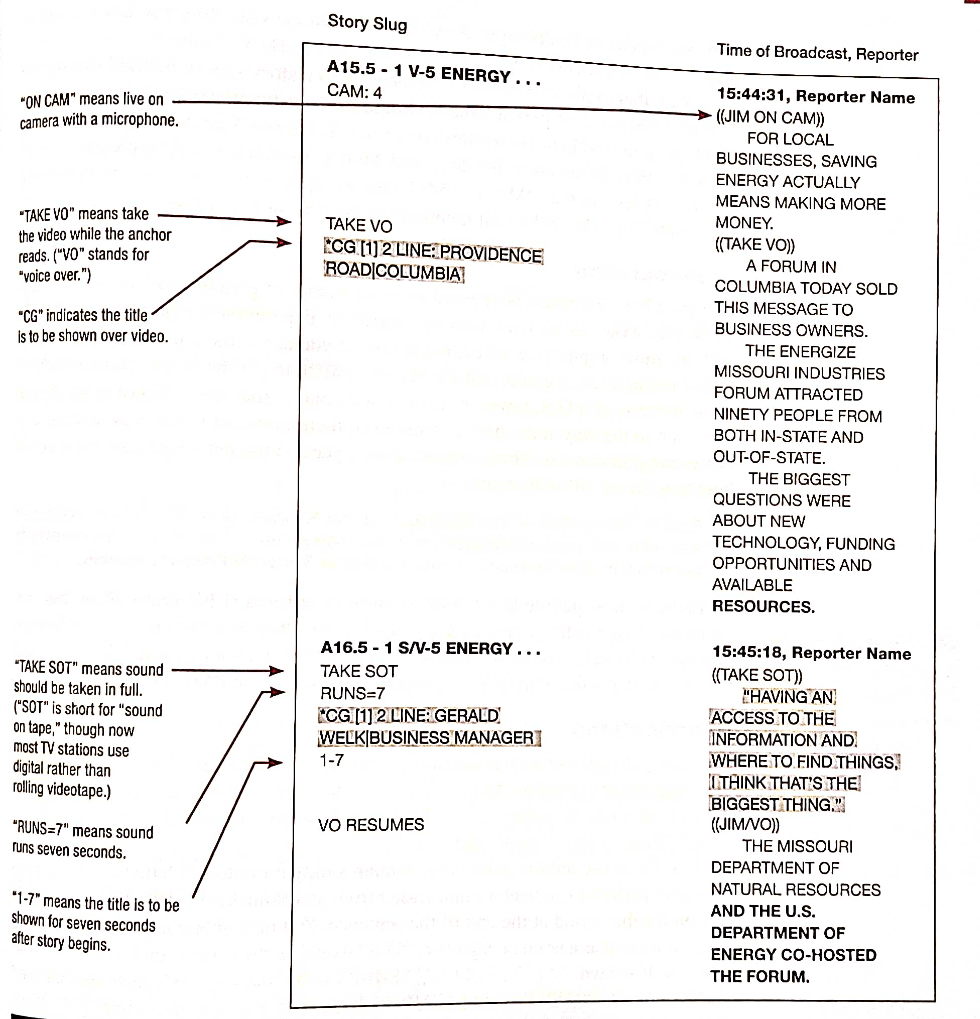
Fill in the Broadcast Script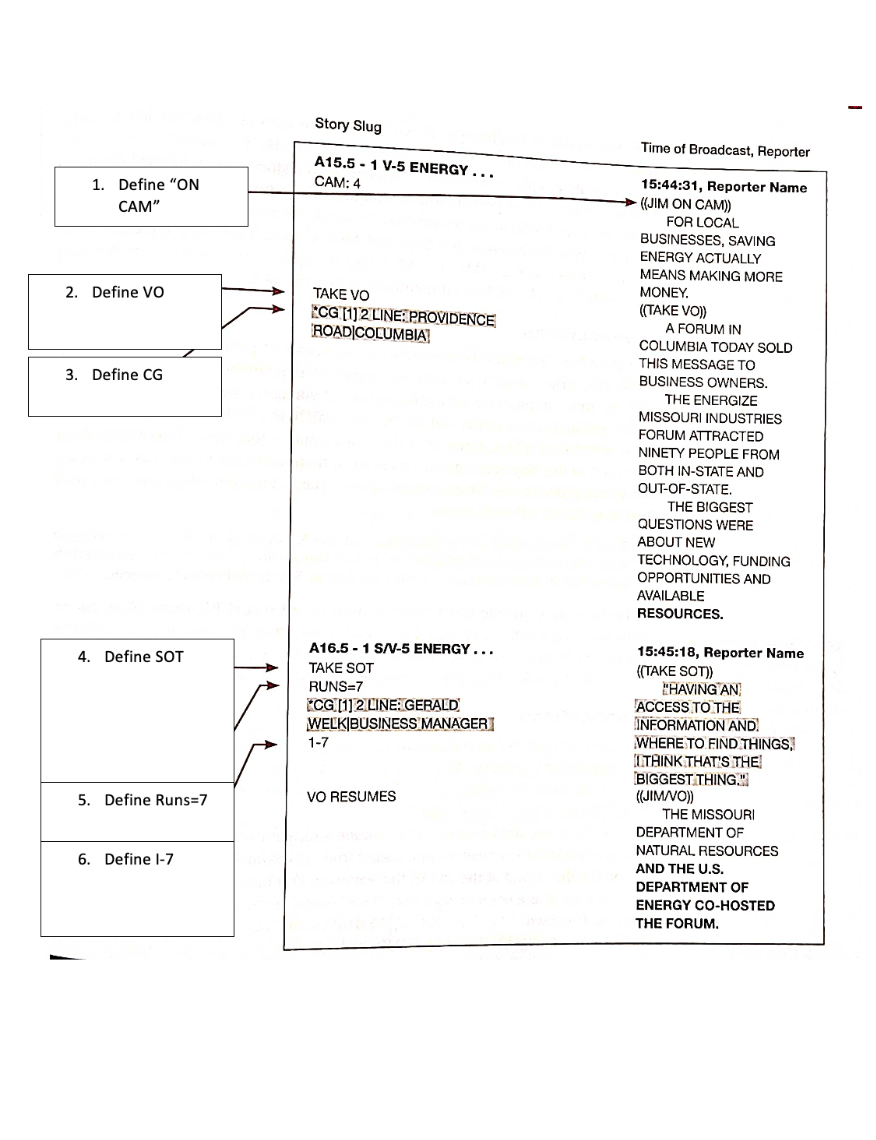
What five freedoms does the First Amendment protect?
1. Freedom of speech
2. Freedom of press
3. Freedom of religion
4. Freedom to petition
5. Freedom to assembly
True or false. Journalist are allowed to alter or digitally manipulate the content of a photograph if needed to tel their story.
The Associated Press Statement of News Values could not be clearer: “AP pictures must always tell the truth. We do not alter or digitally manipulate the content of a photograph in any way.”
Match the Ethics Vocabulary
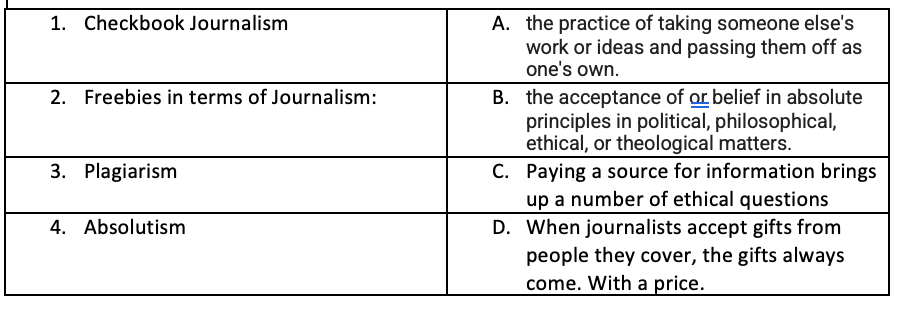
- C
- D
- A
- B
What is the difference between "affect" and "effect?"
Affect: to influence (verb): “The garden’s yield was affected by the lack of water.”
Effect: to make or accomplish (verb); result (noun): “The new reward system effected great changes in the workers’ morale.” “One effect of the drought was a poor tomato crop.”
When writing a news story for TV, the writer must write to what?
1. Video
What is the difference between libel and slander?
This general area of law is called defamation law. Libel and slander are types of defamatory statements. Libel is a defamatory statement that is written. Slander is a defamatory statement that is oral.
Name one of these questions to make good ethical decisions as a journalist.
1.What do I know? What do I need to know?
2.What is my journalistic purpose?
3.What are my ethical concerns?
4.What organizational policies and professional guidelines should I consider?
5.How can I include other people, with different perspectives and diverse ideas, in the decision-making process?
