I am suspicious for this when a patient presents with Chest Pain, hypotension, bradycardia, distended jugular veins and clear lung sounds and an S3 murmur at the left lower sternal border.
What is a Right Ventricular Myocardial Infarction (RVMI)?
My patient admits with jaw pain radiating to the right shoulder and arm. These are the tests should I anticipate being ordered.
What are cardiac markers and 12 lead EKG?
These are the most common causes of acquired long QT syndrome (LQTS).
What are:
Antidysrhythmics
Antibiotics
Antidepressants/Antipsychotics
Antiemetics
This is the equation to determine
Cardiac Output.
What is Heart Rate x Stroke Volume?
This setting is indicated on the pulse generator to the left.

What is the rate?
There are ST elevations in Leads V2 and V3. I expect this vessel to be involved and for my patient to emergently go to the cath lab for revascularization.
What is the left anterior descending (LAD)?
My patient had an NSTEMI 24 hours ago and they are now have increasing oxygen needs. Their current vital signs are: HR 120, BP 85/46 (59), RR 30, and Oxygen Sats 91% on 4L NC. Physical assessment with cold clammy skin, diminished pulses, dyspnea, lung sounds crackles, U/O 20 mL last 2 hours. I recognize these are signs of this condition.
What is cardiogenic shock?
This is the most important thing to remember about the 12 lead EKG in suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome.
That the provider needs to interpret the EKG within 10 minutes?
Other risk factors for developing acquired LQTS include:
What are:
Electrolyte abnormalities
Bradycardias or dysrhythmias resulting in frequent pauses
Subarachnoid hemorrhage or other neurologic events.
These are the three components of Stroke Volume.
What are:
Preload
Afterload
Contractility
This pacemaker malfunction can occur if the pacemaker fires but does not result in myocardial depolarization.
What is Failure to Capture?
My patient is going to the cath lab to be evaluated for pulmonary hypertension. They are looking at the right side only so I would expect this type of site recovery.
What is venous?
My patient has an ascending aortic dissection. I know they are at risk for this life threatening complication when they develop stabbing chest pain, SOB, dry cough, tachycardia, hypotension, JVD, dizziness, anxiety and muffled heart sounds on auscultation.
What is cardiac tamponade?
Acute Coronary Syndrome includes these 3 disease processes leading to myocardial ischemia leading to cell death, or infarction.
What are STEMI, NonSTEMI, & Unstable Angina?
A lengthened QT interval indicates an increased risk of what type of dysrhythmia?
What is ventricular tachydysrhythmia or torsades de pointes?
You’re taking care of a patient in atrial fibrillation w/rapid ventricular response (HR 170s).
In what ways will this impact contractility, preload, and afterload?
Contractility: Decreased
Preload: Decreased
Afterload: Increase
This is the ability of the pacemaker to sense the heart’s intrinsic electrical activity.
What is Sensitivity?
These two medications are often prescribed after a patient has a stent placed.
What is ASA and P2Y12 inhibitor (clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor, cangrelor)?
My patient has S1, S2 and S3 heart sounds, fine crackles in the bases, severe headache and confusion. Their current vital signs are: HR 110, BP 210/120 (150). I recognize this as a medical emergency and they are at high risk for this complication.
What is stroke?
“PQRST” method evaluates chest pain. It differentiates these specifically.
What is P = provoke/precipitate
Q = quality
R = radiation
S = severity
T = timing?
What is a normal QT interval value?
What is:
QT interval <0.44 sec
This provides a global perspective of respiration at the cellular level and is measured using a pulmonary artery catheter.
What is venous oxygen saturation (SvO2)?
This type of pacing could cause ventricular fibrillation if the pacemaker stimulus lands on a T wave.
What is fixed or asynchronous pacing?
When my patient comes from the cath lab, I have these three priority assessments.
What are vital signs, insertion site, pulses?
A patient presents with stabbing CP and palpitations that worsen with inspiration. He is in Afib , HR 110, BP 90/45 (65), RR 30 Sat 92% on 2L NC. 3+ edema in BLE, JVD. I hear this sound at the apex and suspect pericarditis.
