How many layers of skin are found within the epidermis?
5 layers
The school nurse is educating the physical education department at a middle school about methods to reduce easily transmissible infections, such as head lice (pediculosis) and tinea (fungal) infections. What teaching points should be included? Name at least one prevention strategy for each type of infection.
Tinea - wear shower shoes, make sure shoes and socks are clean and dry, wipe down gym equipment and mats in between use with an approved gym equipment wipe, wash infected items in hot water, treat fungal infections promptly to limit their effects and transmission to others
Pediculosis - don't share hats, helmets, hair ties, brushes, etc. with others. Wash clothing, bedding, towels in hot water and dry in a hot dryer (includes car seat covers), use medicated shampoo as directed and comb through each hair strand until all living lice and eggs have been removed. Boil the comb.
Vision can be assessed in several different ways. Name one method of visual assessment.
Snellen Eye chart
Tumbling E test or animals (children who don't know their letters yet or adults with aphasia)
Eye dilation and exam
Peripheral vision tests with lights or fingers
Pupillary assessment
Abnormalities of the inner ear structures
Hearing loss/Deafness in that ear
Other congenital problems, such as urinary tract anomalies (birth defects) or a genetic syndrome
What is the pathophysiology of this condition?
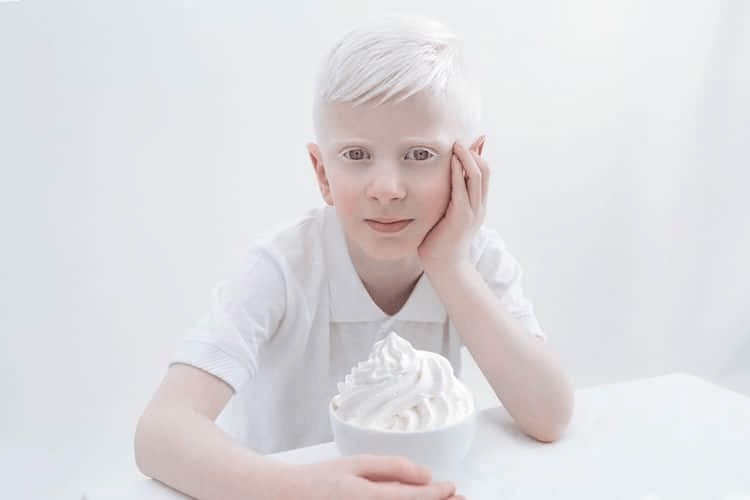

Albinism - little to no melanin is produced causing a lack of pigment on the skin, hair, and irises.
(inherited condition)
What does diplopia mean?
Double vision
The integumentary system has four main functions. Name two of these functions.
Sensory
Immunity
Temperature regulation
Water balance
The nurse is caring for a 50-year-old client at a well-check visit. Which immunization is recommended for this client to prevent complications from a childhood infection with varicella?
Shingles Vaccine (Shingrix) prevents neuralgia and blindness, and may reduce dementia risk
What type of pain is vague, diffuse, and results from noxious stimuli to internal organs?
Visceral pain
The nurse is checking in a preschooler at the eye clinic. What symptoms would the nurse expect the client or parent to report if a vision problem was present? Identify two symptoms.
Rubbing the eyes
Head tilt
Squinting
Bumping into things
Developmental delays
Client reports
The nurse is teaching a nursing student about pressure ulcers. Identify two risk factors that contribute to pressure ulcers.
advanced age
impaired circulation and tissue perfusion
immobilization
malnutrition
decreased sensation
incontinence
Describe the meaning of purulent exudate.
Purulent drainage is thick, pus-like fluid that can vary in color, ranging from yellow to green to brown. This type of drainage is never normal and typically signals infection. Purulent drainage consists of dead tissue cells, white blood cells, bacteria, and other fluids. It is often associated with a foul odor (malodorous) due to the presence of bacteria and decaying tissue.
The integumentary system contains four different components (think tissue types). Name two of these components.
Skin
Hair
Mucous membranes
Glands
The nurse is teaching a class about the dangers of excessive ultraviolet light and sun burns. Which layers of the skin are affected by a sun burn with blisters?
