This makes it more likely that a neurotransmitter will bind to its receptor on the receiving cell (on the post-synaptic membrane).
What is an Agonist?
A major difference between neurotransmitters and hormones is that neurotransmitters are transported in the nervous system and hormones are transported via this system.
What is the circulatory system (bloodstream)?
Spatial location and sensory messages.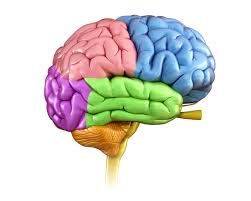
What is the parietal lobe (in the pink)?
This is what occurs when repeated exposure to a medication or drug causes the related receptors to downregulate, lessening the effect of the substance.
What is Tolerance (can also be referred to as habituation)?
The dorsal side of the spinal cord is toward the ________________. The ventral part is toward the ________________.
What are back and stomach, in that order?
During a stressful/threatening situation, the _______________ is upregulated and the _______________ is downregulated.
What are the Sympathetic and the Parasympathetic Nervous Systems (in that order)?
This is the condition when the cell is at rest and the inside of the cell has a negative charge and the outside has a positive charge.
What is Polarization?
Where the auditory cortex is located.
What is the temporal lobe (in the green)?
This occurs when the summed impulses are excitatory enough to reach the Threshold Potential (-55mV) and it causes Na+ channels to open and let Na+ rush in.
What is an Action Potential?
This is what we think of when the basal ganglia are mentioned.
What is motor control (movement, motor functioning, etc.)?
When an impulse is above the Resting Potential of -70mV but not strong enough to reach the Theshold Potential of -55mV, it is known as this (and will still cause a depolarization).
What is an EPSP (Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential)?
When the cell is at rest, there is a greater concentration of these cations inside of the cell.
What are Potassium (K+) ions?
This is made of many neural networks and is associated with emotional processing.
What is the limbic system?
These are the 3 main parts of the Limbic System we focus on in our class.
What are the amygdala, hippocampus, and cingulate gyrus/cortex?
This is what takes place when negatively charged ions (such as Chloride) come into the cell.
What is hyperpolarization?
As the axon forms separate branches toward the end of the axon, these contain the synaptic vesicles that have within them the neurotransmitter molecules.
What are Terminal Buttons (Axon Terminals)?
A neurodegenerative disease that attacks the muscles in the body, named for a famous major league baseball player.
What is ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) or Lou Gehrig's Disease?
These are the 3 structures of the brain (1) that make up the brainstem. The brainstem controls _________________ (2) behavior.
1) What are the midbrain, pons, and medulla? 2) What is UNconscious behavior?
This is typically the quickest administration method to get a medication into the bloodstream.
What is via a needle into a vein?
These are synapses that form on the cell body (from impulses coming into the cell).
What are axosomatic synapses?
In the Terminal Buttons, these (1) open up as a result of the Action Potential and cause the Synaptic Vesicles to move to and open the pre-synaptic membrane, allowing the NT's to spill out into the Synaptic Cleft. This (2) is what the process is called.
1) What are Calcium (Ca+) ion channels? And (2), what is exocytosis (as the NT's leave the cell)?
In the Terminal Buttons (Axon Terminals), the synaptic vessicles are transported to the pre-synaptic membrane due to the influx of this ion?
What is Calcium (Ca+)?
This region of the brain is located at the back of the skull and regulates coordinated movements, balance, and rhythm.
What is the cerebellum?
In addition to protection of the axon, this is a major function of the myelin sheath.
What is the formation of the Nodes of Ranvier, which significantly speed up the propagation of the nerve impulse down the axon (10-30 times faster)?
This is where the gray matter is located in the spinal cord.
What is inside (opposite of how the brain is)?