This relationship is known as Kepler's Third Law
What is T2 = r3
This equation defines Newton's Second Law
F = ma
The value of this constant is 6.67*10-11Nm2/kg2
Big G
This is location where the ball in the picture should be released in order to hit the target. 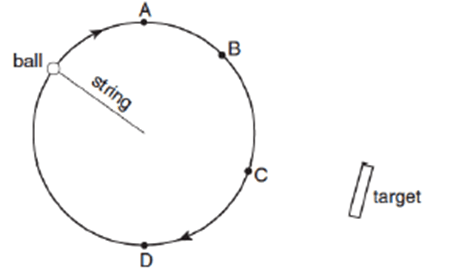
B
This is the country where Newton was born.
England
The shape of the planets' orbits are elliptical with the Sun located at one of the focii.
This statement defines the motion of all objects, known as Newton's First Law
An object in motion will stay in motion, in a straight line at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net outside force
This is the force of gravitational attraction between the Earth and the Moon.
mE = 5.98*1024kg
mM = 7.35*1022kg
r = 3.84*108m
1.98*1020 N
This is the name given to any force that causes an object to travel in a circular path and the direction this force points (2 parts)
Centripetal Force, towards the center
This astronomer was Kepler's friend and mentor
Tycho Brahe
This statement is known as Kepler's Second law and describes the speeds of orbiting bodies at different locations
An imaginary line connecting the Sun and any planet sweeps out equal amounts of area in equal lengths of time
This statement is known as Newton's Third Law and is the reason you aren't falling through your chair.
For every force there is an equal and opposite force
This is the gravitational field strength of the Earth (m = 5.98*1024 kg) at a distance of 6,370km from the planet's center.
g = 9.8 N/kg
This is the acceleration (number and direction) of a ball on a 1.5m long string moving at 3.5m/s in a circle
a = 8.2 m/s2 towards the center
This is a shape that has an eccentricity of 1
a straight line
This period of time is how many years it takes for an object to orbit the Sun if it is 25 times further away from the Sun as the Earth.
125 years
This is the acceleration of a 10kg rope during a tug-of-war game when one team pulls with 7,845N and the other team pulls with 7,840N.
a = 0.5 m/s2
This is the mass of an object who's gravitational field strength is found to be 13 N/kg at a distance of 2.35*1012 m
1.07*1036 kg
This value is the centripetal force on an orbiting satellite which has a mass of 150,000kg and orbits the Earth at a speed of 5,500 m/s. The radius of the Earth is 6,370km and the satellite orbits about 300km above the Earth's surface.
680,285 N
This planet is the most eccentric in our solar system
Mercury
SN 1604
According to Newton's Third Law, this is the force opposing the Earth's gravitational pull on the Moon, Fg E-M
Force of the Moon on the Earth, Fg M-E
This is the net gravitational force on a 1kg ball located 100km below the Earth's surface, assuming the Earth is spherical and has equal density everywhere. (draw a picture!!!!!!)
This length of time in minutes is the orbital period for the International Space Station. The ISS makes a circular orbit around the Earth, the net force on the ISS is 3.78*106 N, the mass of the ISS is 400,000kg, the ISS orbits 6,773,000m above the center of the Earth.
t = 88.6 min