The splitting apart of breaking up of U-235 is defined as what?
Nuclear Fission
What are the 3 types of radiation that we talked about in class?
Alpha, beta, gamma
What is something that is always emitted in alpha radiation?
A helium nucleus or an alpha particle
What is one beneficial use of radiation?
Radiation therapy, radiotracing, carbon dating
What is the atomic number of the new isotope produced after radon undergoes alpha decay?
84
Two atoms that combine together and release a ton of energy in the process is defined as what?
Nuclear Fusion
List the types of decay in order of penetrating power (greatest to least).
Gamma, beta, alpha
What is an alternative name for a beta particle (-)?
An electron
What is something Radiologists wear when taking an x-ray? Why can't they just wear their scrubs?
Lead apron. Cannot just wear scrubs because x-rays can penetrate through fabric. They cannot penetrate lead.
What is the mass number of Uranium-235 after it undergoes alpha decay?
231
Both Fission and Fusion reactions release massive amounts of what in addition to their respective atomic nuclei?
Energy
The atomic symbol includes two numbers: atomic mass and atomic number. What does the atomic mass number tell you?
How many protons and neutrons an atoms nucleus contains.
What is the charge of an alpha particle?
+2
Name 3 ways they tried to "clean up" Chernobyl.
Scraping off the surface radiation, burring radioactive material in trenches, washing off machinery, killing animals, etc.
What two things are produced if carbon-14 undergoes beta decay (-)?
Nitrogen-14 and an electron
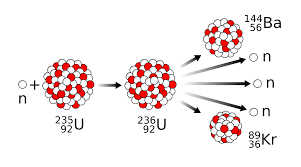
What subatomic particle is primarily responsible for causing chain reactions involved in fission?
Neutrons!
In chemical reactions, electrons are responsible for the new products. What subatomic particles are at play in nuclear reactions?
All of them. Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What happens to the mass number in beta radiation? What happens to the atomic number in beta radiation?
Stays the same. Goes up by one.
What is critical mass?
The minimum amount of fissile material needed to maintain a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction
What changes about an atom if it is only undergoing gamma decay?
Nothing. Gamma rays have no charge or mass.
Explain how fusion in the sun works.
Hydrogen-1,2,3 atoms fuse together over time and release energy in the form of heat and light and will eventually emit a helium as a product.
Compare the strengths of the strong force and the electromagnetic force in an element that is actively undergoing radioactive decay.
Electromagnetic force > strong force when something is decaying.
Describe why in alpha radiation the mass number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2
2 protons + 2 neutrons = Change in mass of 4
2 protons = Change in atomic number of 2
If the control rods in a nuclear reactor are completely withdrawn, what would happen to the reactor? What state would the reactor reach?
The fission would increase exponentially and the reactor would be in a supercritical state.
Explain why in beta radiation the mass number changes by 0 and the atomic number increases by 1
Neutron gets changed into a proton and an electron. Proton mass = neutron mass so it doesn't change, but atomic number does change because protons increased.