Newton's First
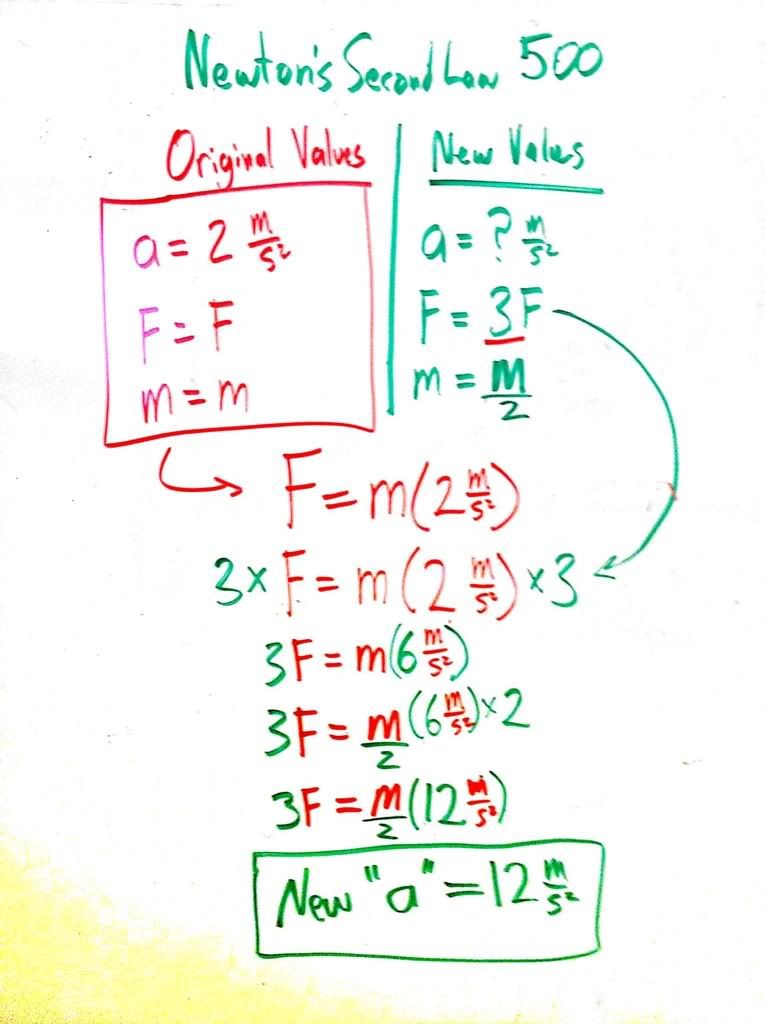
Newton's Second
Newton's Third
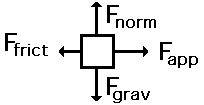
Free Body Diagrams
#4SIZ
100
Newton's First Law states that...
An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion (with a constant velocity) will stay in motion (with a constant velocity) until acted on by a net force
100
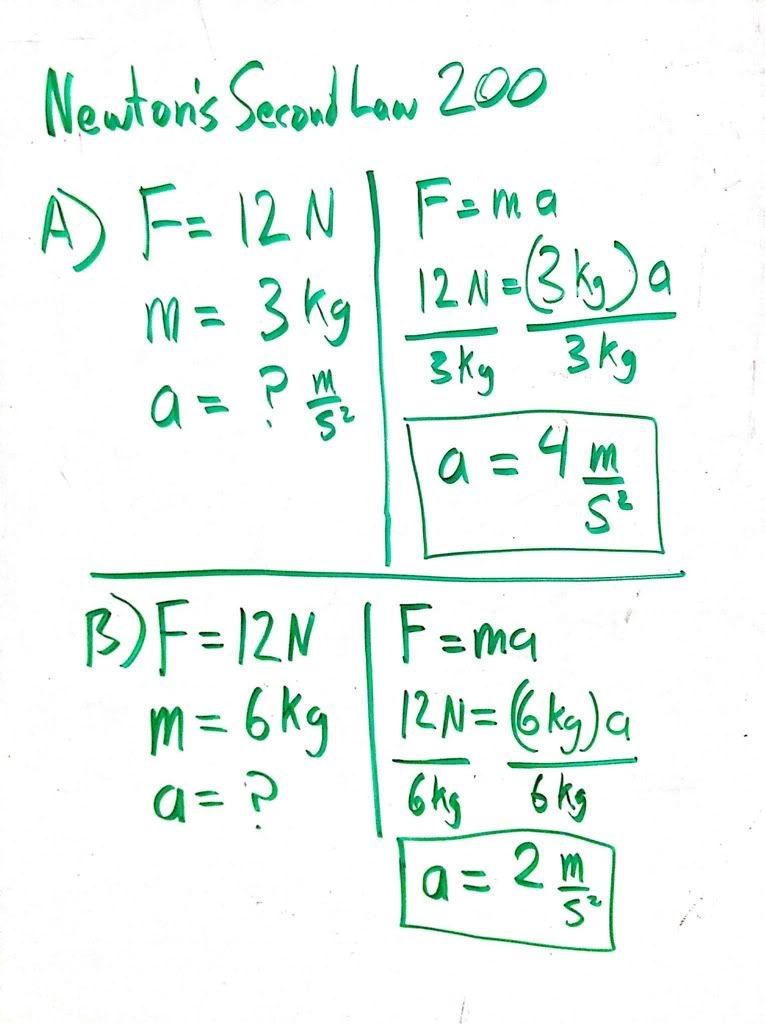
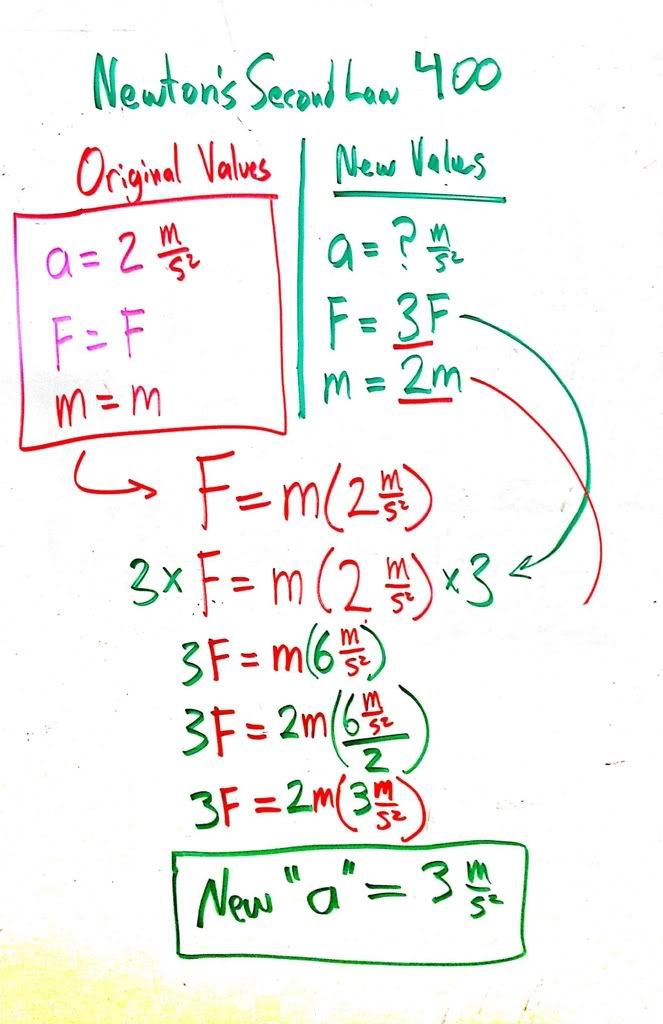
Newton's Second Law states that...
F=ma In other words, acceleration is proportional to the net force on an object and inversely proportional to its mass.
100
Newton's Third Law states that...
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, in other words, forces come in pairs and that those forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
100
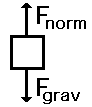
A Free Body Diagram
Free-body diagrams are used to display multiple forces acting on an object and only shows the external forces acting on the object.
100
What force causes objects to travel in a circular path?
Centripetal Force
200
Is a force necessary to keep an object moving? Explain & given an example.
Newton's first law of motion declares that a force is not needed to keep an object in motion. For example, slide a book across a table and watch it slide to a rest position. The book in motion on the table top does not come to a rest position because of the absence of a force; rather it is the presence of a force - that force being the force of friction - that brings the book to a rest position. In the absence of a force of friction, the book would continue in motion with the same speed and direction - forever! (Or at least to the end of the table top.) A force is not required to keep a moving book in motion. In actuality, it is a force that brings the book to rest.
200
While driving down the road, a firefly strikes the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus?
Trick Question! Each force is the same size. For every action, there is an equal ... (equal!). The fact that the firefly splatters only means that with its smaller mass, it is less able to withstand the larger acceleration resulting from the interaction. Besides, fireflies have guts and bug guts have a tendency to be splatterable. Windshields don't have guts. There you have it.
200
What force is directly applied from one object to another?
Applied Force
300
What is "inertia"?
The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion is called "inertia" and varies with the object's mass. The more inertia that an object has, the more mass that it has. A more massive object has a greater tendency to resist changes in its state of motion.
