Urea, Uric Acid, Ammonia, Creatine, Creatinine, amino acides
What are NPN's
Ammonium from urease reaction can measure
The color change of an pH indicator
Congestive Heart Failure
Shock
Hemorrhage
Dehydration with increase Albumin
Pre-Renal Azotemia
What is azotemia?
Elevated concentration of urea
Normal ratio Nitrogen / Creatinine
10:1 to 20:1
This is inversely related to plasma Creatinine
What is the GFR
A 30-year-old marathon runner collapses after a race. His labs show:
BUN: 36 mg/dL (normal: 7–20 mg/dL)
Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL (normal)
Urine: dark and concentrated
He’s been running for hours with minimal water intake.
What is dehydration (prerenal azotemia)?
The one NPN is the compound present in highest concentration in the blood?
Urea
NH4 + 2-Oxoglutarate -----?------> Gutalmate
GLDH
Glutamate dehydragenase
Acute and Chronic renal failure
Renal Azotemia
Define Uremia and Gout
Very High plasma urea concentration and renal failure
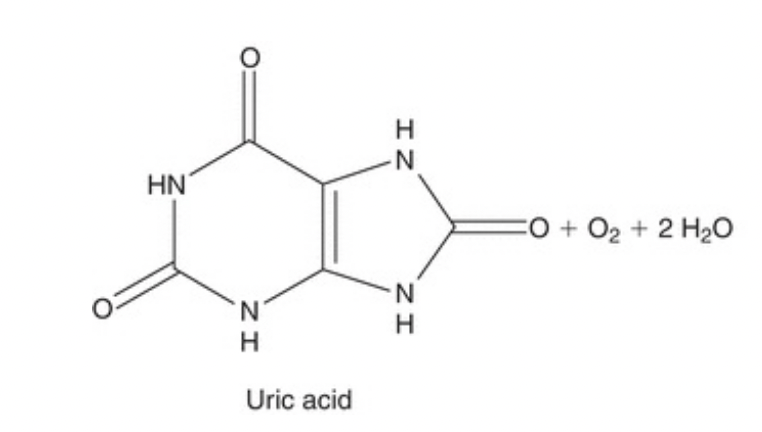
Elevated concentration of uric acid
BUN
6-20mg/dl
90ml/min/1.73m2
What is the ref range of GFR
Case 2 – Creatinine: “The Slow Rise”
Case Clue:
A 62-year-old man with diabetes presents for routine labs:
BUN: 25 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.8 mg/dL (previously 1.0 mg/dL)
GFR: decreased
He reports fatigue but no acute illness.
Question:
What chronic condition is most likely responsible for this gradual rise in creatinine?
What is chronic kidney disease?
NPN comes from the catabolism of: name both
protein and nucleic acids
This enzyme's function is to store ATP in muscle
CK
Creatine Kinase
BUN: [Cr]p = 10-15 with increase abdominal pain
What is post renal Azotemia
There is a reduced renal blood flow. It is a prerenal, renal or post renal?
Prerenal
Serum Creatinine
Male 0.9-1.3 mg/dl
female 0.6-1.1 mg/dl
GFR=30-59 mL / min
State 3 Renal Failure
Case Clue:
A 45-year-old man complains of sudden pain, redness, and swelling in his big toe.
Labs show:
Uric acid: 9.5 mg/dL (normal: 3.5–7.2 mg/dL)
Creatinine: normal
History: high-protein diet and frequent beer intake
What is the likely diagnosis associated with this elevated uric acid?
