What is the first stage of perceptual experience that can be influenced by prior knowledge and expectations?
Processing
This part of the eye performs 70-80% of focusing
The Cornea (the lens accommodates the rest)
What unit is used to measure sound intensity level?
Decibels (dB SPL)
When endorphins bind to opiate receptors, what happens to Substance P release?
It is inhibited, resulting in less pain
These papillae do NOT contain taste buds.
Filiform papillae
The smallest amount of stimulus energy required for detection is known as the:
Absolute Threshold
This fluid-filled space can build pressure, eventually crushing the optic nerve:
The aqueous humor.
Bonus points: What is this disorder called?
Which sound localization cue works best for high-frequency sounds due to acoustic shadowing?
Interaural intensity (or level) differences (IID/ILD)
What are the two ways we discussed that 2nd pain can be modulated, one in which it increases and one in which it decreases instead?
Wind-up & DNIC
How is the olfactory pathway different from all other sensory pathways?
It bypasses the thalamus
The process of presenting stimuli in a random order, a random number of times is this psychophysical method:
Method of Constant Stimuli
The threshold is the stimulus that is detected 50% of the time
In this illusion, which can be explained by Lateral Inhibition, squares of the same color can appear different based on their surroundings
Simultaneous Contrast
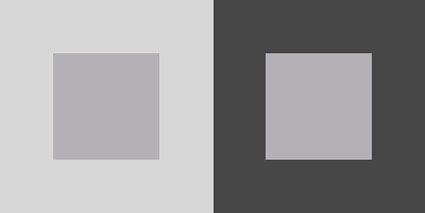
Based on this audiogram, which type of hearing loss(conductive or sensorineural) is shown?
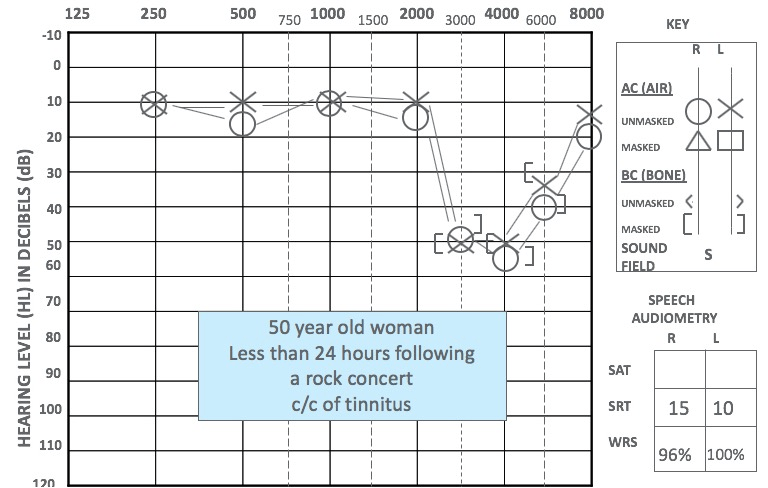
Sensorineural hearing loss
(X, O here represents different ears)
Which mechanoreceptors are rapidly adapting (RA)?
Meissner corpuscles and Pacinian corpuscles
Bonus: Why Pacinian is RA?
This theory of taste perception proposes that flavor is encoded by patterns of activity across many neurons rather than a single “labeled line.”
Population coding
How can scientists reduce bias when measuring thresholds with Fechner’s original methods?
Forced Choice Procedure
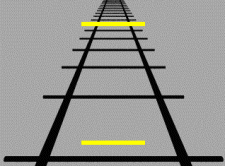
This illusion uses the cue of linear perspective to trick the brain into thinking two identical shapes differ in size due to perspective cues
Ponzo illusion
This cochlear mechanism involves outer hair cells changing length to amplify basilar membrane vibrations.
The motile response
When choosing the softest bedsheet by moving a finger across the fabric, which cue is used to perceive texture, and which receptor is most involved?
Temporal cue; Pacinian corpuscles
The brain region that is most associated with enjoyment and wanting more for taste
OFC
This law states that as the intensity of a standard stimulus increases, the difference threshold (DL) also increases proportionally.
