This structure, located at the end of the bronchioles, is the site where gas exchange occurs between the air and the bloodstream
What is the alveolus (plural: alveoli)?
This breath sound has a high pitched popping sound due to fluid/secretions or sudden opening of airways.
What are crackles?
This is the primary physical therapy intervention for peripheral vascular diseases.
What is a walking program?
A 60-year-old male with a history of angina pectoris reports chest pain that occurs with physical exertion but resolves with rest. He is referred to physical therapy for an exercise program. Which of the following is the most appropriate approach for initiating physical therapy in this patient?
A) Begin with high-intensity aerobic exercise to increase cardiovascular fitness
B) Avoid all exercise until the patient is pain-free for at least 1 week
C) Start with low to moderate-intensity exercise, monitoring for any signs of chest discomfort
D) Focus on strengthening exercises only, avoiding any cardiovascular activity
What is C) Start with low to moderate-intensity exercise, monitoring for any signs of chest discomfort?
A 58-year-old male with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents for physical therapy. During the evaluation, he demonstrates an inability to increase his breathing rate or tidal volume during exercise, and he reports significant shortness of breath after walking 100 feet. His oxygen saturation is 88% on room air. Which of the following would be the most appropriate intervention to improve this patient’s exercise tolerance?
A) Increase the intensity of aerobic exercise to improve cardiovascular fitness.
B) Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation levels above 90% during exercise.
C) Encourage the patient to exercise without supplemental oxygen to improve ventilatory efficiency.
D) Focus on strengthening the lower extremities without addressing respiratory function.
B) Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation levels above 90% during exercise.
This structure, located between the left atrium and left ventricle, prevents the backflow of blood during ventricular contraction. The closing of this valve is associated with the second heart sound (S2), heard during the cardiac cycle when the ventricles contract and blood is ejected into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
What is the aortic valve?
A 70-year-old male with a history of smoking, diabetes, and hypertension presents to physical therapy with complaints of leg pain and cramping while walking, which resolves with rest. On examination, his pulses are diminished in both feet, and an ABI measurement is taken. The result is 0.45. What does this ABI result indicate about the patient's condition?
What is severe peripheral arterial disease (PAD)?
A patient presenting with dyspnea at night, orthopnea, dry cough, cyanotic extremities, and an abnormal heart sound might have this disease.
What is congestive heart failure?
This stage of hypertension is defined by systolic blood pressure between 130-139 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure between 80-89 mmHg, and it is typically managed with lifestyle modifications, with or without the addition of antihypertensive medications.
What is Stage 1 hypertension?
A 65-year-old male with a history of chronic bronchitis presents with increased sputum production and decreased oxygen saturation. The physical therapist is instructed to use postural drainage to target the apical segments of the right and left upper lobes. In which position should the patient be placed to optimally drain the apical segments?
What is the patient should be seated, leaning slightly backward, with the head and chest elevated?
This is the other primary muscle of inspiration along with the diaphragm. It is oriented obliquely upward and back, which helps elevate the ribs.
What is the external intercostals?
A 50-year-old female with a history of asthma presents to the emergency department with wheezing and shortness of breath. Her arterial blood gas results are as follows:
pH: 7.48
PaCO2: 32 mmHg
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
PaO2: 75 mmHg
What is the most likely acid-base disturbance, and what is the underlying cause of this disturbance?
What is respiratory alkalosis and hyperventilation?
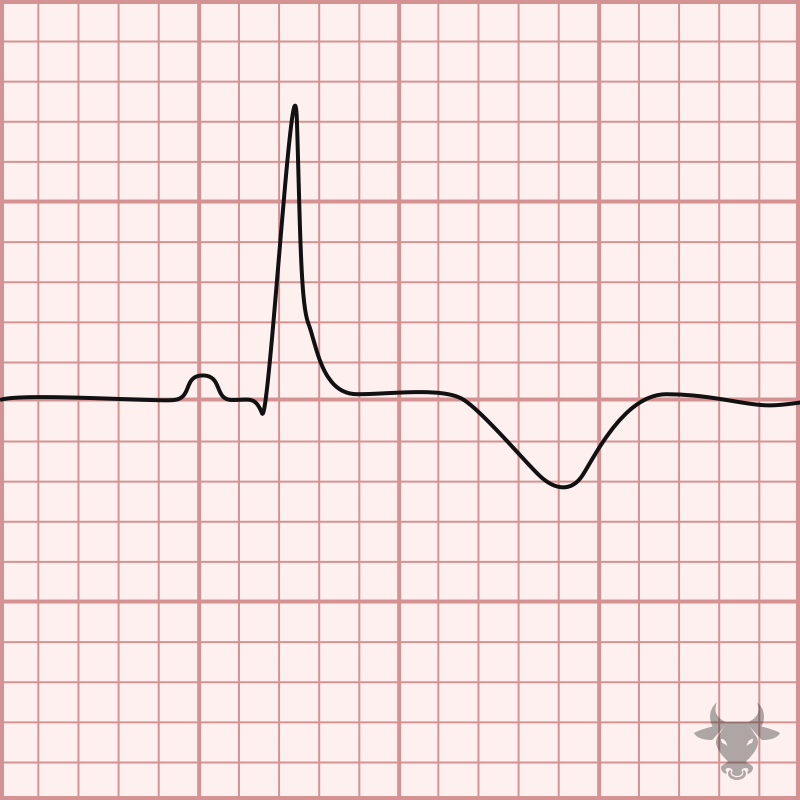
A patient presents with the EKG in the picture, they are most likely showing signs of this disease.