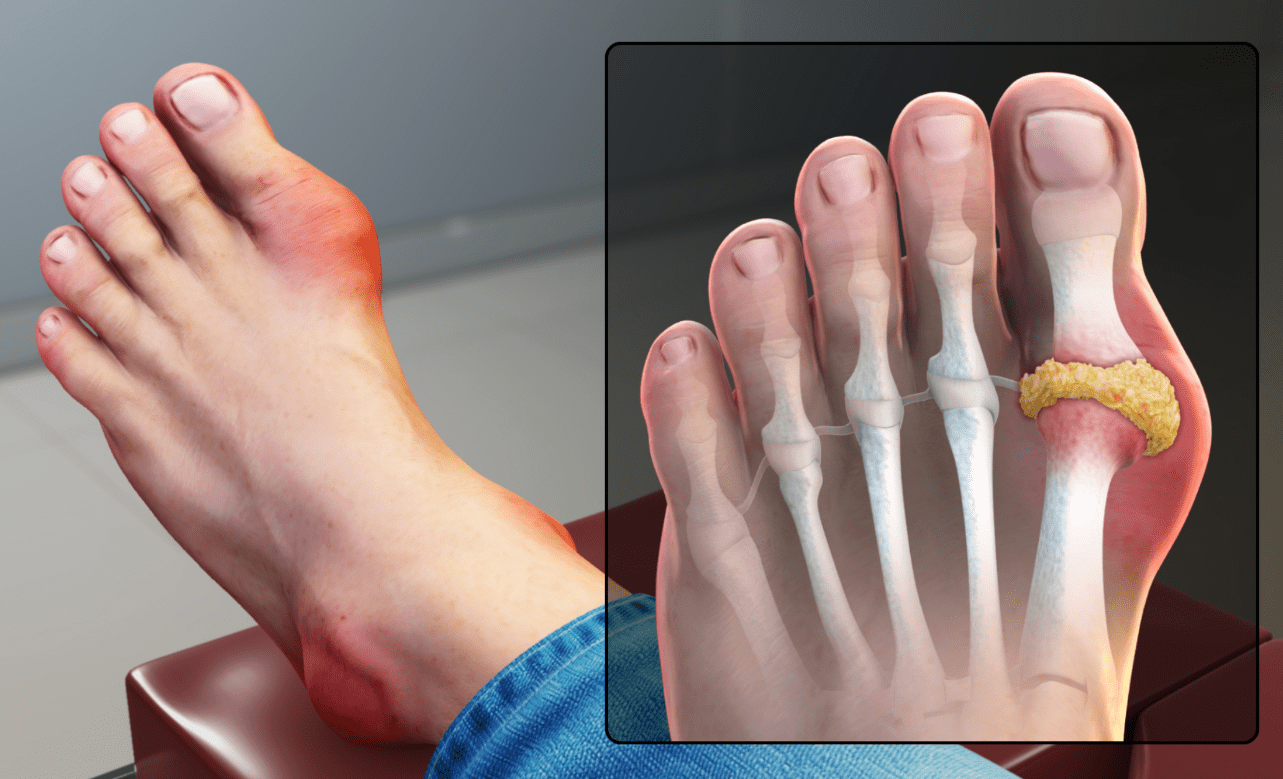
What is gout?
? 
Which enzyme can be helpful to detect bone disorder?
ALP Alkaline Phosphatase
Test indicator of glomerular filtration (GFR)
Creatinine Clearance
Low Protein intake
Severe Vomiting and diarrhea
Liver Diseas
Pregnancy
Low or decreased Urea Concentration
BUN: [Cr]p = 27
Pre Renal Azotemia
A 28-year-old bodybuilder comes in for a physical.
Labs show:
Creatinine: 1.8 mg/dL (slightly elevated)
BUN: normal
He reports using creatine supplements daily and intense weight training.
He feels well otherwise.
What is the most likely reason for this elevated creatinine level?
What is increased muscle mass or creatine supplement use (non-pathologic elevation)
Associated with inherited deficiency of urea cycle enzymes
What is Hyperammonemia
The Conway method exploited the volatility of this NPN
Ammonia
BUN : [Cr]p = 6 with increased BUN
Uremia
What condition is if urea and creatinine are both elevated with back pain? Pre, renal or post?