300
Many people are familiar with the fact that a rifle recoils when fired. This recoil is the result of action-reaction force pairs. A gunpowder explosion creates hot gases that expand outward allowing the rifle to push forward on the bullet. Consistent with Newton's third law of motion, the bullet pushes backwards upon the rifle. The acceleration of the recoiling rifle is ...
a. greater than the acceleration of the bullet.
b. smaller than the acceleration of the bullet.
c. the same size as the acceleration of the bullet.
The force on the rifle equals the force on the bullet. Yet, acceleration depends on both force and mass. The bullet has a greater acceleration due to the fact that it has a smaller mass. Remember: acceleration and mass are inversely proportional.
300
What force is always perpendicular to the surface of contact?
Normal Force
400
Mac and Tosh are arguing in the cafeteria. Mac says that if he flings the Jell-O with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. Who do you agree with? Explain why.
Tosh is correct. Inertia is that quantity which depends solely upon mass. The more mass, the more inertia. Momentum is another quantity in Physics which depends on both mass and speed. Momentum will be discussed in a later unit.
400
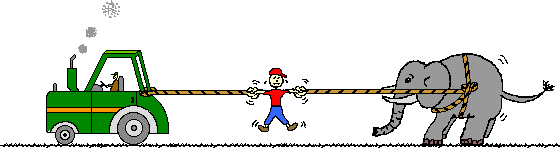
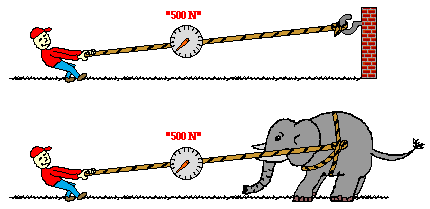 In the top picture, Kent Budgett is pulling upon a rope that is attached to a wall. In the bottom picture, the Kent is pulling upon a rope that is attached to an elephant. In each case, the force scale reads 500 Newton. Kent is pulling ...
a. with more force when the rope is attached to the wall.
b. with more force when the rope is attached to the elephant.
c. the same force in each case.
In the top picture, Kent Budgett is pulling upon a rope that is attached to a wall. In the bottom picture, the Kent is pulling upon a rope that is attached to an elephant. In each case, the force scale reads 500 Newton. Kent is pulling ...
a. with more force when the rope is attached to the wall.
b. with more force when the rope is attached to the elephant.
c. the same force in each case.
Kent is pulling with 500 N of force in each case. The rope transmits the force from Kent to the wall (or to the elephant) and vice versa. Since the force of Kent pulling on the wall and the wall pulling on Kent are action-reaction force pairs, they must have equal magnitudes. Inanimate objects such as walls can push and pull.
400
What force is caused by an object's weight and the texture of a surface and is opposite the direction of motion?
Frictional Force
500
Ben Tooclose is being chased through the woods by a bull moose that he was attempting to photograph. The enormous mass of the bull moose is extremely intimidating. Yet, if Ben makes a zigzag pattern through the woods, he will be able to use the large mass of the moose to his own advantage. Explain this in terms of inertia and Newton's first law of motion.
The large mass of the bull moose means that the bull moose has a large inertia. Thus, Ben can more easily change his own state of motion (make quick changes in direction) while the moose has extreme difficulty changing its state of motion. Physics for better living!
500
The elephant's feet push backward on the ground; the ground pushes forward on its feet. The right end of the right rope pulls leftward on the elephant's body; its body pulls rightward on the right end of the right rope. The left end of the right rope pulls rightward on the man; the man pulls leftward on the left end of the right rope. The right end of the left rope pulls leftward on the man; the man pulls rightward on the right end of the left rope. The tractor pulls leftward on the right end of the left rope; the left end of the left rope pulls rightward on the tractor. etc., etc.
500
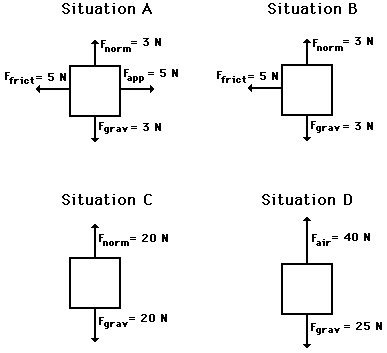
A) The net force is zero Newtons. All the individual forces balance each other (i.e., cancel each other out).
B) The net force is 5 Newtons, left. The vertical forces balance each other (i.e., cancel each other out). The leftward force (friction) remains unbalanced.
C) The net force is zero Newtons. All the individual forces balance each other (i.e., cancel each other out).
D) The net force is 15 Newtons, up. The upward force of air resistance is only partially balanced by the downward force of gravity - 15 N of upward force remains unbalanced.
500
What force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object which is attached to it.
Spring Force