)
Tx: high dose IV steroids
Antipsychotic notorious for causing agranulocytosis
Clozapine
French physician, anatomist and anthropologist. Best known for his research on ___ area, a region of the frontal lobe that is named after him. This area is involved with language. His work revealed that the brains of patients with aphasia contained lesions in a particular part of the cortex, in the left frontal region. This was the first anatomical proof of localization of brain function.
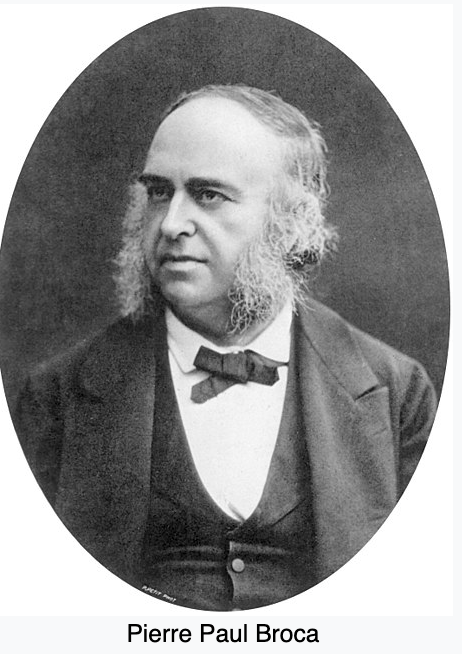

Paul Broca
Sarcoidosis
______ "buzz word" for finding on MRI showing hyperintensity surrounded by hypointensity in basal ganglia. Seen in pantothenate-kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN)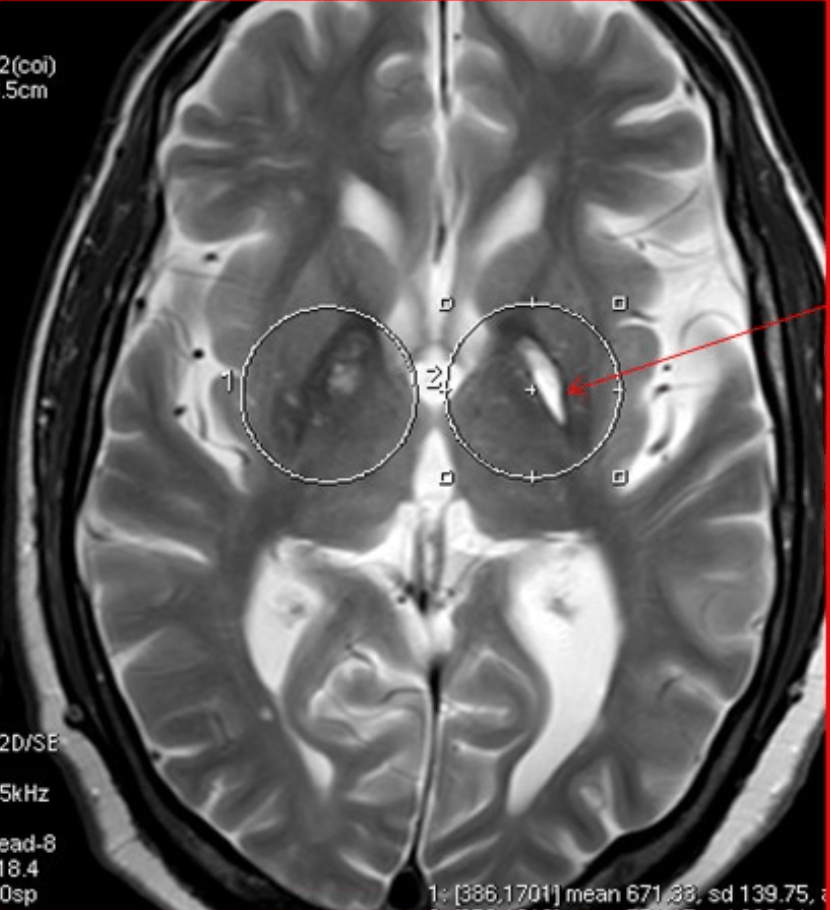
This MS medication inhibits the mitochondrial enzyme, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Associated with n/v/d, elev LFTs, and alopecia. Pregnancy Class X
Teriflunomide (Aubagio)
Taste posterior one- third of tongue
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Deep branch from ACA that supplies anterior limb of internal capsule, inferior part of head of caudate nucleus, and anterior part of globus pallidus
Recurrent artery of Heubner
Botox MOA
Onabotulinumtoxin A: cleaves the SNAP 25 protein (which is a SNARE)
Endocytosis of toxin into cell membrane of motor nerve and into its cytoplasm. Cleaving SNAP 25 prevents ACh containing vesicles from fusing with membrane and prevents ACh release into NMJ. Muscle contraction blocked.
