A 9-year-old child with ADHD does not respond to methylphenidate. This medication should be tried next.
Amphetamine/ Dextroamphetamine
Dopaminergic neurons in the mesocorticolimbic system originate from this structure.
Substantia nigra
This OTC supplement is used to target symptoms of trichotillomania.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
This neurotransmitter has a major role in the acute reinforcing effects of drugs of abuse.
Dopamine
This monthly long-acting medication can be used in the treatment of alcohol use disorder
Vivitrol (naltrexone ER)
Memantine exerts its cognitive preservation effects through this mechanism.
NMDA receptor antagonism
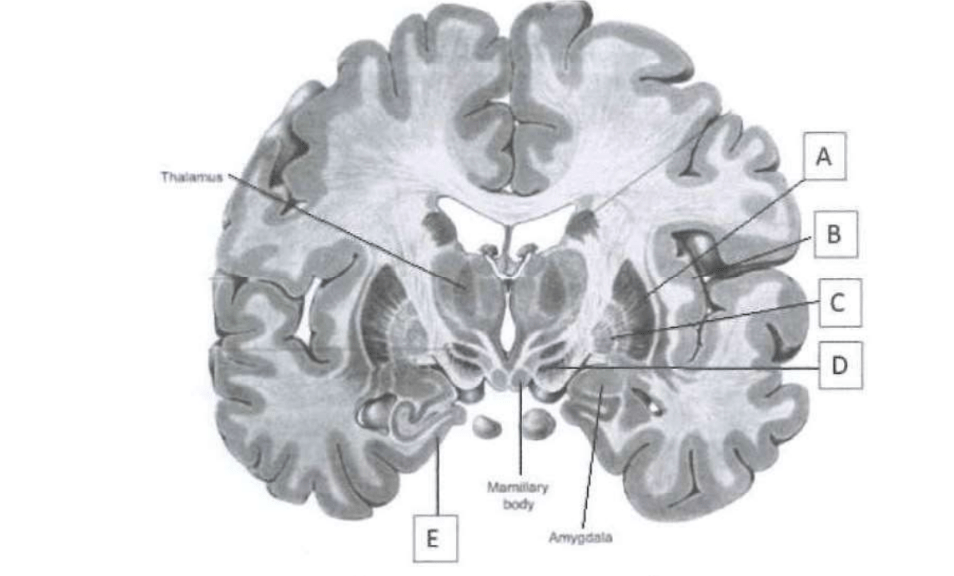 This label indicates the insula in the coronal section of the cortex.
This label indicates the insula in the coronal section of the cortex.
Answer: B
Taken prior to conception, this OTC may reduce the risk of major congenital malformations in women taking anti epileptic medications.
Folic Acid
This neurotransmitter system most directly regulates impulsive or affective aggression.
Serotonergic
This substance is associated with the highest rate of conversion to schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
Cannabis
This antipsychotic carries the lowest risk of QT prolongation.
Aripiprazole
This area of the brain is implicated in maintaining wakefulness.
(Ascending) Reticular Activating System
Co-prescription of this class of analgesics is likely to cause a clinically significant rise in lithium levels.
NSAIDs
This neurotransmitter is contained in sleep-promoting neurons of the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus.
GABA
Cigarette smoking induces the metabolism of this atypical antipsychotic.
Clozapine (or Olanzapine)
This is the mechanism of action of valbenazine, a medication used to treat tardive dyskinesia.
Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 2 (VMAT-2) inhibition
Histaminergic neurons that regulate sleep originate from this brain nucleus.
Tuboromammillary Nucleus (TMN)
A patient with a history of alcohol use disorder presenting with ataxia, nystagmus, and confusion is likely deficient in this vitamin.
Thiamine (B1)
This cell type is implicated in both neural circuit formation in the developing brain and scavenging for damaged neurons, plaques, and infectious agents.
Microglia
Most substances of abuse activate this dopaminergic pathway, leading to addictive behavior.
Mesolimbic
In the CATIE study, this antipsychotic was considered most effective due to its low rate of discontinuation and high reduction in psychopathology.
Olanzapine
This label indicates the putamen.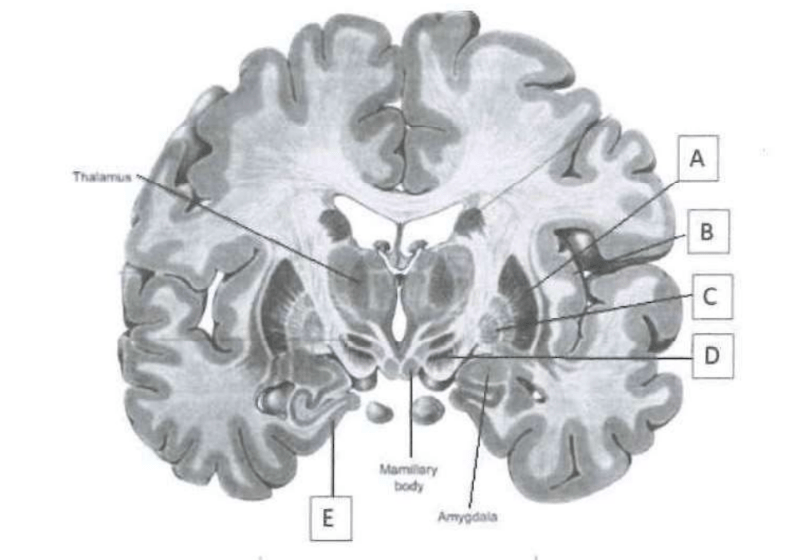
A
A 72-year-old patient's examination is remarkable for profound sensory ataxia with loss of vibratory sensation and cognitive issues described as irritability, fluctuating with somnolence. This is the most likely nutritional deficiency associated with these findings.
Cobalamin (B12)
Developmental delay, cardiac abnormalities, palate defects, immune deficiency, and an increased risk of schizophrenia characterize this genetic syndrome.
DiGeorge Syndrome
Activation of this receptor is thought to be responsible for the anti-anxiety and sedative hypnotic effects of alcohol.
GABA-A