Which of the following is the type of exercise that involves a muscle contraction in which the length of the muscle remains constant while tension develops toward a maximal force against an immovable resistance?
A. Isokinetic
B. Isotonic
C. Isometric
D. Eccentric
C. Isometric
What is the primary function of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)?
A) To reduce fever
B) To relieve pain and inflammation
C) To treat bacterial infections
D) To lower blood pressure
B) To relieve pain and inflammation
Which of the following modalities could you use if the goal is deep heating?
A. Moist Heat Pack
B. Ultrasound
C. Diathermy
D. All of the above
E. B & C
E. B & C
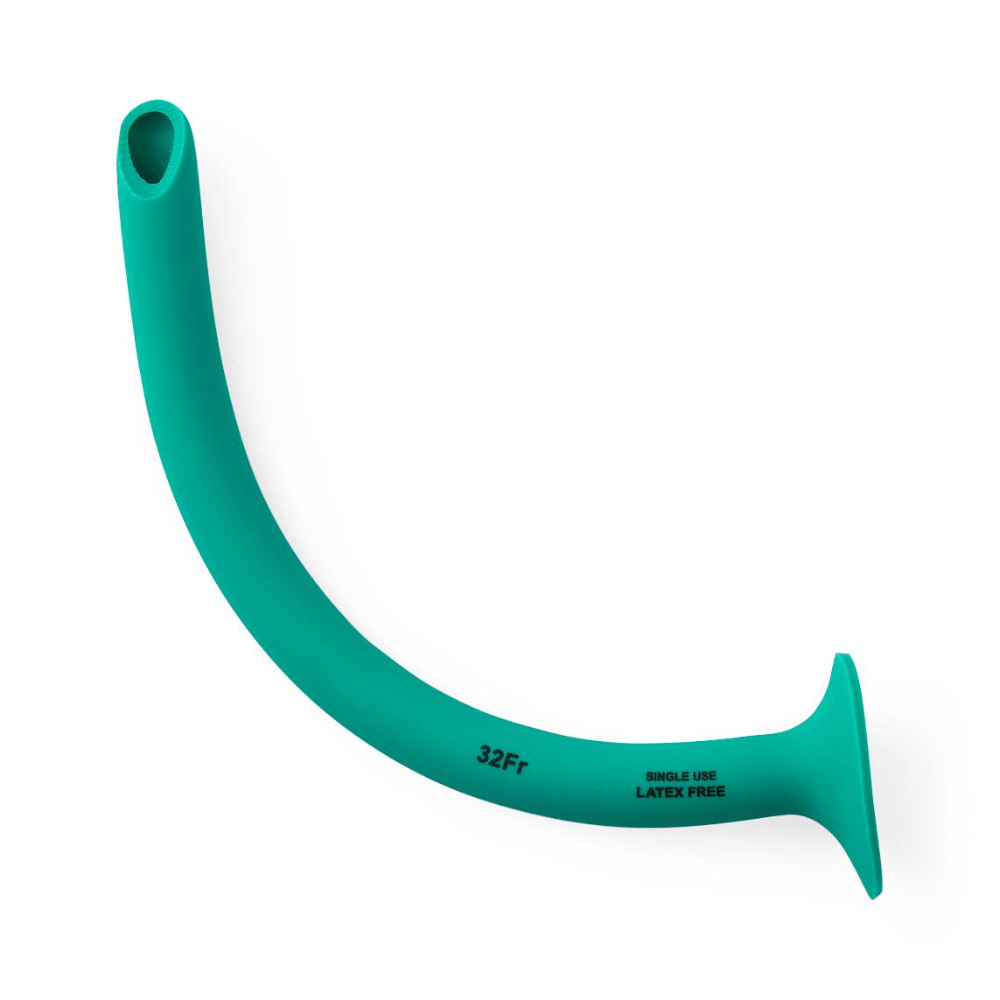

What is this device called?
A) Oropharyngeal Airway
B) Supraglottic Airway
C) Nasopharyngeal Airway
D) Extraglottic Airway
C) Nasopharyngeal Airway
Which of the following is a common complication associated with untreated type 1 diabetes in athletes?
A) Hyperthyroidism
B) Hyperglycemia
C) Hypertension
D) Hypoglycemia
D) Hypoglycemia
How might you increase the difficulty of a rehab exercise without adding more weight/resistance?
A. Dual-tasking
B. Perturbations
C. Active-assisted exercises
D. A&B
D. A&B
Which of the following best describes how beta-blockers work in the body?
A) They increase heart rate and blood pressure.
B) They block the effects of adrenaline on the heart.
C) They stimulate the production of insulin.
D) They enhance the absorption of calcium in bones.
B) They block the effects of adrenaline on the heart
Which of the following is NOT accurate regarding effects of thermotherapy?
