During fission, what particle must be absorbed by the nucleus to trigger the split?
A neutron
What particle is released during alpha decay?
2 protons + 2 neutrons
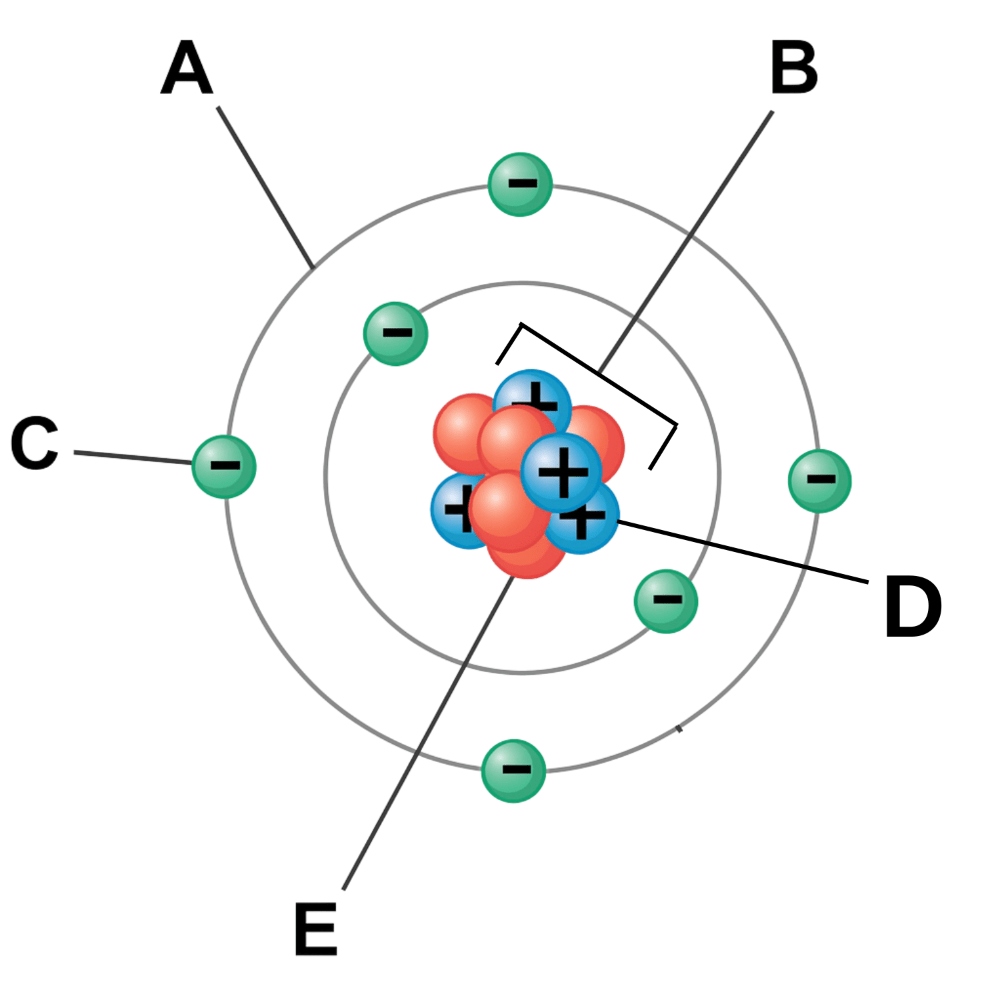 Which particle has a positive charge? (Labeled D)
Which particle has a positive charge? (Labeled D)
Proton
What is the blanket of gases around Earth called?
Atmosphere
Which layer makes up most of Earth’s volume?
The mantle.
What is the flow of energy from warmer places to cooler places called?
Heat
What is the process where two nuclei combine?
Nuclear Fusion
In beta decay, what does a neutron turn into?
A proton + an electron
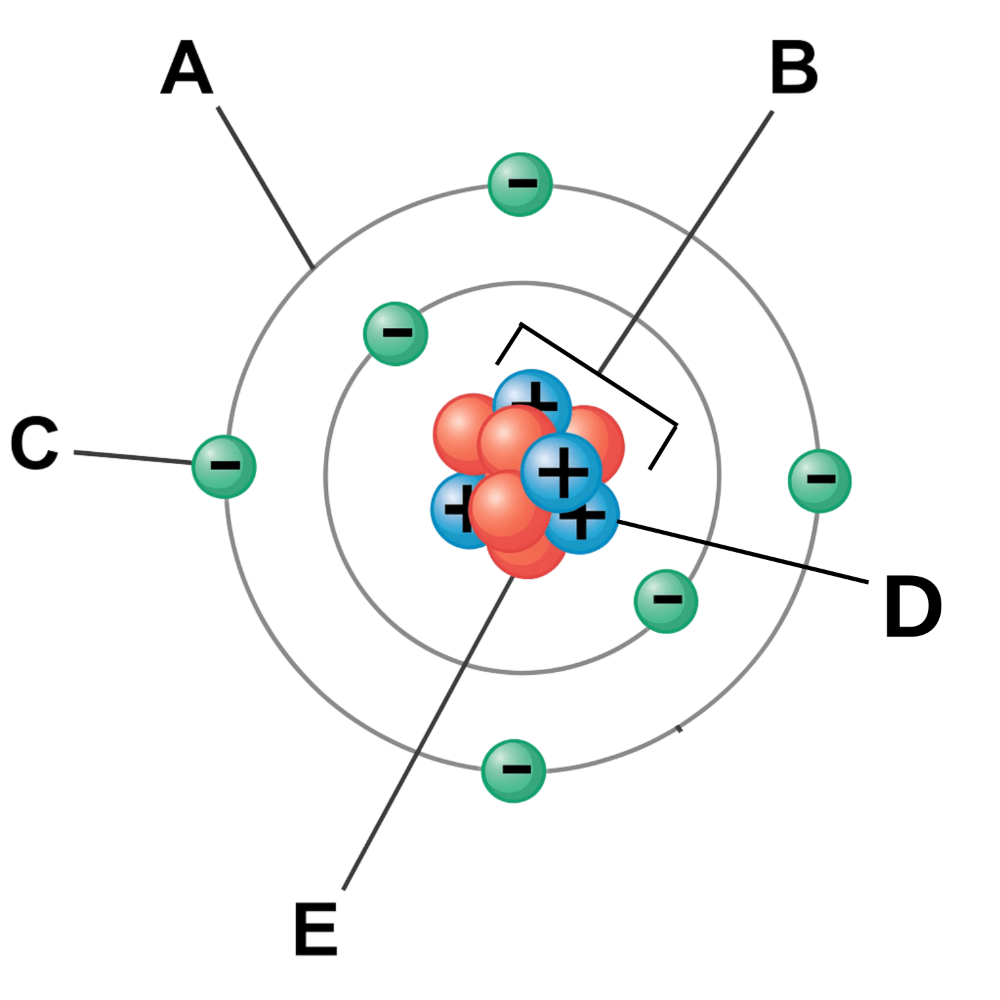 What is the center of the atom called? (Labeled B)
What is the center of the atom called? (Labeled B)
Nucleus
Which layer contains weather?