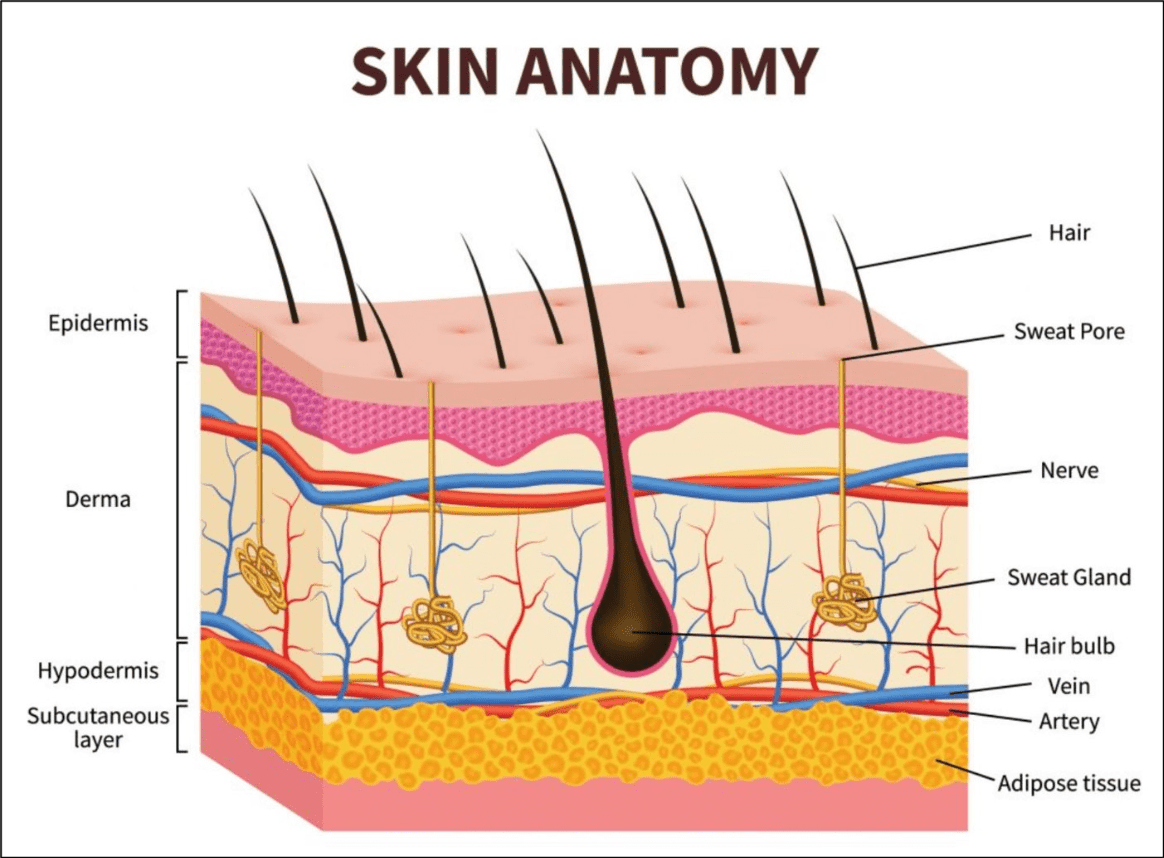
Second degree burns (blisters) are partial thickness burns affecting the epidermis and dermis.
What type of pain results from noxious stimuli to the skin, joints, muscles, and tendons and is easy to pinpoint?
Somatic pain
The nurse is assessing a young child and observes the child's orientation of the eyes. What is the interpretation of this image?
