A 50 year old man was admitted to the hospital with mental status changes, incoordination, tremor and leg stiffness for the past week. The patient also took two tablets of Tylenol for two days over the past week to see if it would help with the leg stiffness, but it made his symptoms worse. Liver function enzymes were elevated with ALT 540, AST 435, and further testing revealed hepatic copper accumulation, elevated urine copper, and low serum copper. What would be the best next test?
Penicillamine with pyridoxine (25 mg/d).
Trientine is a less toxic chelator and is supplanting penicillamine when a chelator is indicated.
For patients with hepatitis or cirrhosis but without evidence of hepatic decompensation or neurologic/psychiatric symptoms, zinc is the therapy of choice although some experts advocate therapy with trientine. Zinc has proven efficacy in Wilson’s disease and is essentially nontoxic. It produces a negative copper balance by blocking intestinal absorption of copper, and it induces hepatic metallothionein synthesis, thereby sequestering additional toxic copper. All presymptomatic patients should be treated prophylactically because the disease is close to 100% penetrant.
Hyperconnectivity within the default mode network (DMN), particularly involving the medial prefrontal cortex and posterior cingulate cortex, is implicated in this psychiatric condition
Major depressive disorder
A patient with a movement disorder was found to have the CT head findings below. What do the hyperdense signals in the radiograph represent?

A polysomnogram should not be ordered for clinical suspicion of which condition?
1. restless leg syndrome
2. narcolepsy
3. circadian rhythm related disorder
4. sleep apnea
5. sleep related seizure disorder
3.
You are seeing a patient with idiopathic parkinson's disease who developed refractory severe depression. The patient's neurologist has been actively trying to treat the patient's Parkinson's disease with a regimen of sinemet, pramipexole, and rasigiline. You started the patient on sertraline for depression. However, the patient continues to struggle with both Parkinson's Disease and associated depression. A few months later, the patient returns and tells you they are feeling much less depressed due to improvement in their motor symptoms. It turns out the patient's neurologist suggested this “cutting-edge” therapy, targeting the subthalamic nucleus.
Deep Brain Stimulation
When performing a neurological exam, the examiner asks the patient to place one hand on another hand, then alternate the top hand between palm facing up and down. This test screens for function of which brain region?
Cerebellum
Reduced top-down control from the ventromedial prefrontal cortex over the amygdala is a key circuit dysfunction implicated in this psychiatric disorder.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
A patient presents to the emergency room with one week history of intermittent dizziness, headaches, visual blurriness. Friend mentions that the patient has been more somnolent, then today had an hour long episode of dysarthria.
CT head shows the following. Which vessel is affected in this condition that leds to the patient's symptoms of oculomotor, behavioral, and visual symptoms?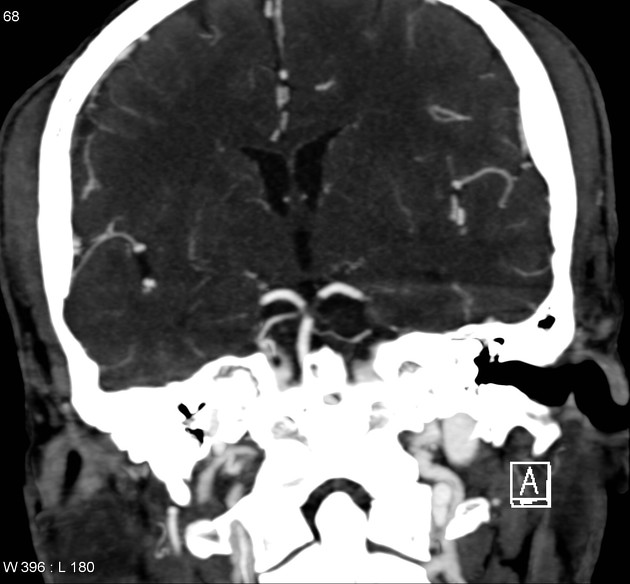
Basilar artery.
This is the top of the basilar syndrome
A 67yo patient has been progressing with several month history of slow decline in memory and language abilities. Family members have noticed increased anxiety and episodes of anger. The psychiatrist decides to order neuroimaging. The family asks whether a CT or MRI should be ordered. Which of the following statements would be an appropriate statement to say?
