What is the shortened Nernst Potential equation?
V=61.5 log Co/Ci
What are the downward deflections in voltage-clamp recordings?
Inward currents
How many types of K+ channels did we cover?
6 channels
Why do LGIC's have reversal potentials of approximately 0mV?
due to LGIC's being non-selective channels
What type of receptor is a hair cell with stereocilia?
Mechanoreceptor
What is the long Nernst potential equation?
V = (RT)/(zF) ln (Co/Ci)
The 2 pulse voltage clamp has a pre pulse and a test pulse. What is measured during the test pulse?
Current flow is measured during the test pulse
What is going to happen if KCNQ channel is inhibited?
burst firing; M current is activated at sub threshold voltages
Once the ligand/agonist binds to the LGIC what drives the current through the channel?
Voltage
Out of the 5 tastes, which 2 have a mechanism that involve inotropic channels?
Sour and Salty
What are the Nernst potentials for Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-
Na+=+67mv
K+=-98mv
Ca2+ = +129mv
Cl-=-90mv
The 2 pulse voltage clamp allows us to measure what about VG NA+ channels?
Measure inactivation mechanics
LVA regulates the number of AP and prevents hyper-excitability.
HVA contributes to AP duration.
Cys-loop receptors are unique to which LGIC subfamily?
Nicotinic Receptor
How does the presence of light cause the closing of CNG channels?
Light activates PDE, which causes breakdown of cGMP. cGMP is what causes CNG channels to open
What is the Nernst potential of Cl- at 37 degreesC when extracellular concentration is 100 and intracellular concentration is 10?
-61.5 mv
Increasing the time between pulses in a two pulse experiment gives us what value?
The rate of recovery
Explain the role of Ih current in AP firing
(name the channels, mechanism of activation, effect on AP, and what happens if the channel gets blocked)
HCN channels are activated by hyper polarization, causing inward Na current and this helps the cell to reach the threshold (assists firing).
If blocked, there is an increased time between APs
Name all of the LGIC families and include the number of transmembrane segments and subunits associated with them.
P2X receptors: 2TM segments, 3 subunits
Glutamate receptors: 3TM segments, 4 subunits
Nicotinic receptors: 4TM segments, 5 subunits
Name the receptor that can detect multiple stimuli types and name 3 different types of stimuli it detects
TRPV1 receptors:
Mechanical, Thermal, and Chemical
How does a mutation that affects the gating of Na+ channel impact the Nernst potential of sodium ion at rest and why?
Gating of Na+ channels does not affect the Nernst potential because it is dependent on concentration.
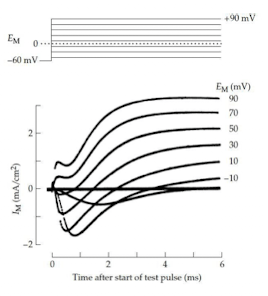
What is occurring in this image?
As the clamp voltage approaches the Nernst potential for Na+, the Na+ current begins to change from inward to outward.
A-type current
(What channels generate this current? Be specific ; where are they located and what could explain its location in a cell?)
Kv4 (+ Kv1.4) channels (LVA fast-delayed rectifiers) ; primarily concentrated at dendrites (fast activation to dampen (and encode) AP firing, while fast inactivation allows dendrites to sense fast sequences of APs (fast inactivation allows high-tuned sensitivity)
Name the different classes of positive allosteric GABA Channel Modulators.
Benzodiazepines, Barbiturates, Ethanol, Anesthetics, and Neurosteroids
Explain the mechanism of olfactory signaling in OSNs.
Odorant enters nose and activates GPCRs
GPCRs activate cAMP synthesis
cAMP opens CNG channels and Ca2+ activated Cl- channels
Flow of Cl- outward causes depolarization