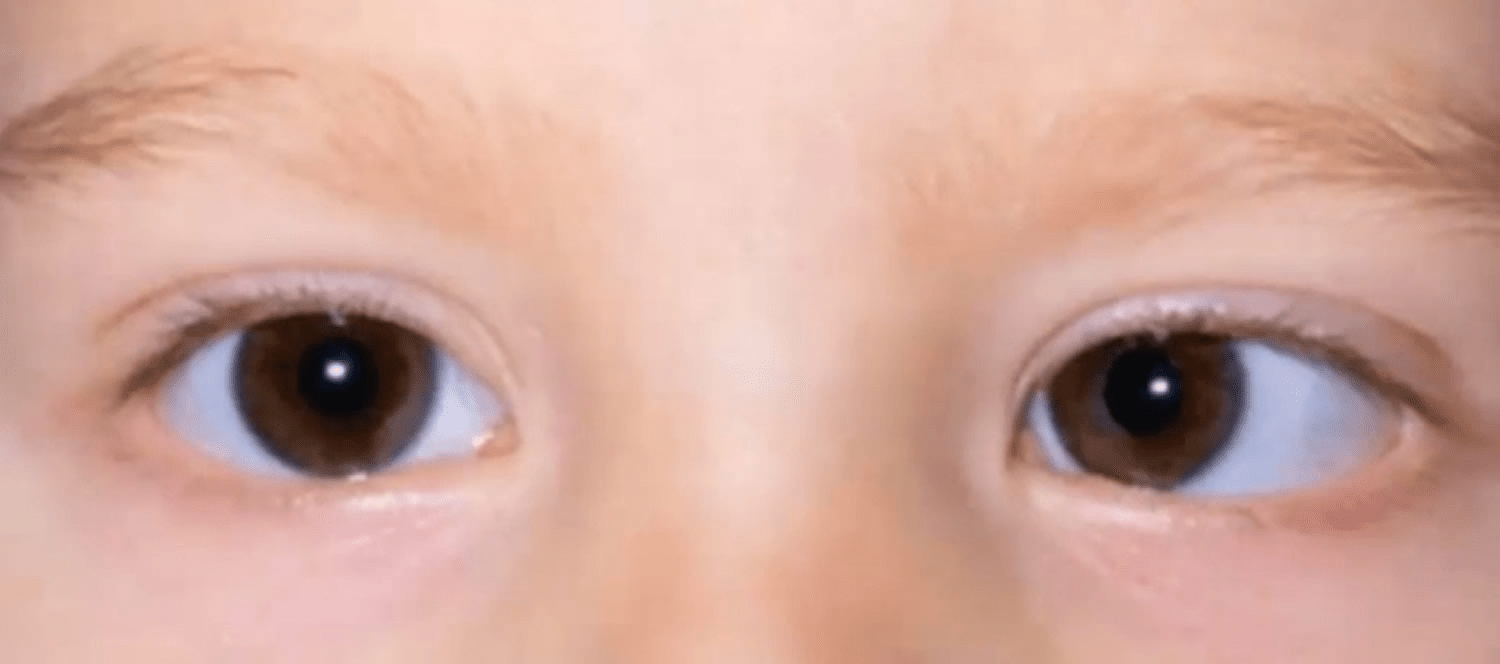
Ambylopia (lazy eye) or Strabismus (crossing of both the eyes)
What is phantom pain?
Pain exists after the removal of a body part (amputation). Severed neurons may result in spontaneous firing of spinal cord neurons because normal sensory input has been lost.
What is the difference between a malunion and nonunion of a fractured bone?
Malunion = fracture that healed in the wrong position. Most commonly happens in fingers and toes as casting can be difficult.
Nonunion = a fracture that does not heal; can occur as the result of poor nutrition, some disease processes, and infection.
The nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about the effects of aging on the skin. Identify three effects of aging on elderly skin.
sensation changes
decreased blood flow to touch receptors
decreased amount of touch receptors
loss of elasticity, integrity, and moisture of the skin
skin becomes fragile-easy bruising
large, pigmented spots called age spots can develop
The nurse is caring for a client with a major burn. Prompt treatment is needed to prevent which type of shock in the first 48 hours?
Hypovolemic shock - clients with major burns are treated with aggressive IV hydration therapy to prevent/treat hypovolemic shock. After the fluid resuscitation period, infection can set in and cause septic shock.
What type of pain results from peripheral nerve disease (like diabetes) or injury? Patients lose sense of touch and pressure, develop paresthesia (numbness) and pain simultaneously. Pain may be prickly, stabbing, or burning in nature.
Neuropathic pain
The telephone triage nurse receives a call from a client who reports a buzzing or humming sound coming from his left ear intermittently. He recently began taking a new medication a few days ago. What is this condition called?
Tinnitus - a ringing, buzzing, humming, whistling, roaring, or blowing
The nurse is educating the parent of an infant about the importance of treating ear infections. Identify three complications of ear infections.
tympanic effusions
rupture of the tympanic membrane
scar tissue formation
conductive hearing loss
mastoiditis
meningitis
osteomyelitis
What is the difference between presbyopia and presbycusis?
Presbyopia = difficulty focusing the eyes resulting from age-related changes
Presbycusis = age-related hearing loss
The nurse is caring for a client on bedrest. What prevention methods can the nurse include in the plan of care to reduce the risk of pressure sore development? Name three prevention strategies.
Braden Scale
Pressure relieving devices, frequent turning
Specialized beds/mattresses
Preventing infections
Nutritional support (high protein)
A nurse is caring for a client who reports the development of hives all over the body after taking penicillin for strep throat. What actions should the nurse take? Name three actions.
