What are the 2 types of ion channels that exist?
- Voltage gated
- Ligand gated
Does atropine treat all cholinergic symptoms?
Does not bind to nicotinic receptors, it does not treat neuromuscular dysfunction.
Name the actions of alpha 1 and 2
alpha 2a = predominantly in the CNS - sedative, hypotension and analgesia. peripheral vasoconstriction.
alpha 1 = vascular vasoconstriction
Name some drugs that have MAOI qualities
- Methylene blue (mainly MAO-A)
- Linezolid (non specific)
What are some symptoms of excessive dopamine and diminished dopamine
Excessive = Choreoathetosis, tics. Paranoia, psychosis, drug craving, addictive behaviour.
Diminished = Extrapyramidal disorders – acute dystonia and parkinsonism
Where is most of the bodies serotonin located?
The gut - enterochromaffin cells of the intestine
What is the mechanism of isoniazid toxicity causing seizures?
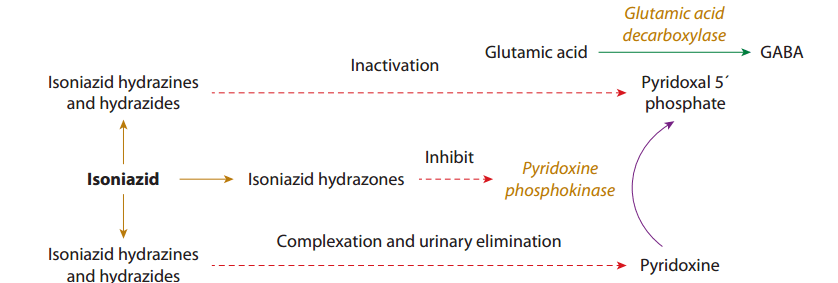
What overdose substance can cause refractory seizures, hypokalemia and SVT. What is its toxic mechanism?
Caffeine / methylxanthines
Adenosine antagonist
Describe how neurotransmitters are released
- Depolarization occurring due to wave of Na+ opens voltage gated Ca2+ channels. Influx triggers exocytosis of vesicles containing neurotransmitters.
In cholinergic toxicity which effects are mediated by muscarinic and which by nicotinic?
Muscarinic = classic SLUDGE
Nicotinic = muscle fasciculations or paralysis due to activation of the neuromuscular junction.
Yohimbine is a selective competitive antagonism of alpha2, what clinical effects would you expect?
hypertension, tachycardia, anxiety, fear, agitation, mania, mydriasis, diaphoresis, and bronchospasm
What is the role of MAO
Neuronal MAO(B)- deaminates cytoplasmic amines including neurotransmitters
Hepatic & Intestinal MAO(A) - prevent large quantities of dietary bioactive amines from entering circulation
Why does tardive dyskinesia occur?
Chronic usage of antipsychotics, especially first generation, can cause increased dopamine receptor sensitivity and upregulation. Excess dopamine in the synapse can also cause more reuptake and vesicular dopamine contributing.
Name a drug that affects:
- 5HT1
- 5HT3
- 5HT1 B/D agonist - triptans (Cranial blood vessels possess 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors, whose activation produces vasoconstriction and decreased inflammation)
- 5HT3 antagonist - ondansetron (large concentration at the chemoreceptor trigger zone – activation causes)
For the following name whether it is a GABA agonist or antagonist indirect/direct
Cephalosporins, Muscimol, Ethanol, Flumazenil, Baclofen
Cephalosporins = Direct GABA-A antagonist
Muscimol = Direct GABA-A agonist
Ethanol = Indirect GABA-A agonist
Flumazenil = Indirect GABA-A antagonist
Baclofen (also GHB) = Direct GABA-B agonist
What does adenosine do in the brain?