1. An MRI takes less time and would be appropriate
2. A CT cannot be performed if a patient has a history of heart implants, thus an MRI should be performed
3. An MRI would be better at detecting vascular and demyelinating disease and should be ordered
4. An MRI can be readily accessible and here used for rapid screening of acute processes in the brain
5. A CT is useful for detecting brain volume changes that might help explain the clinical picture
3.
A 30 year old woman presents to the emergency room with 2 weeks of paranoid delusions, decreased sleep, and erratic behaviors including calling family in the middle of the night. The patient has been previously medically and psychiatrically healthy. CBC, electrolytes and a drug screen are all unremarkable. The patient is tachycardic to 110s but otherwise vitals are within normal limits. Pregnancy testing is negative. Neuroimaging is subsequently considered. What would be the most appropriate type of neuroimaging to obtain to assist with diagnostic clarification?
MRI brain with and without contrast
During a neurological examination, the patient stretched their arms out in front of their body with palms facing upwards and eyes closed. One arm involuntarily dropped and the forearm rotated so the palm faced downwards. This finding indicates a lesion in which neuronal tract?
corticospinal tract
Pronator drift is an indicator of upper motor neuron (UMN) weakness. The test reveals subtle weaknesses not evident in normal voluntary movements and is commonly used to assess for potential brain lesions involving the corticospinal tract, which may not yet produce other overt signs of UMN lesions, such as pronounced muscle weakness.
A 52-year-old man is brought to the ED by his partner after he began putting non-food objects in his mouth and attempting to undress in public. He appears unusually calm, does not recognize familiar faces, and is constantly touching and exploring objects around him. He has experienced HSV encephalitis a few months ago.
His symptoms are caused by disruptions of brain structures, including the amygdala and hippocampus, in which neurocircuit?
What is the limbic circuit (or amygdala-hippocampal-prefrontal circuit)?
A patient with 3 months history of depressed mood, progressive gait difficulties, and cognitive decline was ordered for a CT head, showing the following finding. What would be the next immediate best step in confirming the diagnosis and in treatment?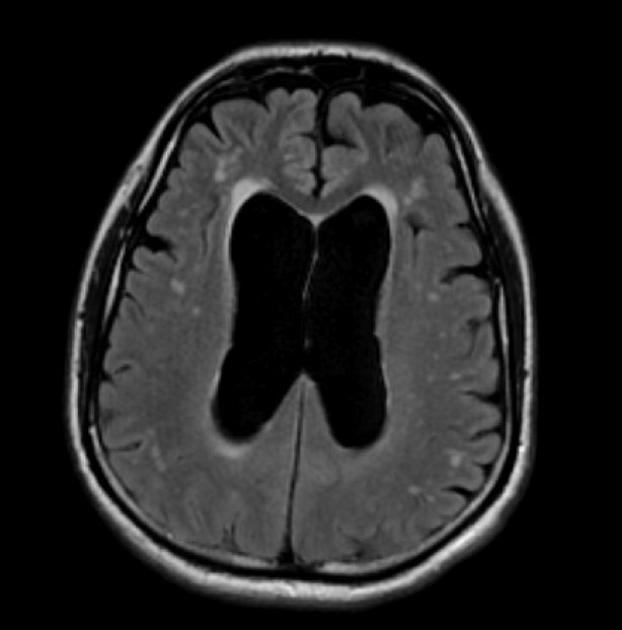
Large volume spinal tap.
(In the long term, consideration of VP shunt)
A young individual was involved in a high-speed motor vehicle accident, where they were driving and hit by another speeding vehicle. During this event, their head and neck moved rapidly forward and backward during acceleration and deceleration. Their head did not hit anything. Following this, which would be the most concerning brain injury to look for that would correlate with the clinical picture?
1. epidural hematoma
2. skull fracture
3. diffuse axonal injury
4. subdural hematoma
5. brainstem herniation
3.
DAI is caused by blunt injuries, and shearing forces
A patient is referred to neuropsychological testing due to concerns with visuospatial function, including recognizing and remembering people's faces, remembering directions, and drawing complex figures. Which of the following tests should definitely be included in testing?