Stop taking the medication/obtain a prescription for a different antibiotic
Monitor airway, breathing, circulation
Administer medications - antihistamines, corticosteroids, and possibly epinephrine (if ABCs are compromised)
The nurse is teaching a group of school age children about safety. What teaching should be included to teach about the eyes to prevent problems? Identify three teaching points.
Do not run with sharp objects like pens or pencils
Wear eye protection - sports, gym class (think prescription goggles), science class/experiments
Do not touch your face/eyes/nose - bacteria can easily penetrate mucous membranes and transmit infections
Report vision changes immediately - floaters, curtain-like vision, inability to see, eye pain, etc.
Seek medication attention immediately by ophthalmologist if any trauma occurs to the eyes/face
The nurse is teaching a client about treatment for the condition in the image. Identify three teaching points that should be included in the care of the child.
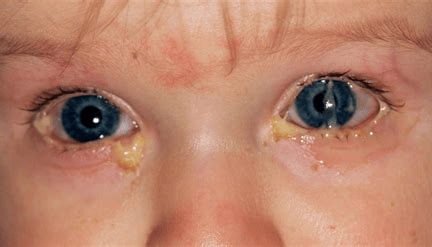
Use a moist, warm compress to remove matted drainage from the eyes/eyelashes. Be careful to avoid spreading the infection from one eye to another, or person to person.
Wash hands before and after eye drop instillation. Place the drops in the lower conjunctival sacs.
Do not share eye drops with anyone.
The nurse is caring for a client who reports central vision loss. Which health condition does this describe?

Macular degeneration - deterioration of the macular area of the retina leading to irreversible central vision loss.
It is caused by impaired blood supply to the macula, leading to waste accumulation and ischemia.
The physician is assessing a client with a casted fracture and becomes concerned when they identify pallor, paresthesia, and increased pain despite taking analgesia. What does this mean?
The client’s extremity is pale, they feel numbness or tingling, and they have pain despite taking pain medication. These symptoms are concerning for a nerve compression syndrome or compartment syndrome. Pain may be caused from ischemia, or decreased tissue perfusion.
The nurse is teaching a client in the dermatology clinic about the ABCDEs of skin abnormalities. What do each of the letters represent?
A - Asymmetry
B - Border irregularity
C - Color variations
D - Diameter larger than 6 mm
E - Evolving - Any skin growth that changes in appearance over time
Also:
Any skin growth that bleeds or will not heal
Early detection is crucial to positive outcomes
Identify the type of skin abnormalities based on the image and description.
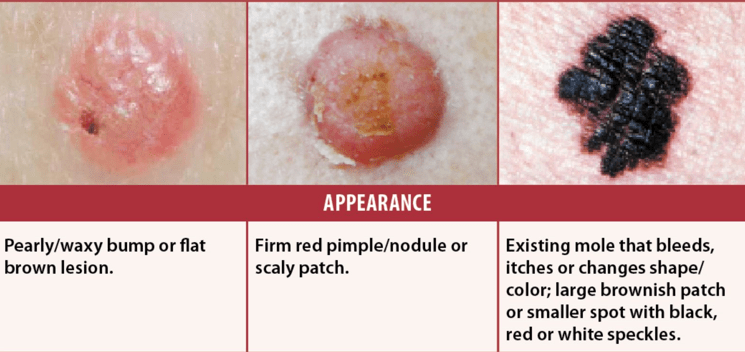
From left to right - basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma
Vision deteriorates - less able to distinguish details
Age-related eye changes may begin as early as 30 years of age
Less tear production
Corneas become less sensitive
Pupil size decreases and reacts more slowly
Lens becomes yellowed, less flexible, and slightly cloudy
Presbyopia: difficulty focusing the eyes
Fat pads supporting eye decrease and eyes sink back into skull
Eye muscles weaken, decreasing ability to rotate eye fully and limiting visual field
Visual acuity may gradually decline
Aging increases the threshold needed to perceive sensory input, so the amount of sensory input needed to be aware of the sensation becomes greater
Physical changes account for most of the other sensation changes
The nurse is admitting a client in the ophthalmology clinic who describes his vision as a curtain closing and sees dark spots/floaters. What is this condition and how serious is it?

Retinal detachment is an acute condition that occurs when the retina separates from its supporting structures. The retina becomes ischemic and causes vision loss.
Medical emergency - treatment includes several types of surgeries and cold therapy
The nurse is educating a client about the pathophysiology of an infectious skin condition. What is this organism and what is the medical condition it causes?