What is a pericardial friction rub?
Your patient is having an inferior wall infarction. You are hesitant to give Nitroglycerin. You know that it will decrease this.
What is pre-load?
This is the treatment for sustained Torsades de Pointes (TdP) or TdP that converts to ventricular fibrillation.
What is follow ACLS guidelines and defibrillate?
Your patient had a precipitous drop in blood pressure and their MAP is <55. Using the image below, at what rate can you start your levophed?
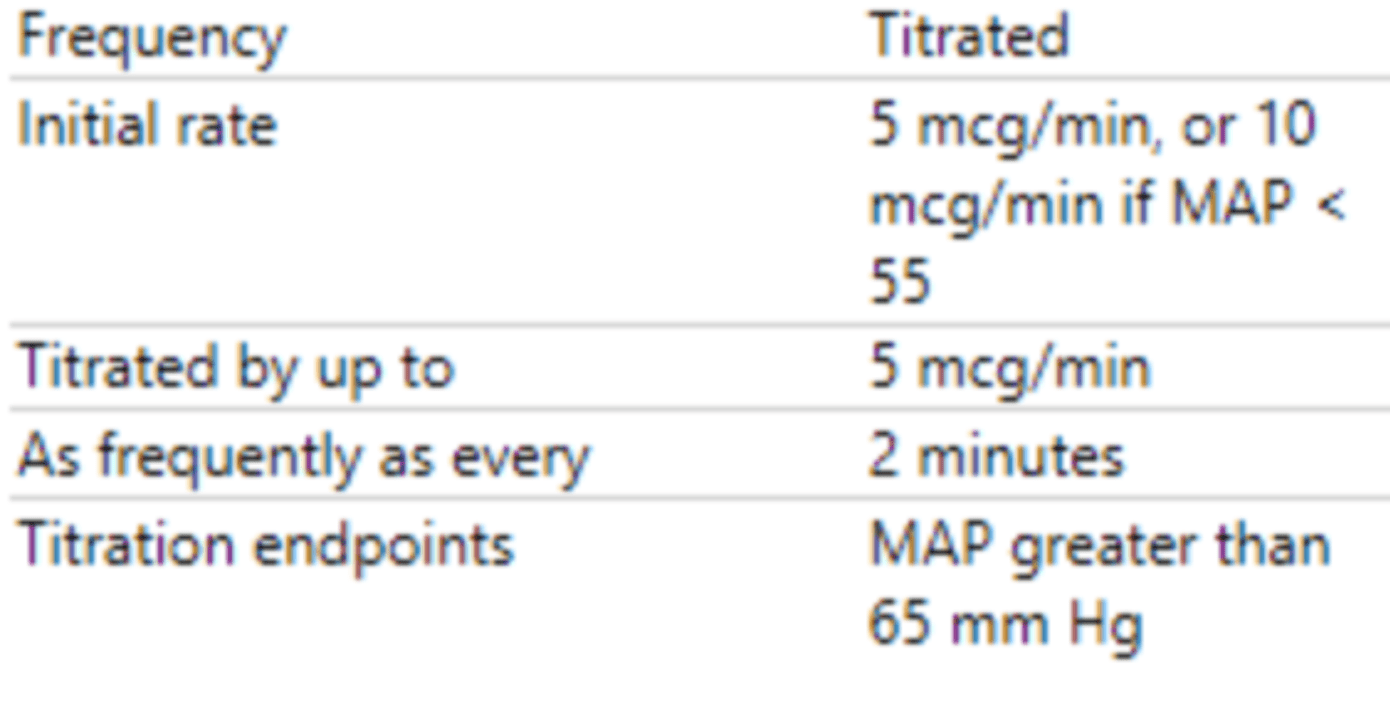
What is 10 mcg/min?
When atrial and ventricular epicardial wires are placed, atrial leads are typically placed to the _________ and ventricular wires are placed to the __________ of the sternum.
What is atrial leads exit to the RIGHT and ventricular leads exit to the LEFT of the sternum?
These two sites are commonly used as access for a left heart cath.
What are the radial and femoral arteries?