Antibody associated with multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction block
GM1
Duration of symptoms distinguishing schizophrenia, schizophreniform disorder, and brief psychotic disorder
Brief psychotic disorder <1month
Schizophreniform disorder >1 to <6 months
Schizophrenia >/6 months
Canadian neurologist whose notable contributions include first detailed descriptions of lacunar strokes, identification of TIAs as stroke precursors, identification of link between carotid atherosclerosis and stroke, and the description of a variant form of Guillain–Barré syndrome which bears his name.

C. Miller Fisher
Pentad of TTP
Fever
Anemia (microangiopathic hemolytic)
Thrombocytopenia
Renal dysfunction
Neurologic s/s
FATRN
Name 3 structures that make up Guillain- Mollaret triangle
Dentate nucleus of cerebellum
Inferior olive
Red nucleus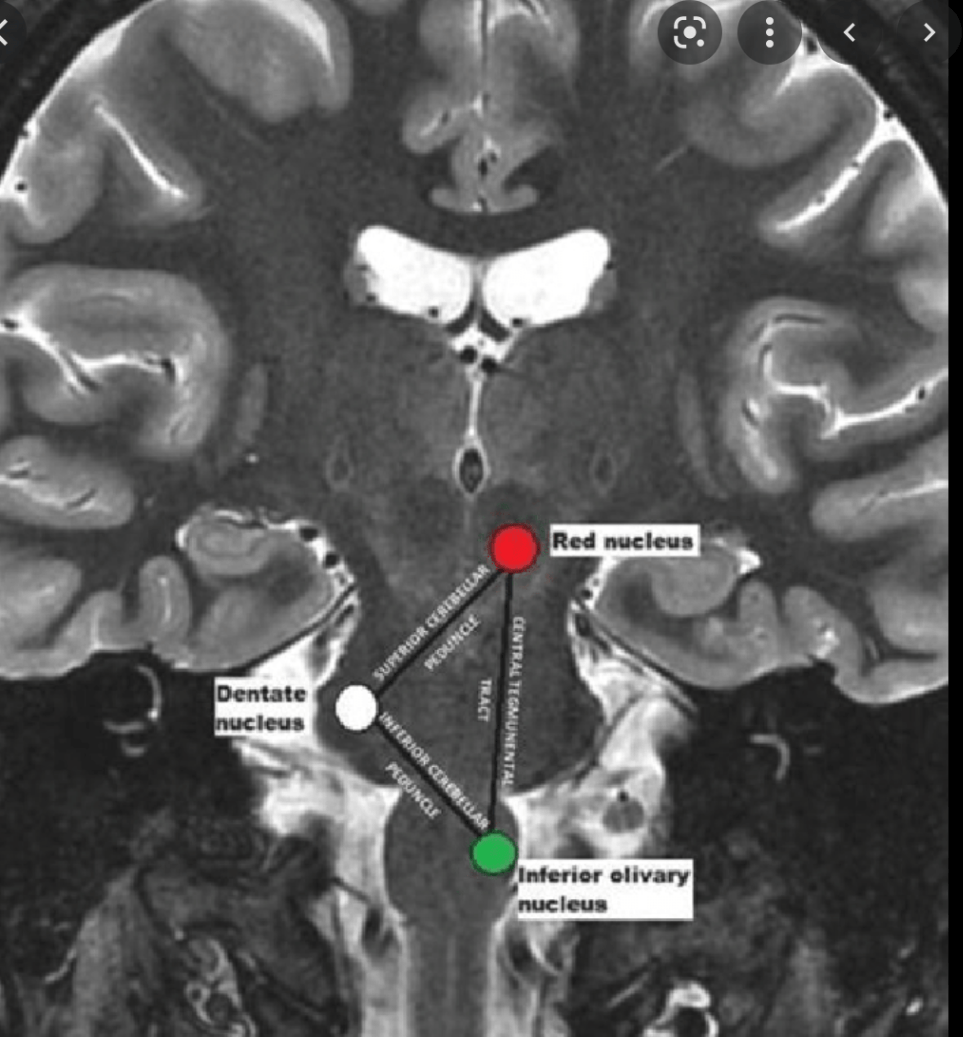
a. It appears to be a separate neuro-immunologic disorder