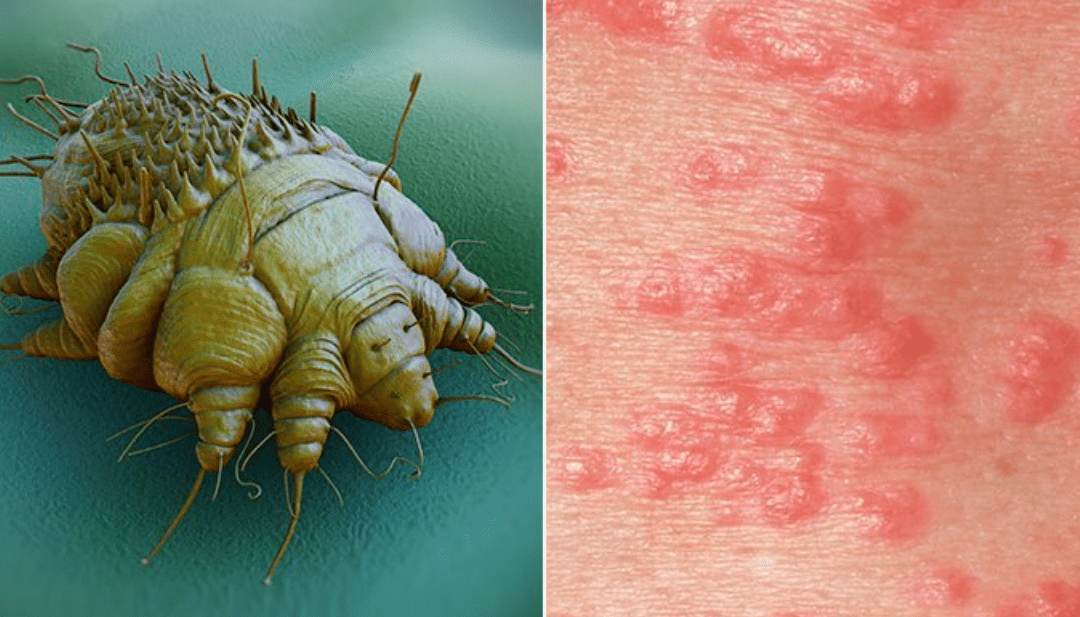
Mite; scabies
How would the nurse describe the differences between neuropathic and intractable pain?
Neuropathic pain = results from damage to the peripheral nerves by disease or injury (chronic pain)
Intractable pain = chronic pain that is progressing, unrelenting, and severely debilitating; does not respond well to medications and is common with severe injuries, such as crush injuries
The nurse is teaching a client about wound care. What are local and systemic clinical manifestations of a wound infection? Name at least one of each.
Local infection - Swollen, warm and tender areas of erythema.
Systemic infection - manifestations include fever, leukocytosis, and/or malaise
What is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects keratinocytes of the skin?
Psoriasis
cause is unknown
Exacerbations can be triggered by environmental factors, trauma, infection, alcohol consumption, certain medications or autoimmune conditions
The severity of psoriasis varies but usually has periods of exacerbation.
The nurse is teaching a group of teenagers about the structure and function of the ears. Identify three teaching points that should be included to protect the ears/minimize hearing loss throughout the lifespan.
Reduce exposure to loud noises - Hearing loss accelerates in people who were exposed to excessive noise or smoking when they were younger
Do not smoke - Hearing loss accelerates in people who smoked when they were younger
Have ear problems assessed and treated promptly (impacted cerumen, ear pain/infections) to reduce long-term complications of conductive hearing loss.
Wear protective helmets when playing sports - damage to the temporal lobe can permanently affect hearing (sensorineural hearing loss)
The nurse is teaching an adult client about the pathophysiology and treatment of Meniere's disease. Identify two treatments options and one complication associated with this condition.
