This is the most common maternal symptom associated with infant falls
What is fatigue?
Hypothermia may be more common in 34-week gestation infants because they have
What is a limited amount of brown fat?
*Brown fat begins to form at 25 to 26 weeks' gestation, but there are no appreciable brown fat stores until the latter part of the third trimester.
At what gestation do we begin scoring infants for IDF
What is 32 weeks' gestation. Begin readiness scoring when infants are 32 weeks CGA, stable and on respiratory support of NC 2 LPM or less or if any infant is receiving gavage feeds.
When initially setting up a chest tube, what should the wall suction be set to?
What is 80mmHg. Adjust as needed to ensure bellow is in appropriate section of window.
This is who you contact when you need the NICU code cart replaced.
What is emailing Codecartsupply@stamhealth.org?
You are at a delivery, at 3 minutes of age, the baby is breathing comfortably and has central cyanosis. HR=160, RR 64. You attach the pulse oximeter to the baby's right hand and a reliable signal displays an oxygen saturation of 72%. What is your next step?
What is continuing to monitor? The baby does not need supplemental oxygen. An oxygen saturation of 72% is within target range for the age of 3 minutes. 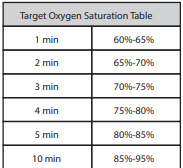
Babies who undergo prolonged resuscitation are initially NPO (given nothing by mouth) due to the potential for which of the following?
What is Ischemic injury to the intestine
Cessation of breathing > 20 seconds; may be associated with bradycardia, desaturation, cyanosis, and/or pallor
What is Apnea?
True or False: You must wait 24 hours to complete CCHD once a baby comes off oxygen?
What is false?
The patient must be stable in RA prior to completing but the AAP no longer specifies a length of time to wait.
What is add 6 to infant's weight in kg.
Example: 1 kg baby = approximate tube insertion depth at the upper lip 7cm
Hypoglycemia, hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, increased respiratory distress, feeding intolerance, and impaired weight gain are all short term or chronic consequences of this.
What is cold stress?
Plethora, or a very ruddy or red appearance may indicate presence of this hematologic problem.
What is polycythemia?
Gestational age and weight cut off for car seat tolerance test.
What is less than 37 weeks gestation and birthweight less than 2500 grams.
It is Friday 04/11/25 morning at 5am. You go to the breast milk refrigerator to prepare milk for your patients 6am feeding. You see there is plain, fresh breastmilk pumped by mom on Monday, 04/07/25 at 4:00pm. Can you use this breastmilk?
What is Yes? Freshly expressed or pumped breast milk is good up to 4 days in the refrigerator set to 40 degrees F or 4 degrees C.
You are at a full-term delivery for a baby with poor tone, no respiratory effort, and a heart rate <60 at delivery. The baby is intubated with positive color change on c02 detector, and you've provided 60 seconds of chest compressions. HR is still 52. What are the next steps and what would the concentration and dose of the medication be for a 3KG baby?
What is administer Epi via rapid push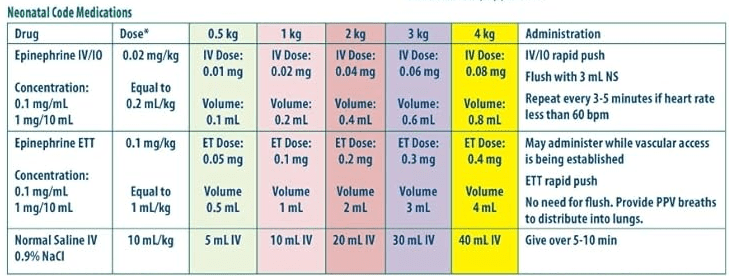 ?
?
Concentration is 0.1mg/mL / 1mg/10mL
ETT dose: 0.1mg/kg equals 1mL/kg ETT
For this patient it would be 0.3 mg =volume 3mL
IV dose: 0.02 mg/kg IV equals 0.2mL/kg
For this patient it would be=0.06mg =0.6ML
Flush for IV/IO doses. Do not flush for ETT dosing
One of the first ways that an infant will try to compensate for a low cardiac output is to increase their
a. heart rate
b. respiratory rate
c. systolic blood pressure
What is A
A 3.7 kg infant was delivered with vacuum assistance at 36-4/7 weeks gestation. There was appropriate prenatal care, and screening labs were all normal. The infant had an uneventful postnatal course until the day of discharge when the infant would not breastfeed and had a temperature of 38.4° C (101.2° F). On clinical exam, vesicles were noted on the infant’s arm and leg. Which of the following infections should be considered?
What is Herpes simplex virus?
Other clinical signs include fever, poor feeding, lethargy, irritability, or seizures.
A baby is born at 30 weeks' gestation. Humidity should be started at what percentage.