b. It usually transitions into MS
c. It never transitions into MS
d. It is the pediatric equivalent of MS
e. It is the same as MS
a. It appears to be a separate neuro-immunologic disorder
However, some pts diagnosed with ADEM later develop relapsing pattern consistent with MS. This may partially be due to tendency in pediatric pop. to diagnose ADEM rather than a first episode of MS
Nuclei for taste sensation
Rostral nucleus solitarius
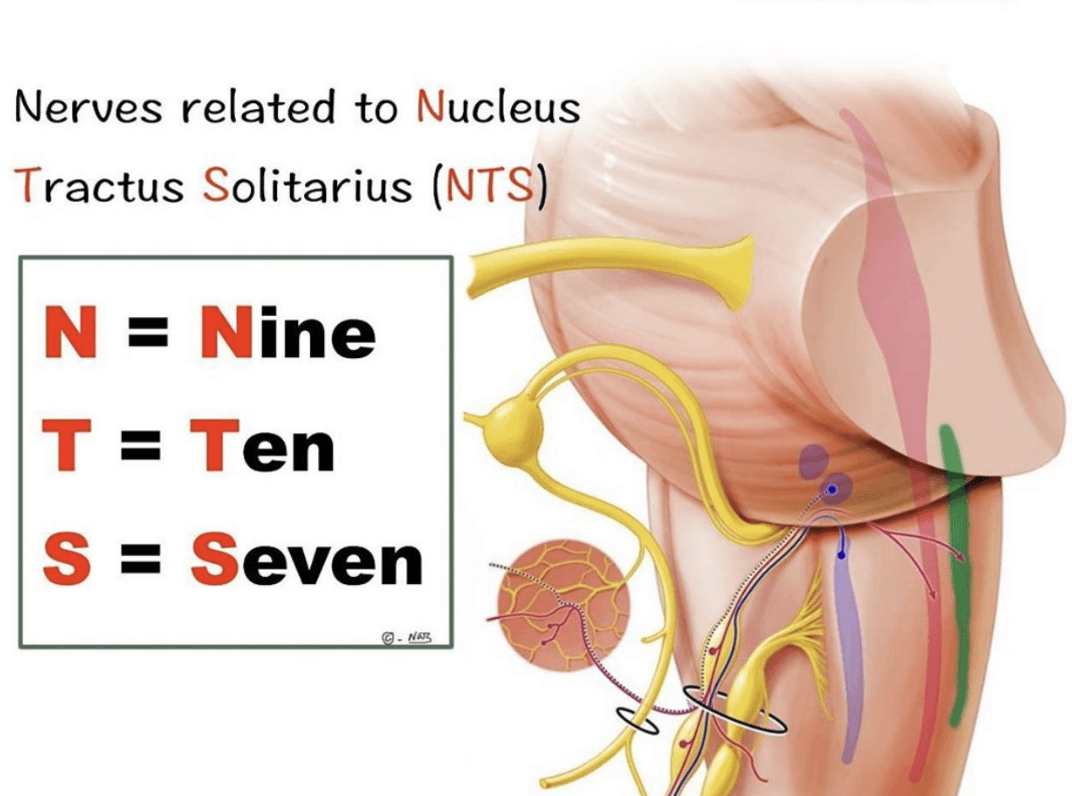 Solitary nucleus, also called nucleus of the solitary tract (SN or NTS) is a series of purely sensory nuclei forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the dorsolateral medulla. Through the center of the SN runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. The SN projects to, among other regions, the reticular formation, parasympathetic preganglionic neurons, hypothalamus and thalamus, forming circuits that contribute to autonomic regulation.