Renal Azotemia
Liver Disease
Fanconi Syndrome
Over-treatment of Allopurinol
What is Decreased Concentration of Uric Acid
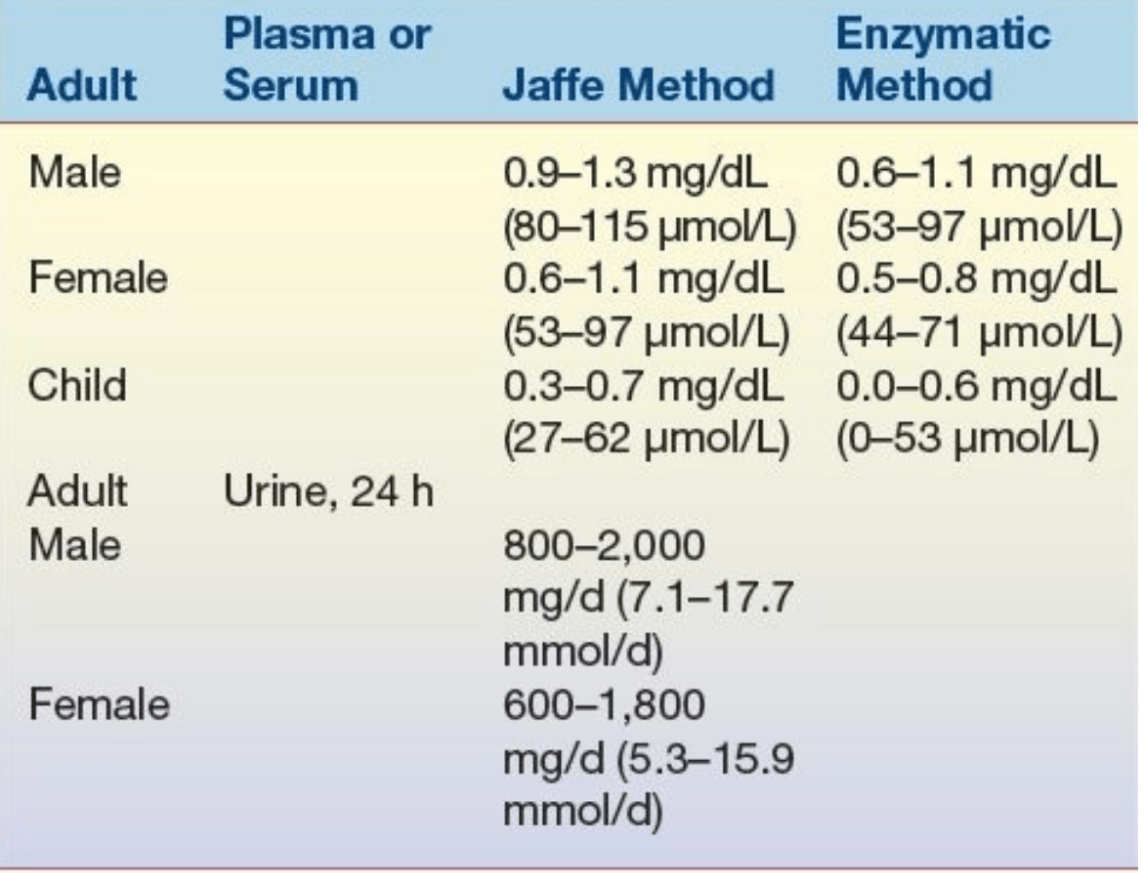 True or False
True or False
Jaffe Method is used with Diabetic patience
Reference range for Creatinine
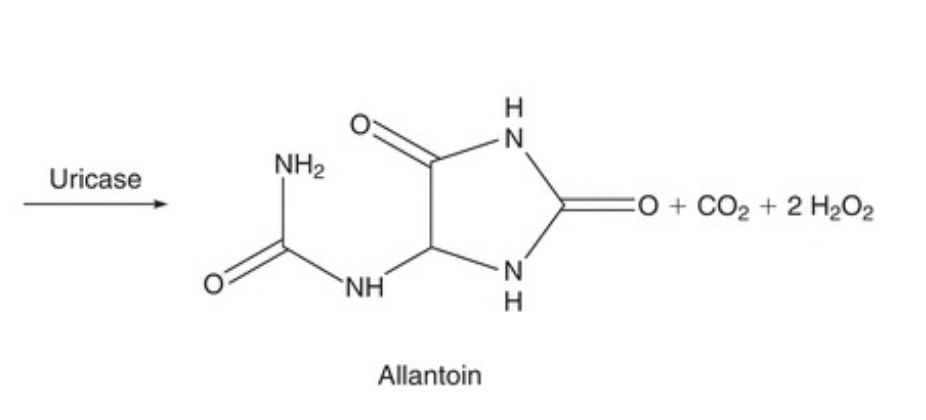
A 3-year-old Labrador Retriever is being evaluated after a high-protein diet.
Labs show:
Uric acid: normal
Allantoin: elevated
Kidney function: normal
What explains the elevated allantoin in this dog?
Uricase is present in dogs