Weber’s Law.
The difference threshold describes the smallest difference between two stimuli that can be detected
This problem refers to the fact that a single retinal image could come from infinitely many real objects
Inverse Projection Problem
According to place coding theory, why does presbycusis primarily affect high-frequency sounds?
High frequency is coded near the base. Every single time a sound wave came in, it stimulated the base of the cochlea. The hair cells are being overused.
This illusion occurs when simultaneous activation of warm and cold receptors produces a painful burning sensation.
Thermal Grill Illusion
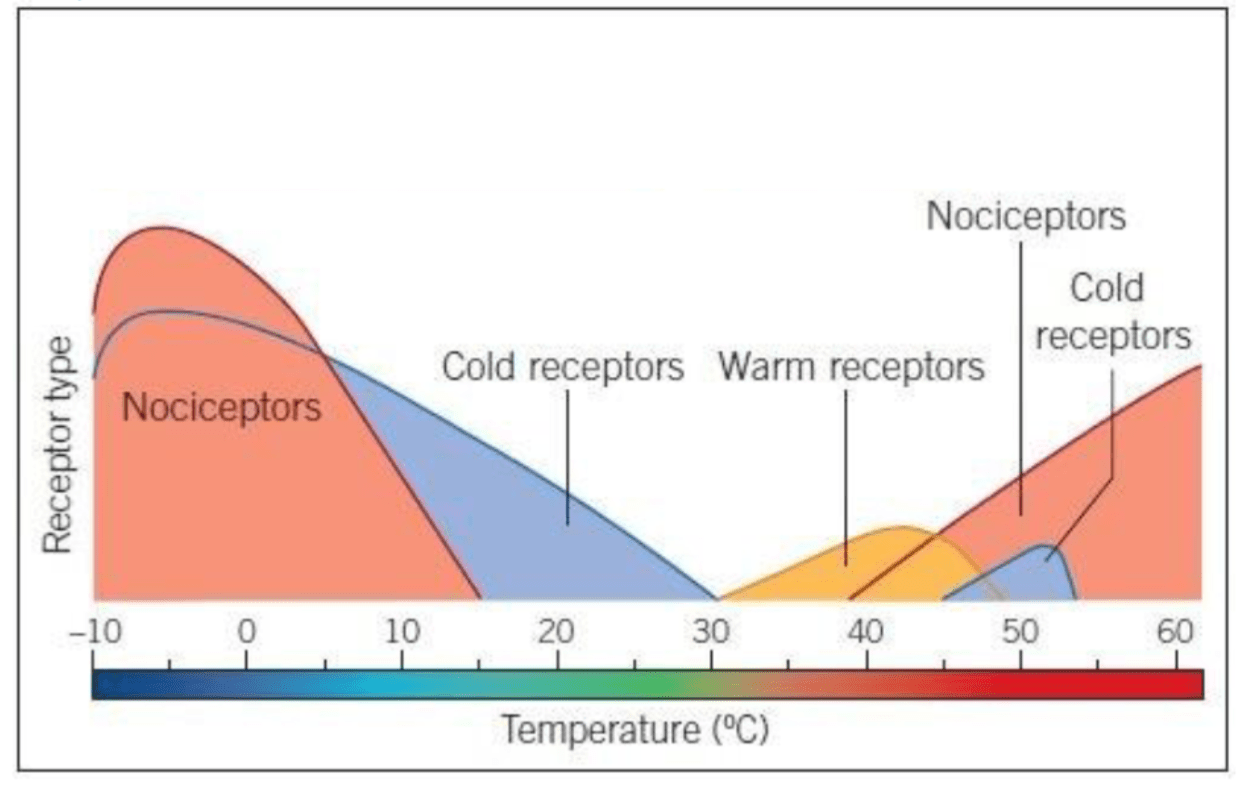
Looking at the graph, this mixed pattern of activation mimics what normally happens around ~45°C, a temperature that also activates heat-nociceptors. The brain interprets this combined signal the same way it interprets noxious heat.
How does Miracle Fruit change the way sour foods taste?
Lemon becomes sweet. It binds to sweet receptors and activates them when there is a low pH.