6.Who are the stakeholders—those affected by my decision? What are their motivations? Which are legitimate?
7.What if the roles were reversed? How would I feel if I were in the shoes of one of the stakeholders?
8.What are the possible consequences of my actions? Short-term? Long-term?
9.What are my alternatives to maximize my truth-telling responsibility and minimize harm?
10.Can I clearly and fully justify my thinking and my decision? To my colleagues? To the stakeholders to the public?
Government Regulatory Agencies
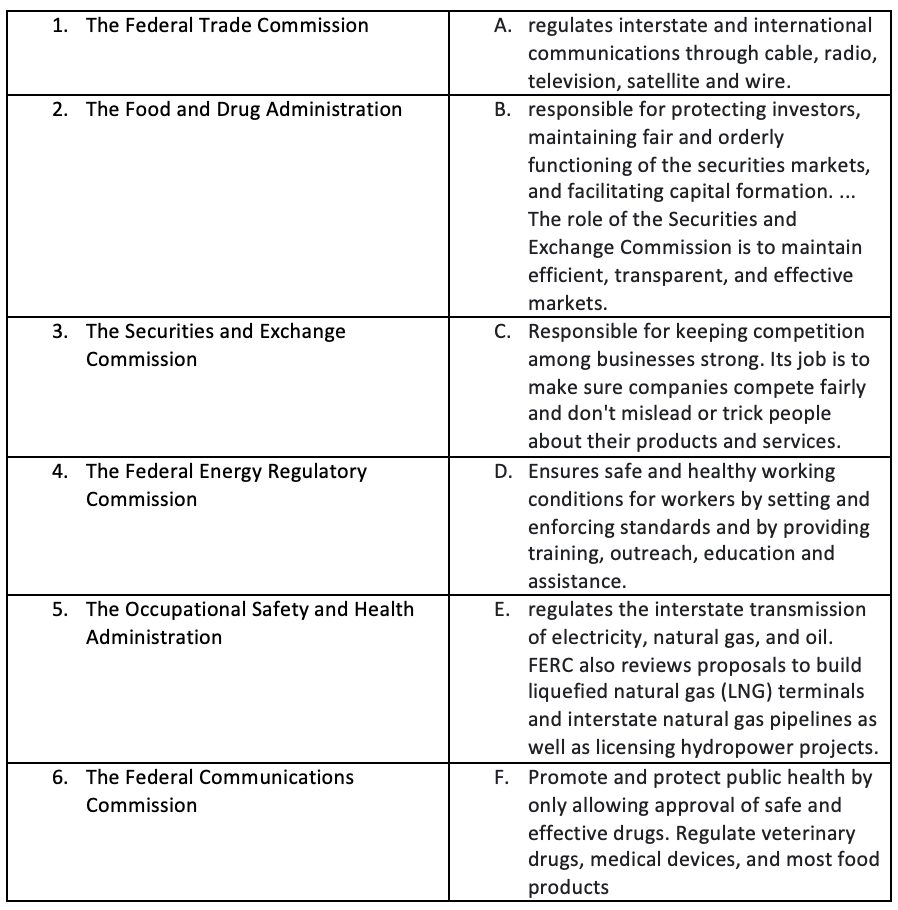
- C
- F
- B
- E
- D
- A
What is the difference between "precede" and "proceed?"
Precede: to come before (verb): “K precedes L in the alphabet.”
Proceed: to go forward (verb): “The diplomatic party proceeded into the restaurant.”
What are three things you need to believe in order to persuade people ethically?
1. People are essentially good.
2. People are intelligent and can learn.
3. People are changeable, and you can gain their attention and acceptance.
There are four possible answers. Give one. You may be committing invasion of privacy by...
1. trespassing on private properly.
2. Portraying someone in a "false light."
3. Causing unwanted publicity that is offensive to a person of ordinary sensibilities.
4. Using someone's image in an ad.
Name one conflict of interest that journalists face.