A. Decrease in pain perception
B. Decrease in metabolism
C. Decrease in muscle spasm/guarding
D. Increase in edema
According to general medical guidelines, what is the recommended action for an athlete experiencing a hypoglycemic episode?
A) Administering insulin
B) Providing a high-protein snack
C) Consuming fast-acting carbohydrates
D) Encouraging rest and hydration
C) Consuming fast-acting carbohydrates
Which of the following is a common symptom of iron-deficiency anemia in athletes?
A) Increased appetite
B) Fatigue and weakness
C) Joint pain
D) Elevated heart rate
B) Fatigue and weakness
Performing a biceps curl is an example of what type of lever?
A. First Class
B. Second Class
C. Third Class
D. None of the above
C. Third Class
An athlete is prescribed an opioid analgesic for severe pain. Which of the following is a critical consideration for the athletic trainer?
A) Monitoring for signs of addiction and dependency
B) Ensuring the athlete stays hydrated
C) Advising the athlete to avoid high-protein foods
D) Recommending increased cardiovascular exercise
A) Monitoring for signs of addiction and dependency
Which of the following is NOT a contraindication for using therapeutic ultrasound?
A. Over areas with a sensory deficit/anesthesia
B. Areas with reduced circulation
C. Using nonthermal ultrasound for acute injuries
D. Over the heart, eyes, ears, genitals
C. Using nonthermal ultrasound for acute injuries
According to the NATA Position Statement on Managing Dental Injuries, it is critical for an avulsed tooth to be put back in place for replantation within how many minutes?
A) 5-10 minutes
B) 10-15 minutes
C) Under 30 minutes
D) Once a tooth is avulsed it cannot be replanted
A) 5-10 minutes
What is the primary concern when treating an athlete with Marfan syndrome?
A) Joint hypermobility
B) Cardiovascular complications
C) Respiratory infections
D) Gastrointestinal issues
B) Cardiovascular complications
Which of the following grades of joint mobilization involves small amplitude movements performed at the end of the joint’s available range?
A. Grade I
B. Grade II
C. Grade III
D. Grade IV
D. Grade IV
An athlete is prescribed a diuretic for hypertension. What potential side effect should the athletic trainer be most concerned about?
A) Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance
B) Increased muscle mass
C) Enhanced appetite
D) Lowered heart rate
A) Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance
Which theory of pain control posits that A-beta fibers carrying sensory information can decrease nociceptive input by reaching the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and synapses with second-order neurons and inhibiting pain information carried by C and A-delta fibers?
A. Descending Pain Modulation
B. Central Biasing
C. Beta-Endorphin release
D. Gate Control
D. Gate Control
Racoon eyes, cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea, and Battle Sign are all indicative of what type of injury?
A) Temporal Lobe Fracture
B) Mandibular Fracture
C) Orbital Fracture
D) Basilar Skull Fracture
D) Basilar Skull Fracture
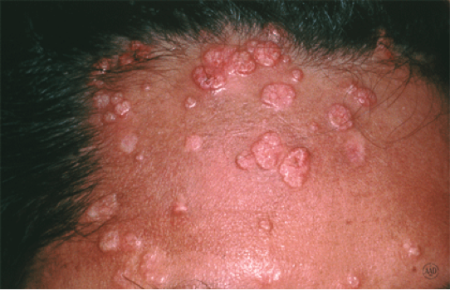
What is the name of this viral skin condition that causes small, raised, dome-shaped bumps with a dimpled center?
A) Herpes
B) Chicken Pox
C) Tinea Corporis
D) Molloscum Contagiosum
D) Molloscum Contagiosum
An athlete is recovering from an ACL reconstruction. Which phase of rehabilitation would first introduce exercises like squats and lunges to improve strength and stability?
A) Acute/Inflammatory phase
B) Fibroblastic repair/proliferation phase
C) Maturation/remodeling phase
B) Fibroblastic repair/proliferation phase
Which of the following medications is most likely to cause a serious interaction when combined with warfarin?
A) Amoxicillin
B) Lisinopril
C) Metformin
D) Aspirin
D) Aspirin
What term refers to the minimum amount of voltage under the negative pole required for depolarization when a direct current is applied to living tissue?
A. Chronaxie
B. Rheobase
C. Temporal average intensity
D. Cavitation
B. Rheobase
Based on the Position Statement for Immediate Management of Appendicular Joint Dislocations, which joint of the body is not recommended to be reduced onsite by an AT?
A) Proximal Radioulnar Joint
B) Patellofemoral Joint
C) Tibiofemoral Joint
D) Interphalangeal Joint
A) Proximal Radioulnar Joint
What is not considered the 3 most common Bloodborne Pathogens that ATs need to be concerned about when treating an open wound?
A) HBV
B) HIV
C) HCV
D) HPV
D) HPV