Solitary nucleus, also called nucleus of the solitary tract (SN or NTS) is a series of purely sensory nuclei forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the dorsolateral medulla. Through the center of the SN runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. The SN projects to, among other regions, the reticular formation, parasympathetic preganglionic neurons, hypothalamus and thalamus, forming circuits that contribute to autonomic regulation.
According to this trial, in patients with 70-99% symptomatic carotid stenosis, two- year ipsilateral stroke rate was 26% with medical tx versus 9% with CEA
NASCET trial
Symptomatic stenosis of 70-99% should be revascularized. Symptomatic stenosis of 50-69% may also benefit with CEA, with greater impact in men than women, in those with previous stroke/TIAs, and with hemispheric versus retinal symptoms
Indomethacin- responsive headaches (x2)
Hemicrania continua, paroxysmal hemicrania
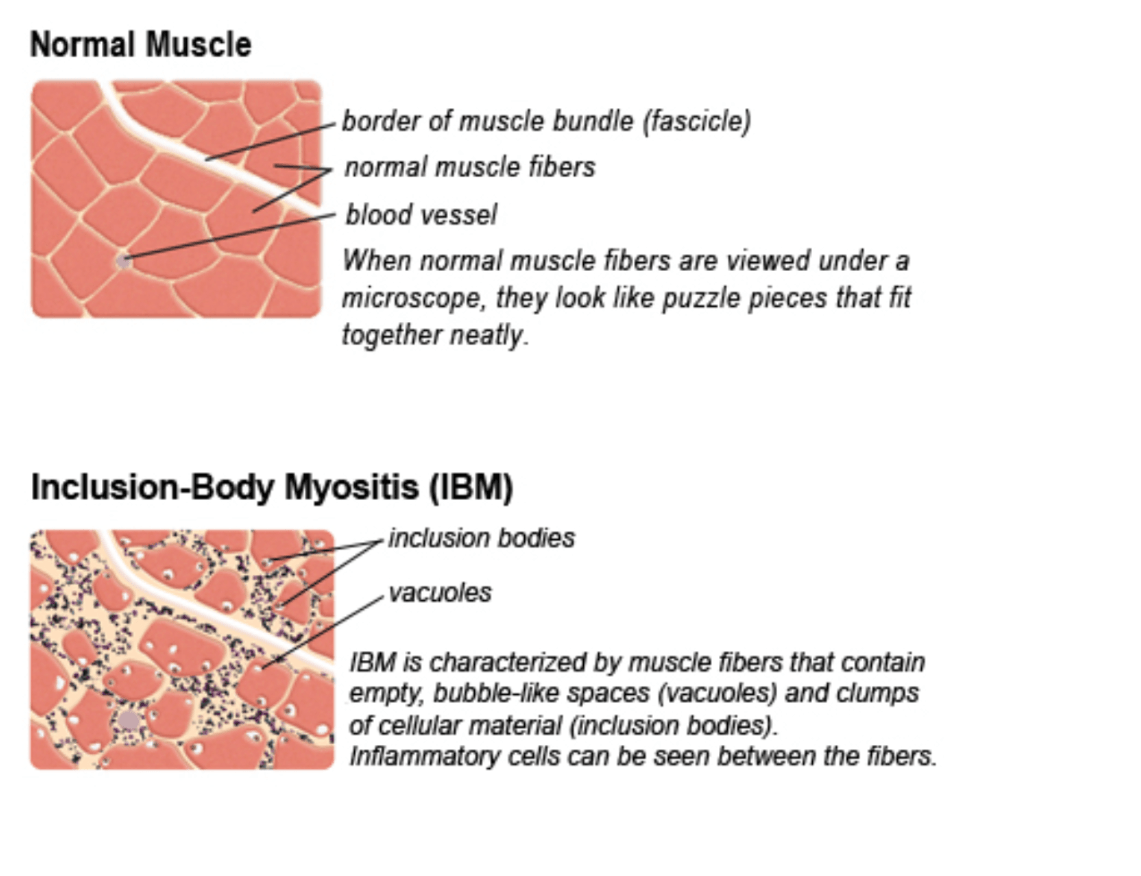
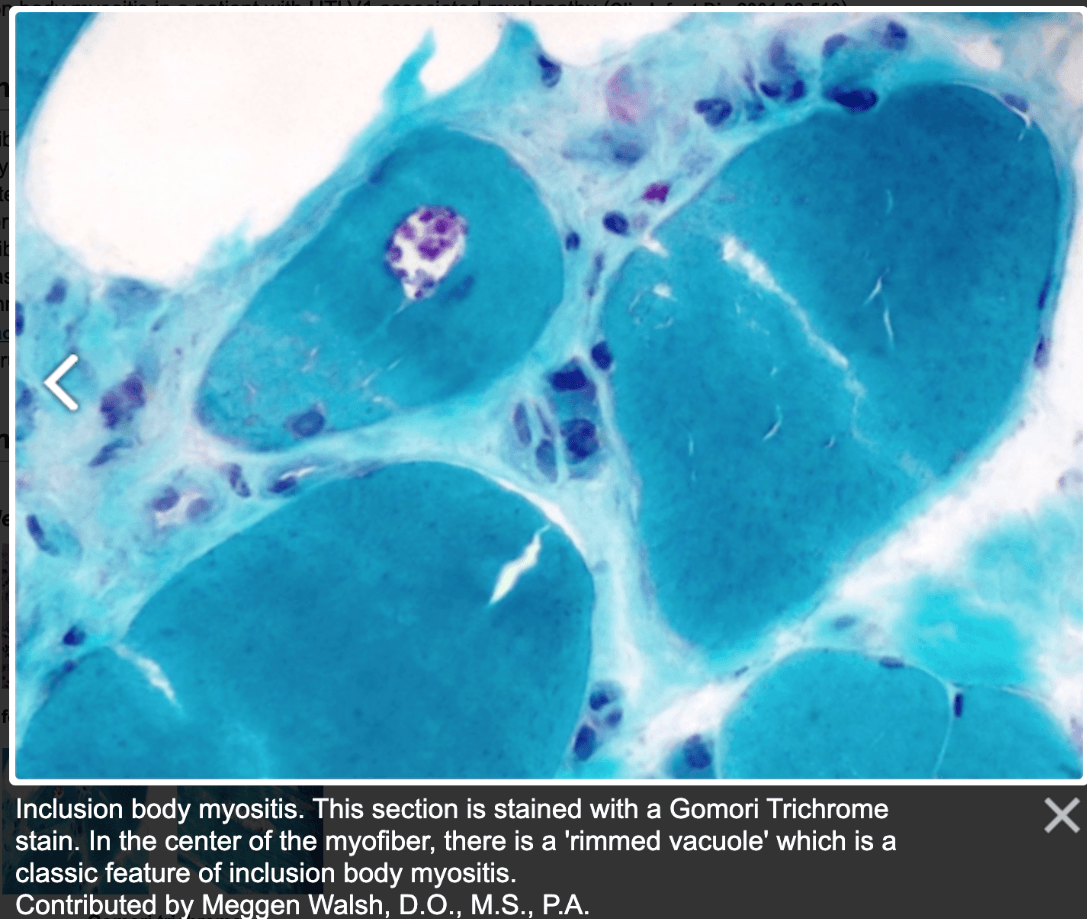
Histologic finding in Inclusion Body Myositis
Rimmed vacuoles
Chronic and intense preoccupation with a perceived defect of appearance or over- concern with minor physical abnormalities. Oftens eek unnecessary and repeated surgical procedures to correct their perceived deformity.
