Components of maternal weight gain.
What are
1) Plasma volume
2) Maternal body tissue (uterus, breast)
3) Fetal tissue (bone, placenta)
Mineral supplementation required for formula fed infants.
What is iron.
Fetal stores of iron are depleted by 4 months. Iron in breast milk can be easily absorbed so no extra supplementation.
Formula fed infants should use iron fortified formula.
Erikson's stages of development for childhood.
What are Trust vs. Mistrust (0-1); Autonomy vs. shame and doubt (1-3); Initiative vs. Guilt (3-6); Industry vs. Inferiority (7-12); Identity vs role confusions (13-18).
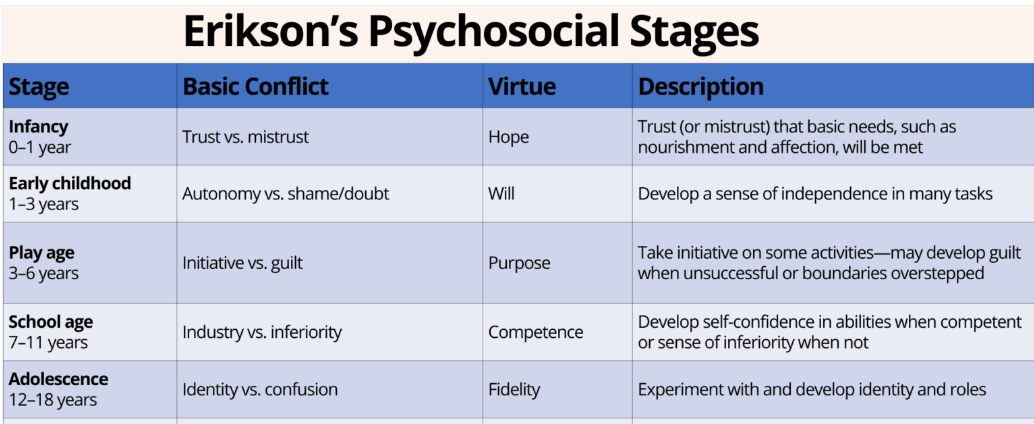
Estimated calorie needs for adults based on activity level.
What are
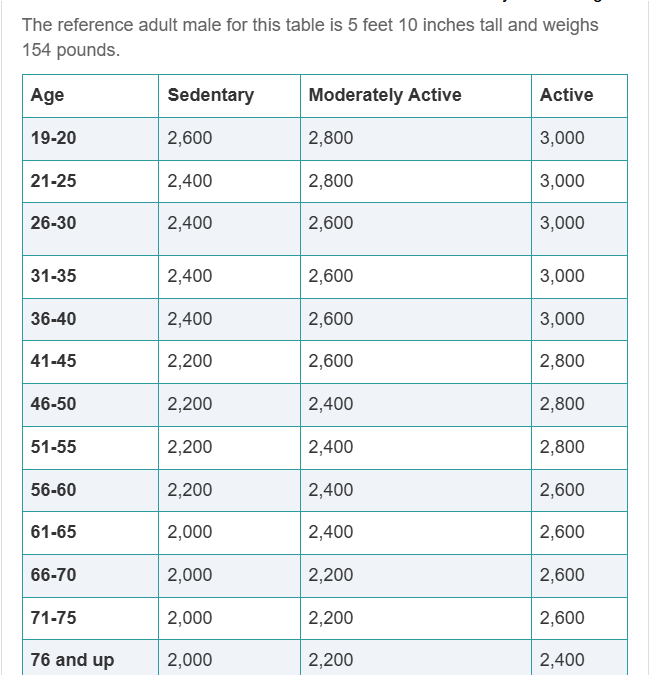
Four affects of aging on nutritional status.
What are 1) decreased appetite; 2) decreased thirst mechanism and dry mouth; 3) decreased taste; 4) decreased food intake d/t dental issues affecting chewing.
Recommended pregnancy weight gain by BMI.
What is
25-35 lbs for normal (BMI 19-24.9)
28-40 lbs for underweight (BMI <18.5)
15-25 lbs. for overweight (BMI 25 - 29.9)
11-20 lbs for obese (BMI >30)
Introducing solid foods to infants begins at this time.
What is 4-6 months.
What are food asphyxiation, lead poisoning, obesity, Iron deficiency, Type 2 diabetes
This vitamin deficiency causes neural tube defects in pregnant women and megaloblastic anemia in adults.
What is folic acid.
Risk factors for malnutrition in older adults.
What are dementia, polypharmacy, poor oral health, overly, alcoholism, depression/loss of spouse; isolation.
Increased protein requirements for pregnant women.
What is 71 grams
Vitamin supplement required by breast fed infants.
What is Vitamin D.
Adolescents are at risk for these vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
What are iron, calcium, Vitamin A & C
Fe - girls d/t menstruation
Ca+ - increase in bone growth
Caloric needs for middle age adults versus young adults.
What is decreased calories after 50 to 1900-2200 for middle age adults starting at 50.
Young adults caloric needs remain the same as adolescents. Young adult women need to maintain calcium levels.
What is Vitamin D.
Ability to synthesize vitamin D reduced.
Excess of these 2 vitamins during pregnancy may be harmful to the fetus.
What is Vitamin A and Vitamin D.
The age to introduce baby to cow's milk.
What is after 1 year old.
Cows milk is less digestible and contains less iron.
Milk should be whole milk until age 2 because they need the full fat content.
Low-fat milk can be introduced after age 2.
Foods high in calcium include
What is kale, broccoli, sardines, milk, yogurt, cheese
Populations at higher risk for foodborne illnesses.
Who are
- children under 5 years
- adults aged 65 and older
- people with weakened immune systems
- pregnant women
Pregnant and immune compromised people (such as transplant patients) should avoid raw fish, unpasteurized dairy and fruit juices, raw sprouts, deli salads, undercooked meat.
Signs and symptoms of dehydration in older adults.
What are confusion, weakness, hot/dry body, furrowed tongue, decreased skin turgor, rapid pulse, elevated urine sodium.
Calorie requirements during each trimester of pregnancy.
What are
First trimester - Normal RDA
Second trimester - increased 340 calories per day
Third trimester - increased by 452 calories per day.
Health Promotion interventions during pregnancy, lactation, and infancy.
What are
*maternal education including on metabolic, physiologic, and hormonal changes during pregnancy.
*Use of credible resources for education including MyPlate, Dietary Guidelines for Americans, and professional medical associations.
*Community support such as SNAP, WIC, and interest groups such as La Leche league
Caloric needs for toddlers, preschoolers, and school age children.
What are
*1300 kcal and 16 grams protein for toddlers
*1800 kcal and 24 grams protein for preschoolers
*2000 kcal and 28 grams protein for school age kids
Health Promotion interventions for adults
What are reducing risk for chronic disorders by limiting foods high in fat, plan time to allow time for meal planning, keep track of dietary intake using MyPlate, focus on routine dietary habits, exercise regularly, refer elderly to food assistance programs such as SNAP, Meals on Wheels, or food banks for assistance with food.
Interventions to support nutrition in elderly.
What are
*do not smoke within 1 hour prior to meal
* vary food by colors and textures
* provide enough lighting to see foods
*avoid noisy dining areas for hard of hearing
*arrange for food delivery to assist