How do you differentiate lipedema from lymphedema?
"Lipedema is typically tender, whereas lymphedema often is not. Bilateral lower-extremity edema that spares the dorsum of the feet is highly suggestive of lipedema."
How much nicotine is typically contained in one cigarette?
2 mg
Remember, you can taper patches! They come in 7,14 and 21mg / 24 hours.
A recommended initial evaluation to consider for patients complaining of anosmia after COVID
Allergy testing.
HPV vaccination is FDA-approved for patients between ___ and ____ years of age.
9 and 45 years of age
True or false: one component of management for treating peripheral edema in patients with peripheral artery disease are compression stockings.
False, it's contraindicated! Perform an ABI prior to recommending compression stockings if you have any concern.
True or false: varenicline is only appropriate for patients who have demonstrated that they are ready to quit smoking.
False!
This is what was traditionally thought. However, a study done by the ATS showed offering varenicline to patients who are not quite ready to quit increases cessation at six months (NNT = 6)
The 3 most common symptoms of long covid after 6 months
Fatigue
Post exertional malaise
Cognitive dysfunction
True or false: you should avoid the influenza vaccine in adults who are allergic to eggs.
False!
Graduated compression stockings with a _______ pressure have been shown to reduce edema, pain, and ulceration caused by chronic venous insufficiency.
20 to 40 mm Hg
For those with lymphedema, you often need at least 40 mm Hg
True or false: Bupropion works better for sustained smoking cessation when used in combination with nicotine replacement therapy.
False--well, not enough evidence to show whether the combo is more effective than NRT alone.
However, it is associated with a 64% higher likelihood of sustained smoking cessation (NNT = 14) compared with placebo or no pharmacotherapy. This is similar to the effectiveness of NRT.
Energy conservation strategies, such as these 4 Ps, can help patients mitigate fatigue.
Planning
Pacing
Prioritizing
Positioning
What is the youngest age that you can be to receive a COVID vaccine?
6 months!
And then 5 years and older can get the booster
Patients with ascites from cirrhosis should be started on a _____ ratio of spironolactone and furosemide for optimal treatment.