What is 60% humidity? 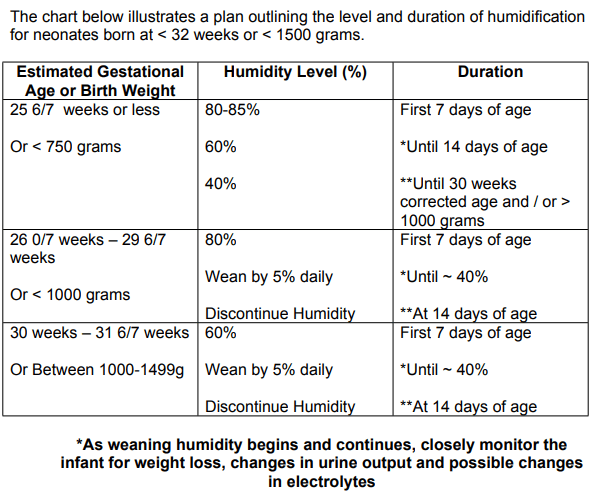
Interval of vital signs taken during the car seat tolerance test.
What is baseline, 30 minutes into the test, 60 minutes into the test, 90 minutes into the test (completion).
Your patient is noted to be in V-Fib, this should be the plan of action.
What is defibrillate starting at 2 jules per kg?
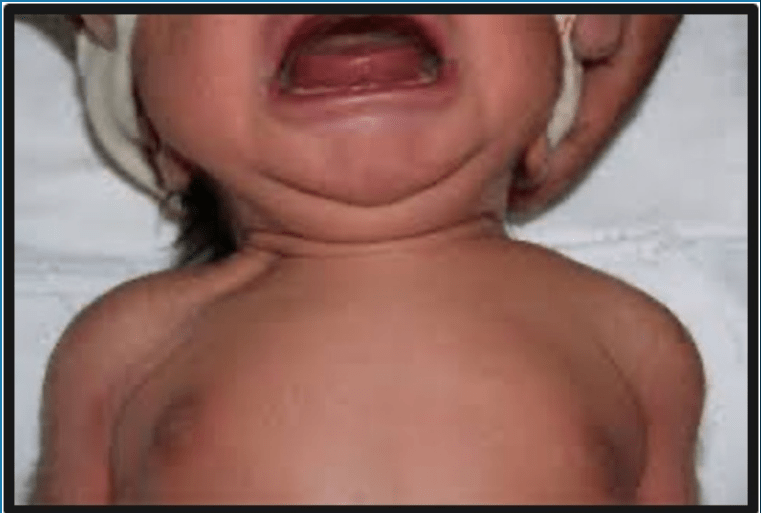 You attend a delivery for an LGA infant and note the following exam finding. What is this called, why does this happen? What would treatment involve?
You attend a delivery for an LGA infant and note the following exam finding. What is this called, why does this happen? What would treatment involve?
What is clavicular fracture.
Risk factors: macrosomia, shoulder dystocia, instrumental delivery.
Treatment: no specific treatment; pinning occasionally used to decrease pain. Pharmacologic pain management.
*The most common bone fracture of delivery.
The recommended total fluid intake of term and preterm neonates on the first day of life are ___ and ___, respectively.
What is 60ml/kg/day and 80 ml/kg/day
What is an APGAR 5?
A:1, P:2, G:1, A:0, R:1 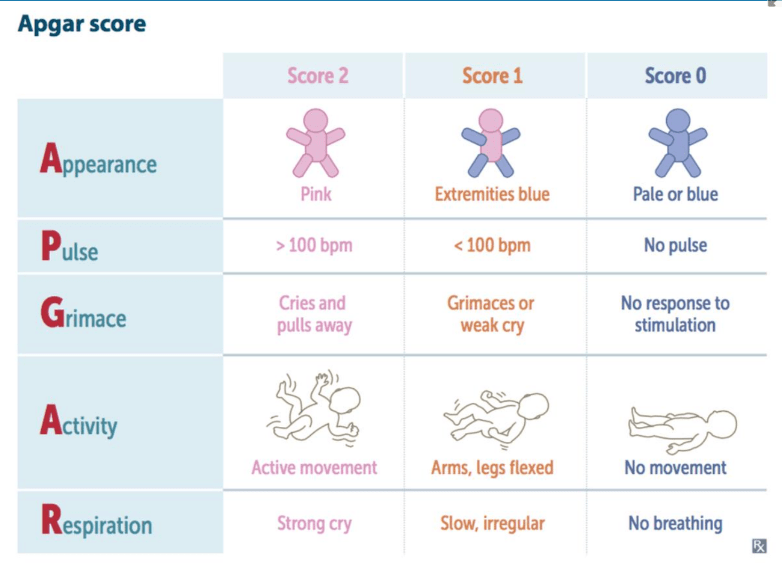
Passing criteria for CCHD.
What is Pulse ox > 95% at both sites and saturation difference < 3%?
An infant with an umbilical artery catheter (UAC) has four white toes on the left foot with black discoloration on the tip of the fifth toe. The toes feel cool to the touch. The toes on the other foot are warm and pink. What is the appropriate action in this case?
a. Remove the UAC
b. Warm the affected extremity
c. Warm the opposite extremity
What is A