1. Friendship
2. Freebies
3. Checkbook Journalism
4. Participation in the news
Key PR Terms
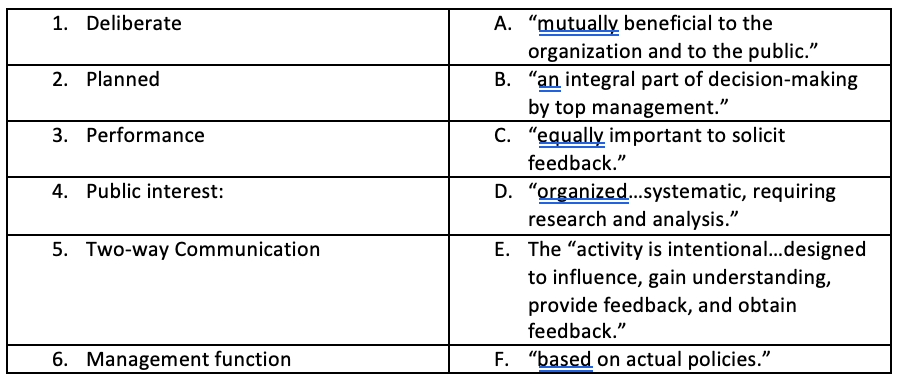
- E
- D
- F
- A
- C
- B
What is the difference between "principal" and "principle?"
Principal: The main one; most important (adjective); the head of an organization, or a sum of money (noun): “A principal witness in the case has been granted immunity.”
Principle: an ideal or a belief; a basic standard of law (noun): “The United States was founded on the principle of freedom.”
What are five choices (there are many) if you want to write in the field of public relations?
1. Media Relations: Seeking publicity and answering questions posed by the media.
2. Publicity: Working to help individuals provide opportunities through media, personal appearances and events to build their reputations and visibility.
3. Government affairs: Spending time. with legislatures and regulatory agencies, sometimes including lobbying.
4. Industry relations and trade publications: Relating to other firms within the industry and to trade associations.
5. Investor, financial or shareholder relations: working to maintain investor confidence and good relationships with the financial world.
6. Research. Conducting investigations into target audiences to discover their habits, preferences, media choices, developing insights into optimal strategies, and reporting findings.
7. Internal communication: Creating and disseminating messages to organizational employees or members in order to inform, attract and retain staff members.
8. Philanthropy: Writing, managing and publicizing an organization's charitable programs.
9. Social media: planning and executing strategies for various social media platforms.
10. Content marketing. Creating blogs, white papers, case studies and e-books to promote an organization or cause by providing useful information to clients and potential clients.
11. Business-to-business communication: Developing messaging and selling products and services from one business to another.
12. Owned media: developing strategies and messaging for organizational websites, Facebook or Instagram, Twitter, blogs and mobile sites.
13. Event planning: planning, proposing and executing promotional events using a variety of media and tactics.
14. Speech writing: Researching and writing materials for delivery by key organizational members, policymakers and political candidates.
15. Account planning: Researching and developing consumer insights, preparing creative briefs and campaign reports.
16. Crisis Communication. Preparing readiness plans and communicating swiftly and accurately to stakeholders in the event of a personnel problem, production failure, environmental issue or similar problematic situation.
There are several ways you can boost your odd of getting important public records. Name one of them.
1. Know the state and federal laws.
2. Know what documents you want.
3. Be polite and persistent.
4. Show the public the importance of the documents.
Name one of the ethical guidelines from the Society of Professional Journalists.
1. Avoid conflicts of interest, real or perceived. Disclose unavoidable conflicts.
2. Refuse gifts, favors, fees, free travel and special treatment, and avoid political and other outside activities that may compromise integrity or impartiality or may damage credibility.
3. Be wary of sources offering information for favors or money; do not pay for access to news. Identify content provided by outside sources, whether paid or not.
4. Deny favored treatment to advertisers, donors or any other special interests, and resist internal and external pressure to influence coverage.
5. Distinguish news from advertising, and shun hybrids that blur the lines between the two. Prominently label sponsored content.