Body dysmorphic disorder
Named after him, ___ sign is dorsiflexion of the great toe elicited by irritation downward of the medial side of the tibia. It is one of a number of Babinski-like responses.The sign's presence indicates a damage to the pyramidal tract.
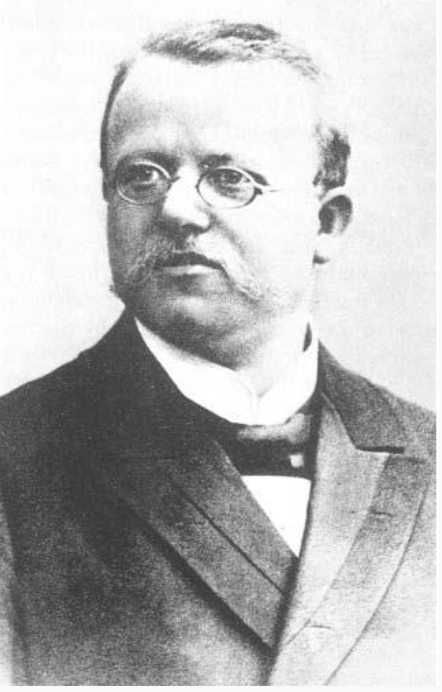

Hermann Oppenheim
Disorder of childhood characterized by acute onset of fever, conjunctivits, mucositis, polymorphous rash, lymphadenopathy, increased risk of coronary artery aneurysms, occurrence of aseptic meningitis
Kawasaki Disease
Specify syndrome with episodes of ataxia and facial twitching. Gene inv: KCN1A. Triggers: exercise, startle. Tx: AED
Episodic ataxia Type I
In Type II, there is ataxia with nystagmus and dysarthria. Tx: DIamox
Orally active modulator of sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) receptors on thymocytes and lymphocytes. Induces uncoupling and internalization of the receptor. Cells become unresponsive to signaling. Reduces relapse in RRMS.
A/E: macular edema and first dose bradycardia- requires 6 hrs observation after 1st administration
Others: elev LFTs, bronchitis. Asso. of risk of severe VZV infxns. Pregnancy Category C
Fingolimod (Gilenya)
Nuclei for parasympathetic output to chest, thorax, and GI tract
Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus
Patients undergoing carotid angioplasty and stenting (CAS) have lower rates of MI compared to those with carotid endarterectomy (CEA). True or False?
True
CREST- higher rate of peri-procedural stroke in CAS and higher rate of peri- procedural MI in CEA group. Differential outcome based on age was noted
CAS favors pts younger than 70, CEA favors pts older than 70
Name (at least 2) type of HAs that are classified as TACs (trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias)
Cluster HA
Paroxysmal hemicrania
Hemicrania continua
SUNCT
SUNA
Mutation in this gene causes central core myopathy. Associated with malignant hyperthermia
RYR1
Clozapine, Olanzapine, Ziprasizone, and Aripiprazole: which 2 cause weight gain?
Clozapine and Olazapine
Spanish neuroscientist, pathologist, and histologist specializing in neuroanatomy and the central nervous system. He and Camillo Golgi received the Nobel Prize in Physiology. He was the first person of Spanish origin to win a scientific Nobel Prize. His original investigations of the microscopic structure of the brain made him a pioneer of modern neuroscience.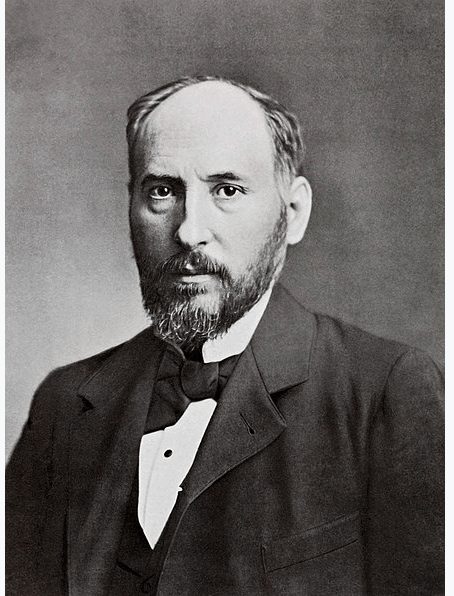
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
Antibodies against ____ are detected in serum of patients with IgM MGUS
Anti- MAG (myelin associated glycoprotein)
Primarily demyelinating
High risk of developing symptomatic multiple myeloma (BM inv, anemia, renal failure, lytic lesions, hypercalcemia)
Antibodies in stiff person syndrome
Autoimmune
Paraneoplastic
anti- GAD
anti- amphiphysin
Seen in MS, visual phenomenon where pts have trouble following moving objects visually. Lateral motion in VF is perceived as having depth component
Pulfrich's phenomenon
Parasympathetic source to head and neck, which nucleus?