5:2
DAILY DOUBLE
1. What is the most-effective pharmacotherapy we have for sustained smoking cessation?
2. How is this medication dosed?
1. Varenicline (Chantix). NNT of 7 for sustained smoking cessation at 6 months when compared with bupropion and NRT.
2. Dosing:
- 0.5mg qday x3 days
- 0.5mg BID x4 days
- 1mg BID x12 weeks in total
Fluid and salt repletion along with compression garments is a potential therapy for patients with this general symptom/complaint associated with long covid.
Autonomic dysfunction
When should you start recommending the Shingrix vaccine?
50 years and older, or:
"people 19 years and older who are immunocompromised, including those on immunosuppressive therapy (optimally administered before starting that therapy) or recovering from an immunocompromising illness"
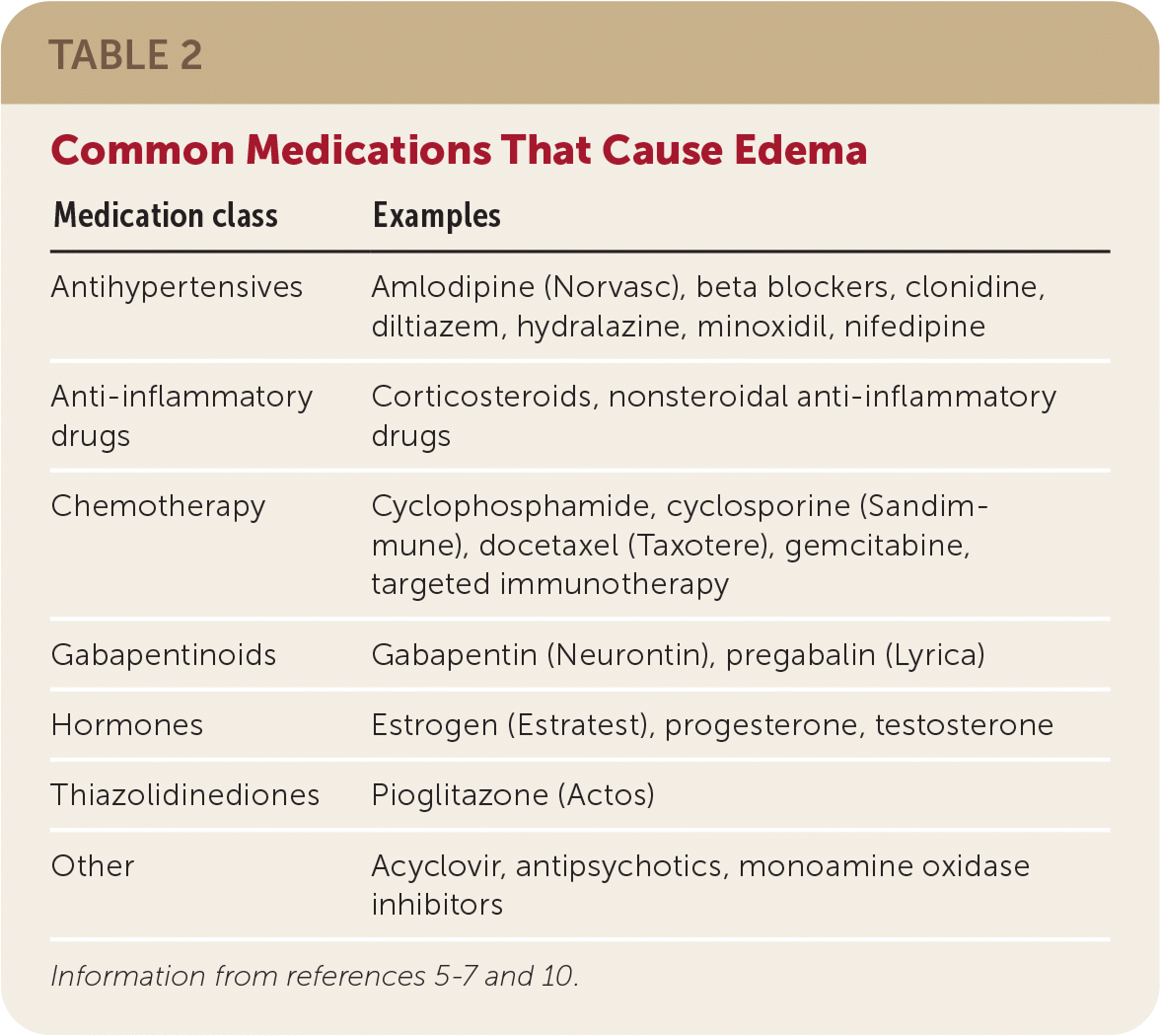
Name 4 meds that can cause peripheral edema.
Name three risks linked to tobacco use during pregnancy.
Tobacco use increases rates of ectopic pregnancy, low birth weight babies, preterm birth, miscarriage, placental abruption, and orofacial clefts.
If smoking cessation is achieved during first 15 weeks, this reduces risk of low birth weight babies to that of never smokers.
Recommended treatments for this symptom complex (which can included anxiety, hypotension, rhinitis, etc) includes H1 and H2 antagonists, cromolyn, and leukotriene inhibitors.
Mast cell activation syndrome
A patient comes in to see you and has previously received the PCV20 vaccine. Do they need the PPSV23 vaccine as well?
Nope
It is recommended that adults 65 years and older who have not previously received a PCV should receive one dose of PCV15 or PCV20. If PCV15 is administered, it should be followed by a dose of PPSV23 after one year; however, the interval can be shortened to eight weeks for individuals with immunocompromising conditions, cerebral spinal fluid leak, or cochlear implant. If PCV20 is used for the first pneumococcal immunization, a subsequent dose of PPSV23 is not indicated.
Remember: Vaccination with one dose of PCV15 or PCV20 is recommended for adults 19 to 64 years of age with medical risk factors, including chronic heart, lung, or liver disease; diabetes mellitus; alcoholism; or cigarette smoking; and patients with immunocompromising conditions.