Primarily limits glutamate and ACh release, thereby preventing excessive postsynaptic neuronal stimulation
How do excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters act post-synaptically
- An excitatory neurotransmitter (ENT) binds to receptors linked to G proteins to prevent K+ efflux or to allow Na+ influx, producing membrane depolarization
- An inhibitory neurotransmitter hyperpolarizes the membrane (makes membrane potential more negative) by binding to receptors linked to G proteins to enhance K+ efflux [4], or to Cl− channels to allow Cl- influx
Why does poisoning with nicotine cause hypertension with subsequent hypotension?
Prolonged depolarization at the receptor eventually causes diminution of responses to receptor occupancy.
Describe the mechanism of action of phenotalamine and why it works for extravasation of epi/norepinephrine, why wouldn’t terazosin work
The concern is alpha 1 or 2 mediated vasoconstriction, thus, you require an alpha 1 and 2 inhibitor, terazosin is only an alpha 1 inhibitor
If you were being forced to take an MAOI right before eating a boatload of cheddar cheese – what type of MAOI should you choose – irreversible or reversible of nonspecific, A or B
Reversible MAOI B inhibition
For the following name whether it is a dopamine agonist or antagonist indirect/direct
Pramipexole, benztropine, haloperidol/prochlorperazine, cocaine
Pramipexole - direct agonist
Benztropine - indirect agonist (inhibit dopamine reuptake)
Haloperidol/prochlorperazine - direct antagonist - at D2 receptor
Amantadine - indirect agonist
How do SSRIs cause platelet dysfunction?
Inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), which is responsible for the uptake of serotonin (5-HT) into platelets
Serotonin is released from activated platelets to interact with other platelet membranes (promote aggregation) and with vascular smooth muscle.
If you were having trouble controlling alcohol withdrawal what adjuncts could be used and why?
Patients experiencing severe alcohol withdrawal have an increased proportion of GABAA receptors containing benzodiazepine-insensitive α4 subunits, and contain fewer GABAA receptors with benzodiazepine-sensitive α1 subunits
May use propofol or phenobarbital that either act on a different site on the GABAA receptor or directly open the Cl− channel
What is the mechanism of action of strychnine?
Competitively inhibits glycine binding to its receptor, decreasing Cl- influx
Neurotransmitters bind to 2 classes of receptors. Name them and an example each.
- Ligand gated ion channels = Ach nicotinic, GABAa, Glycine, Glutamate NMDA, 5-HT3
- G-protein coupled receptors = Ach muscarinic, adenosine, dopamine, GABAb, GHB, norepinephrine, 5-HT1,2,4-7
True or false
Pseudocholinesterase (plasma cholinesterase or butyryl cholinesterase) degrades synaptic Ach.
False
What does NET norepinephrine transporter) do?
Transports neurotransmitters including NE into the neurons. Can also do reverse transport if there is a high concentration of NE inside the neuron (amphetamine can do this)
Many noncompetitive inhibitors - TCA, carbamazepine, methylphenidate
How does the action of GABA-A and B differ?
GABA -A = Ligand gated ion channel – postsynaptic Cl channels = allow Cl to move into and hyperpolarize the neuron
GABA-B = G-protein coupled
- Presynaptic inhibition results from preventing Ca2+ influx so as to impair exocytosis of neurotransmitter vesicles
- Postsynaptic inhibition is mediated by increasing K+ efflux through K+ channels, resulting in hyperpolarization
For the following name whether it is a glutamate agonist or antagonist indirect/direct
Domoic acid, ketamine, Ibotenic acid, PCP
Domoic acid, Ibotenic acid = direct agonist
Ketamine, PCP = NMDA receptor antagonist ( ketamine may directly activate AMPA)
Name
- 2 direct cholinergic agonists
- 2 indirect cholinergic agonists
- 1 naturally natural substance that alters acetylcholine?
- Direct: nicotine(n), succinylcholine(n), varenicline(n), muscarine (m), pilocarpine (m)
- Indirect: Ethanol(n), local anesthetics(n), ketamine(n), physo/riva/neostigmine,
- Substance: atropine, latrotoxin, hyoscine (scopolamine), organic phosphorous compounds