1. Boston Naming Test
2. Stroop Color Test
3. Minnesota Multiphase Personality Inventory
4. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
5. Rey Osterrieth Complex Figure Test
5
A patient has reported one week history of trouble keeping their eyes open, double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulty taking and swallowing. These symptoms worsen with physical exertion, especially at the end of the day. The patient denies any pain. A comprehensive cancer screening will most likely identify which type of cancer as the cause of the patient's symptoms?
Thymoma
A 26-year-old woman presents with a 5-year history of intrusive thoughts about contamination and a compulsive need to wash her hands dozens of times per day. She reports spending over 3 hours daily on cleaning rituals, which she recognizes as excessive but feels unable to stop. Functional imaging is most likely to show hyperactivity in this circuit involving the orbitofrontal cortex, caudate nucleus, and thalamus.
The orbitofrontal cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical loop
A 40year old man was found unconscious in the park in his running gear. Bystanders report he was running then suddenly dropped to the ground. He was brought to the emergency room immediate and a CT head was ordered showing the following. What is the most common, non traumatic, cause of the finding below?

Cerebral aneurysms (rupturing leading to subarachnoid hemorrhage)
Which of the following would be the most useful for differentiating between Alzheimer's Disease and FrontoTemporal Dementia?
1. MRI brain with and without contrast
2. PET with tau-tracers
3. MRI brain angiography
4. CT head
5. MRI brain with thin coronal slices
2.
A patient with a history of cirrhosis is admitted to inpatient medicine for management of ascites and hepatorenal syndrome. The patient is noted to exhibit asterixis, confusion, somnolence, and an overall change in mental status. An EEG will show:
1. triphasic waves on a disorganized background
2. 3 to 4 hz periodic sharp waves
3. generalized slowing on a disorganized background
4. chaotic and disorganized activity with no identifiable pattern
5. isolated spikes in P9
1. (hepatic or renal encephalopathy)
A patient develops acute changes in language abilities. They are noted to be speaking fluently, but regardless of what they are being told or asked, they appear to not understand, and provide responses that are devoid of content, and non sensical. When asked to repeat "today is a good day", they responded "smoodle cake play". Reading is impaired.
Which area of the brain is affected in this condition?
Superior temporal gyrus
A 34-year-old man presents for treatment of stimulant use disorder. He describes intense cravings and continued use of cocaine despite losing his job and damaging several relationships. Neuroimaging studies suggest dysregulation in this dopamine-rich circuit involving the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, and prefrontal cortex.
mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathway (or the reward circuit)
A 55 year old man with a history of schizophrenia on clozapine, residing in a group home, has been noticed by staff members to have a transient weakness on the left side of his body after waking up, followed by difficulty speaking and restless behaviors for the rest of the morning. The patient was brought to the emergency room with CT head showing the following. What is the area of the infarct?
Right caudate
A young woman in her 30s has reported several month history of intermittent episodes of sensitivity to bright lights, left eye pain, and sudden numbness and tingling to her left arm and leg. She has also noted that the symptoms worsen with stress, and she has been feeling much for fatigued recently than usual. A decision to perform a lumbar puncture was made. Which of the following CSF tests should be ordered?
1. 14-3-3 protein
2. fungal and bacterial culture
3. viral PCR
4. amyloid and tau biomarkers
5. IgG and kappa free light chain
5.
"In multiple sclerosis, the cerebrospinal fluid will most likely contain oligoclonal bands of specific types of protein, increased IgG, kappa free light chain, and myelin basic protein."
A patient with treatment refractory epilepsy is referred to psychiatry for worsening depression. The patient shares a history of recurrent, severe seizures characterized by loosing consciousness, followed by generalized shaking, that occurs at least once a week. The patient has tried numerous medications without adequate seizure control and is very frustrated and down by the impact of her epilepsy on her daily functioning. The patient reports feeling down and hopeless. Which would be the most important item to screen for in the visit?
1. History of eating disorder
2. Trauma history
3. Suicidal thoughts
4. Obsessive thinking
5. Perceptual changes
3.
Comorbid psychiatric disorders frequency and severity of seizures are most important factors contributing to higher risks of suicide in patients with epilepsy.