Superior salivatory nucleus
Ipsilateral third nerve palsy and contralateral ataxia, weakness and tremor
Claude's syndrome
Lesion in the dorsal portion of mesencephalic tegmentum
CADASIL gene mutation
NOTCH 3 (missense mutation, chromosome 19)
Presents with migraine with aura, stroke/TIAs, progressive dementia, and other ND findings. Autosomal Dominant.
Condition where there is hypertrophy of extramedullary adipose tissue in the epidural space, and is associated with chronic use of steroids
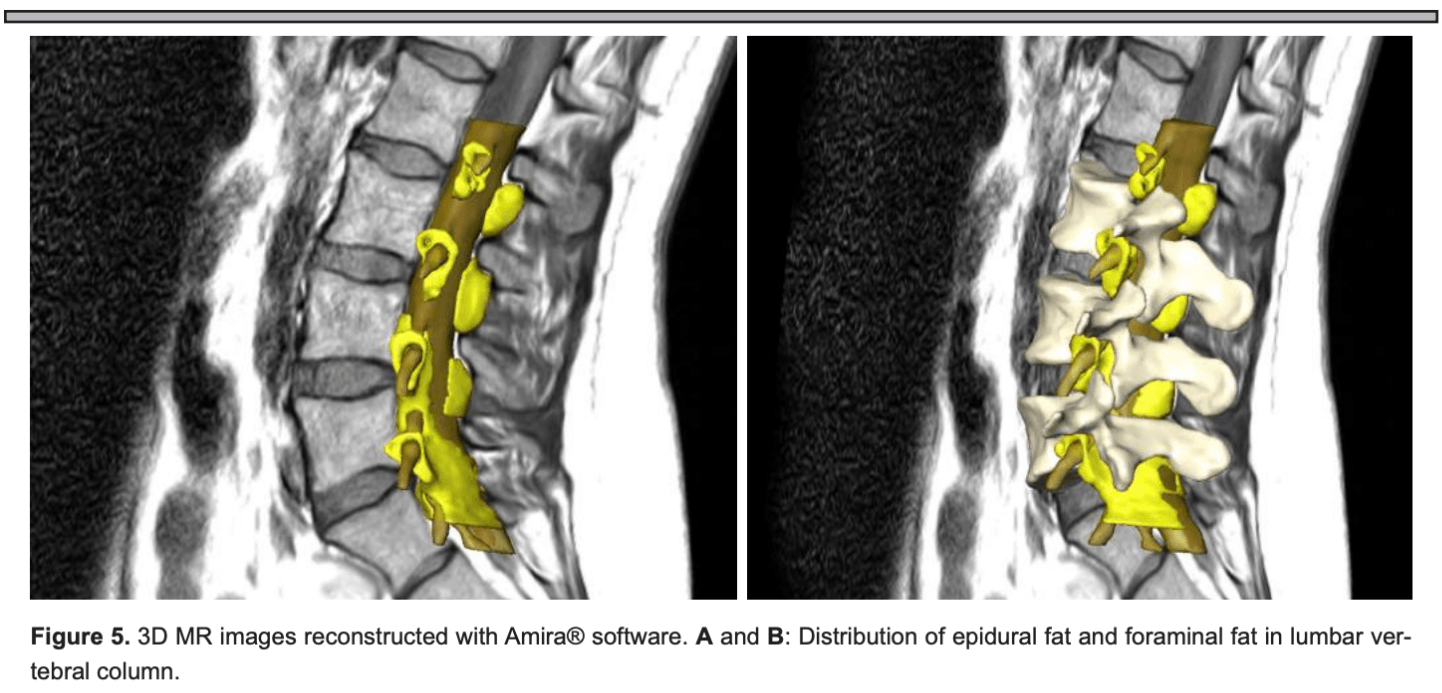
Epidural lipomatosis
Name some whole brain and CSF volume changes seen in patients with schizophrenia
Hint: brain gets bigger or smaller?