Treatments - focus on relieving inner ear pressure with meds (Antihistamine agents, Benzodiazepines, Anticholinergic agents, Diuretics, Antiemetic agents, Limiting dietary sodium intake (to promote fluid retention, Middle ear injections of gentamicin (an ototoxic antibiotic that can reduce balance structures) or corticosteroids)
Avoiding triggers (e.g., alcohol and stress)
Partial or complete surgical removal of the endolymph or inner ear
Vestibular nerve resection
Hearing aids
Physical therapy to improve balance
Complication - permanent hearing loss
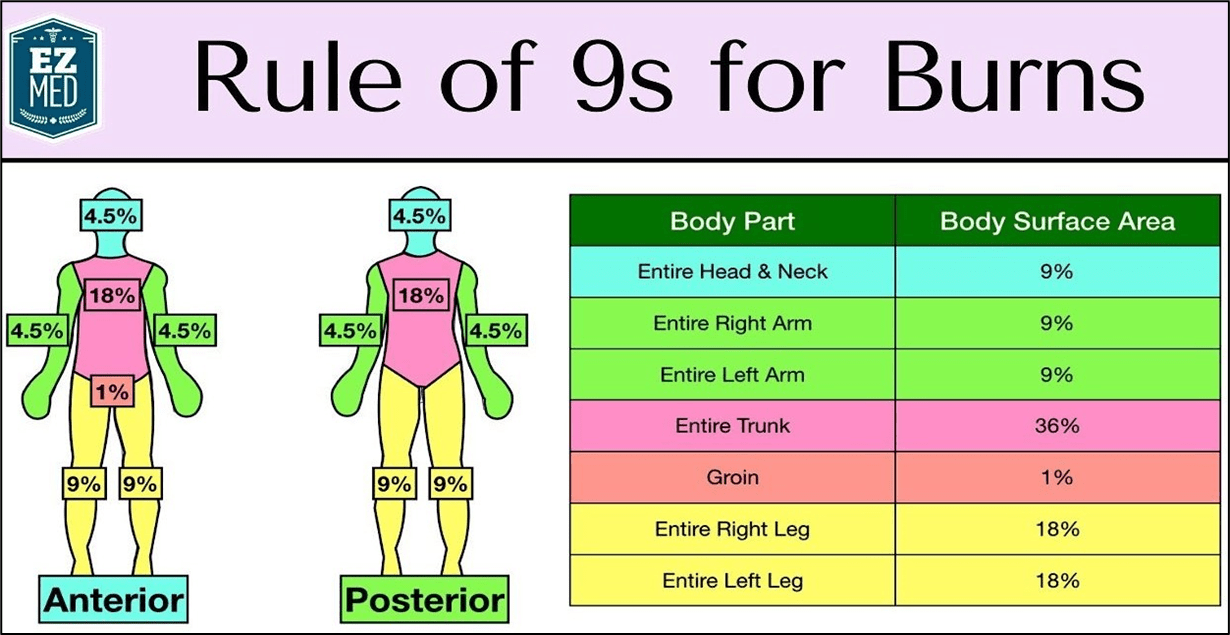
Using the Rule of 9's, what is the percentage of the total body surface area that was burned?
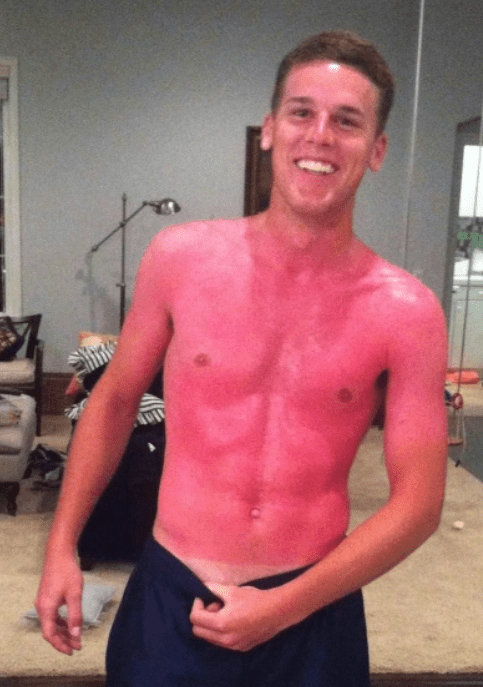

Face and neck (front) - 4.5%
Trunk (Front) - 18%
Arms (Front) - 9%
Total= 31.5%
What is the difference between petechaie and purpura?
Petechiae = Petechiae appears as red, pink, purple, or discolored patches under the skin. They are smaller than 2 millimeters and usually flat. Petechiae can develop in small clusters or patches, resembling a rash. It may spread over a larger area of skin or stay confined to a single area.
Purpura = Purpura appears as red, pink, purple, or discolored patches just under the skin. They are larger than 2 millimeters. They can also develop under the mucous membranes, such as those in the mouth or nose. Purpura forms when tiny blood vessels called capillaries burst and leak, causing blood to pool beneath the skin.