What is a MI?
A 58-year-old male with a history of hypertension and smoking presents to physical therapy after experiencing intermittent chest pain during physical activity that resolves with rest. He describes the pain as a pressure-like sensation in his chest, which occurs when climbing stairs or walking briskly but disappears after a few minutes of rest. His medical history includes elevated cholesterol levels, and his vital signs are stable during the evaluation. Based on these symptoms, what is the most likely diagnosis?
What is angina pectoris (specifically stable angina)?
This type of sputum is typically thick, yellow or green in color, and may have a foul odor. It is commonly associated with bacterial respiratory infections, such as pneumonia or chronic bronchitis exacerbations.
What is purulent sputum?
This double-layered membrane surrounds the lungs, with the inner layer lining the lung surface and the outer layer adhering to the chest wall. The space between these layers contains a small amount of fluid that reduces friction during breathing movements.
What is the pleura?
This is an increased transmission of voice sounds heard over areas of lung consolidation or consolidation due to pneumonia, lung tumors, or other pathology. The clearer, louder voice sounds suggest an abnormal finding in the lung tissue, such as fluid or a mass, which enhances sound transmission. often tested by asking patient to say "99".
What is bronchophony?
This multi-system disease is inherited and impacts the hepatic, digestive, respiratory, and reproductive systems. Cardiopulm symptoms are due to impermeability of epithelial cells that results in viscous mucous.
What is cystic fibrosis?
A 72-year-old female with a history of obesity, hypertension, and recent hip replacement surgery presents to physical therapy with complaints of progressive swelling, warmth, and tenderness in her left lower leg. She reports that the symptoms have worsened over the past few days, especially after prolonged sitting. On examination, there is significant edema in the calf, with a positive Homan's sign. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis, and what immediate action should the physical therapist take?
What is deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? The physical therapist should immediately refer the patient to her physician for further evaluation and possible diagnostic testing
This device is commonly used in the rehabilitation of patients post-surgery or those with respiratory conditions to encourage deep breathing, improve lung expansion, and prevent atelectasis by providing visual feedback on inhalation.
What is an incentive spirometer? 
A 58-year-old male with a long history of poorly controlled hypertension presents to physical therapy with complaints of increasing fatigue, shortness of breath on exertion, and occasional dizziness. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 160/95 mmHg, and he has an elevated jugular venous pressure. An echocardiogram reveals thickening of the left ventricular wall and a reduction in left ventricular compliance. What is the most likely diagnosis based on these findings?
What is left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)?
This test/measure is represented by the following case. A 72-year-old male with a history of hypertension, diabetes, and peripheral arterial disease (PAD) presents for evaluation of his walking ability. During the assessment, the patient describes sharp, cramping pain in the calf of his left leg that begins after walking 50 feet on level ground. The pain intensifies with continued walking, forcing him to stop. After resting for 5 minutes, the pain subsides, and he is able to resume walking without discomfort for a short distance before the pain returns.
What is a Grade 3 on the claudication scale?
A 72-year-old female with a history of smoking presents to physical therapy with complaints of increased shortness of breath, productive cough, and a low-grade fever. Upon examination, she demonstrates tachypnea, decreased breath sounds in the right lower lobe, and increased work of breathing with exertion. Pulmonary function tests show a reduction in forced expiratory volume (FEV1) and a moderate decrease in oxygen saturation during activity. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
A) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
B) Acute bronchitis
C) Pneumonia
D) Pulmonary embolism
What is C) Pneumonia?
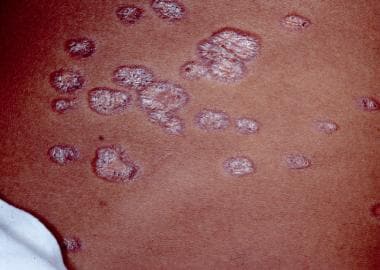 A 45-year-old female with a history of persistent dry cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue, and skin in the picture above presents to physical therapy. She reports having difficulty performing daily activities due to increasing breathlessness. On examination, she has bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy on chest X-ray and a history of erythema nodosum. She also has joint pain, particularly in her knees and ankles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A 45-year-old female with a history of persistent dry cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue, and skin in the picture above presents to physical therapy. She reports having difficulty performing daily activities due to increasing breathlessness. On examination, she has bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy on chest X-ray and a history of erythema nodosum. She also has joint pain, particularly in her knees and ankles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is sarcoidosis?
A 65-year-old male with a history of hypertension and angina is prescribed amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker. During a physical therapy session, the patient reports feeling lightheaded when transitioning from sitting to standing. His resting heart rate is 72 bpm, and his blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg in a sitting position.
Which of the following effects of calcium channel blockers is most likely contributing to the patient's symptoms?
A) Increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure
B) Decreased myocardial contractility and heart rate
C) Vasodilation and potential orthostatic hypotension
D) Increased stroke volume and reduced peripheral vascular resistance
C) Vasodilation and potential orthostatic hypotension