CSF volume increased or decreased?
Reduced brain volumes and higher CSF volumes
Evidence of ventricular enlargement (3rd and lateral) with sulcal widening. Atrophy of frontal and temporal lobes seen, as well as thalamus and hippocampus. PET studies have shown hypo-metabolism in DL prefrontal cortex during activation tasks
German neuro-psychiatrist. He is best known as the inventor of electroencephalography (EEG) in 1924. Discoverer of the alpha wave, which have been eponymously referred to as the "___ wave" 
Hans Berger
Syndrome. Tongue fissuring and angioedema along with neurologic complications of demyelinating and/or axonal neuropathies, myopathies, cranial neuropathies (particularly CN VII palsy)
Melkersson- Rosenthal syndrome
Can be seen in patients with IBD such as Crohn's or UC. Risk of both venous and arterial thrombosis
When using DBS to treat PD, the subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a better target to use than the globus pallidus interna (GPi) in patients with __________.
a. Axial symptoms prevalent
b. Gait issues
c. Higher medication requirements
d. Pronounced dyskinesia
GPi is favorable for those with more axial symptoms, gait issues, depression, and word fluency problems. Many also favor GPi when dyskinesias are especially problematic. In turn, the STN is often favored in those with higher medication requirements, and in those with greater tremor.
____ hand of ____: when, because of sensory deafferentation, the hand feels useless with otherwise normal motor function?
Useless hand of Oppenheim
Caloric testing. Explain.
This study demonstrated that compared to warfarin, high-dose dabigatran (110mg BID) reduces stroke (and systemic embolism) risk without increasing the risk of major bleeding among patients with nv atrial fibrillation.
RE-LY study
Diagnosis of ____ requires a distinct and clearly remembered onset of a continuous and unremitting headache, and it must be present for >3 months
New daily persistent headache (NDPH)
HA associated with NDPH often resembles migraine in its features, with days when there is light or sound sensitivity, nausea, and throbbing pain. Or it may resemble a tension-type milder headache without any of those features.
Lack of evidence for any specific treatment for NDPH
Myophosphorylase deficiency
Case: 19 yo M arrested after denied seating at a restaurant and proceeds to yell and threaten staff. Has longstanding hx of detentions at school for angry outbursts. Has gotten into many fights and previously been arrested for physical aggression against classmate. After each occurrence, he expresses regret though he often attempts to justify his actions. When not aggravated, he is usually pleasant. Most likely diagnosis?
1. Anti-social PD 2. Bipolar disorder 3. Intermittent explosive disorder 4. Oppositional defiant disorder 5. Borderline personality disorder
Intermittent explosive disorder- impulse control disorder characterized by verbal/physical aggression out of proportion to instigating event. May express remorse. Tx: psychotherapy, as well as pharmacotherapy with mood stabilizers or SSRIs.
Father of Central Texas Neurology. Hobbies include Jazzercise and fancy statue collection.

Syndrome. Type of hereditary thrombophilia. Most likely to cause thrombosis involving CNS. VST is most common neurologic manifestation. Ischemic infarcts occur 2/2 paradoxical emboli through intracardiac R->L shunt. Other neuro manifestations include acute onset chorea (can be pronounced during pregnancy), headaches, and seizures
Anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome (APLS)
High arched feet, scoliosis, neuropathy, ataxia, cardiomyopathy. Diagnosis?
Friedrich's ataxia
Trinucleotide repeat GAA expansion in Frataxin gene on chromosome 9. AR.
P.S. medication that improves outcome of CM in Friedrich's ataxia: Idebenone (coq10 analogue)