Law Vocabulary
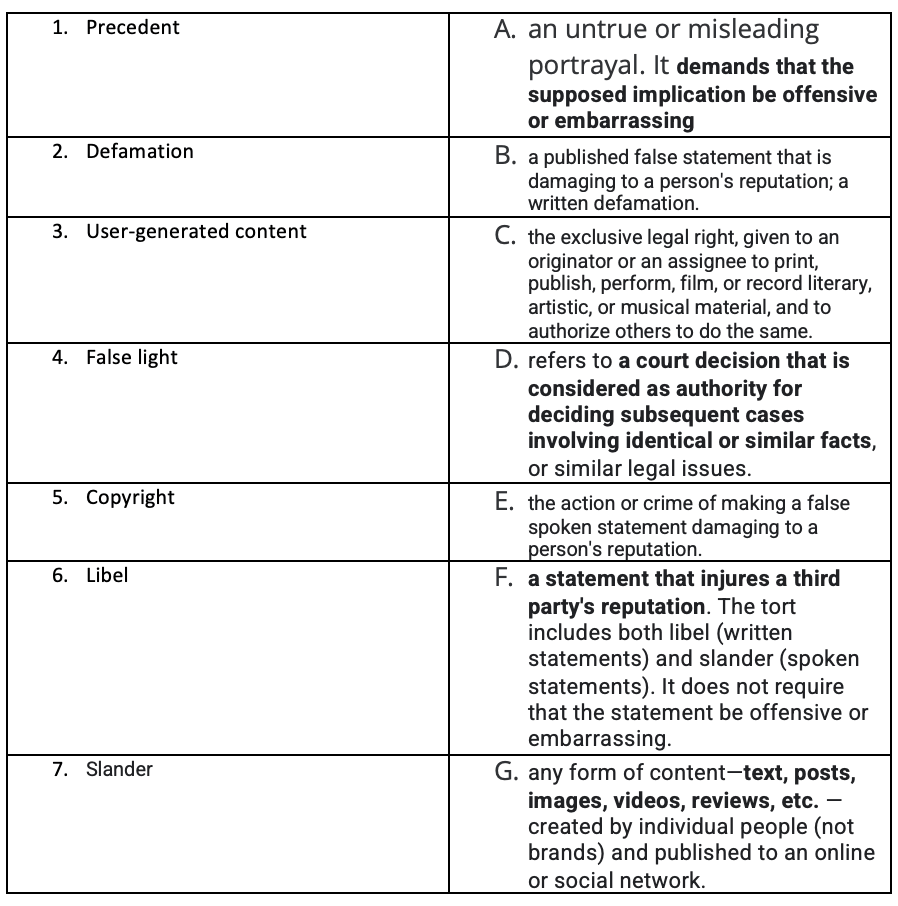
- D
- F.
- G
- A
- C
- B
- E
When do you use "fewer?" When do you use "less?"
Fewer: refers to items that can be counted: “Fewer people showed up at the play tonight than were expected.”
Less: refers to general amounts: “Less snow fell than was predicted.” (Snow can’t be measured by counting.)
Name four characteristics when writing for Television.
1.Immediacy: Radio and television news writers achieve a sense of immediacy in part by using the present tense as much as possible.
2.Conversation Style: ”Ready your copy aloud” It should sound like a conversation.
3.Tight Phrasing: Write conversationally without being wordy. Condense, condense, condense.
4.Clarity: Unlike readers, radio and television news audiences can’t go back to reread a passage they didn’t quite grasp. Their attention waxes and wanes. So you must be clear and precise.
Journalists and strategic communicators also need to know when and how they can use material from other authors. What are some key elements of copyright law?
▫Copyrightable works are protected from the moment they are fixed in tangible form, whether published or unpublished.
▫Copyright protection begins with a work’s “creation and…endures for a term consisting of the life of the author and 70 years after the author’s death.”
▫Works for hire and anonymous and pseudonymous works are protected for 95 years from publication or 120 years from creation, whichever is shorter.
▫There is a “fair use” limitation on the exclusive rights of copyright owners. In other words, it may be permissible to quote excerpts from a copyrighted work without permission.
Name five Ethical problems that journalists face.
1. Deceit
2. Conflicts of interest
3. Advertising pressure
4. Invasion of privacy
5. Withholding information
6. Incorrect and incomplete information
7. plagiarism
TV/Radio Vocabulary

1. H
2. C
3. F
4. B
5. G
6. E
7. I
8. D
9. A
Find five mistakes in this article
…Resources, petitions to sign (no comma) and devastating news.
**are instead of our
They're **their
George Floyd
From helpful tips *too keep in mind
“It’s” imperative instead of “its”
“lose” sight instead of “loose sight
"People are hungry for more information....," *Open quotation mark
"This kind of free public service is essential, " *Missing quotation mark
*here not Hear
Incorrect punctuation after "comforting content." It should be colons not a period.
Black DOES need to be capitalized in "Black therapists."
https://apnews.com/article/archive-race-and-ethnicity-9105661462
- AP’s style is now to capitalize Black in a racial, ethnic or cultural sense, conveying an essential and shared sense of history, identity and community among people who identify as Black, including those in the African diaspora and within Africa. The lowercase black is a color, not a person. AP style will continue to lowercase the term white in racial, ethnic and cultural senses.