Troposphere
Which layer is liquid?
The outer core
Which type of heat transfer moves through empty space by electromagnetic waves?
Radiation
What happens when a large nucleus splits?
Nuclear Fission
Which type of decay releases pure energy, not particles?
Gamma decay
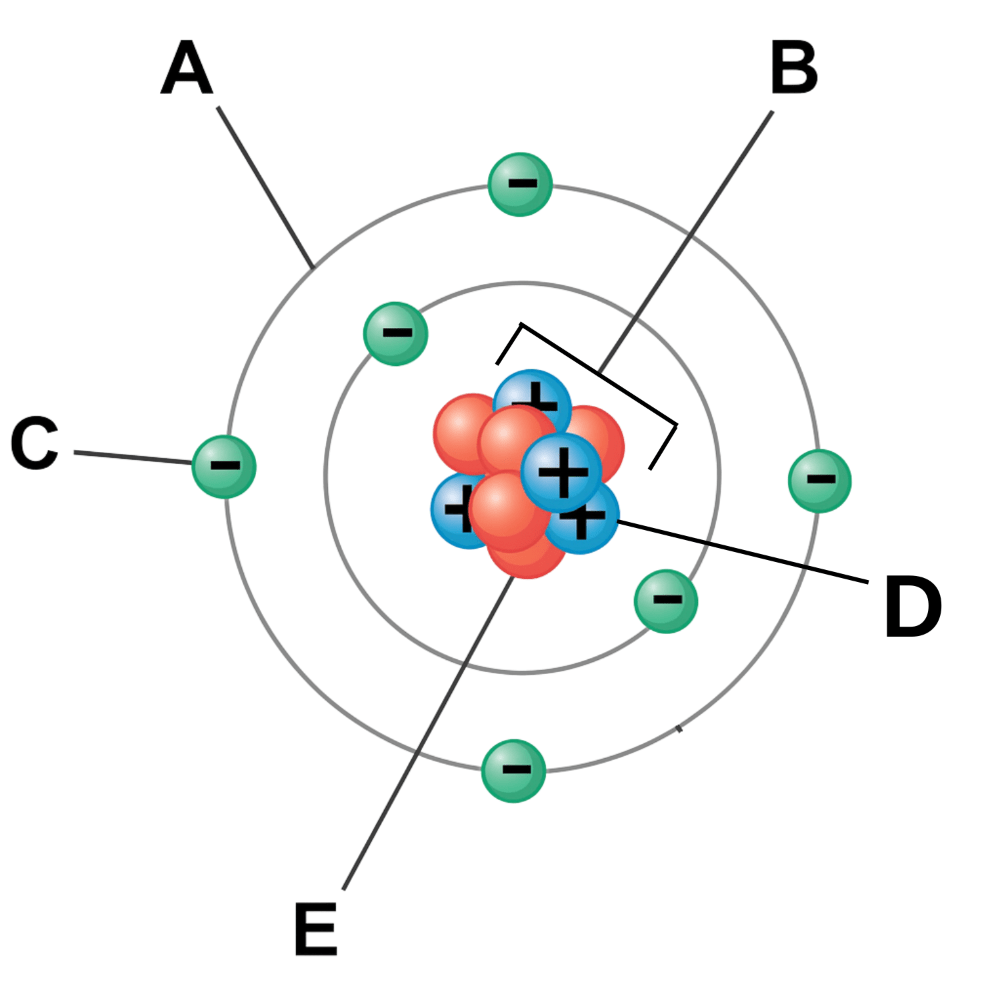 Which particle has a negative charge? (Labeled C)
Which particle has a negative charge? (Labeled C)
Electron
Which layer contains the ozone layer?
Stratosphere
Which layer is solid due to extreme pressure?
The inner core
Which type of heat transfer happens when hotter, less dense fluids rise and cooler, denser fluids sink?
Convection
What do we call changes inside the nucleus that release energy?
Nuclear processes.
Which decay type has greater penetration and must be stopped using aluminum?
Beta decay
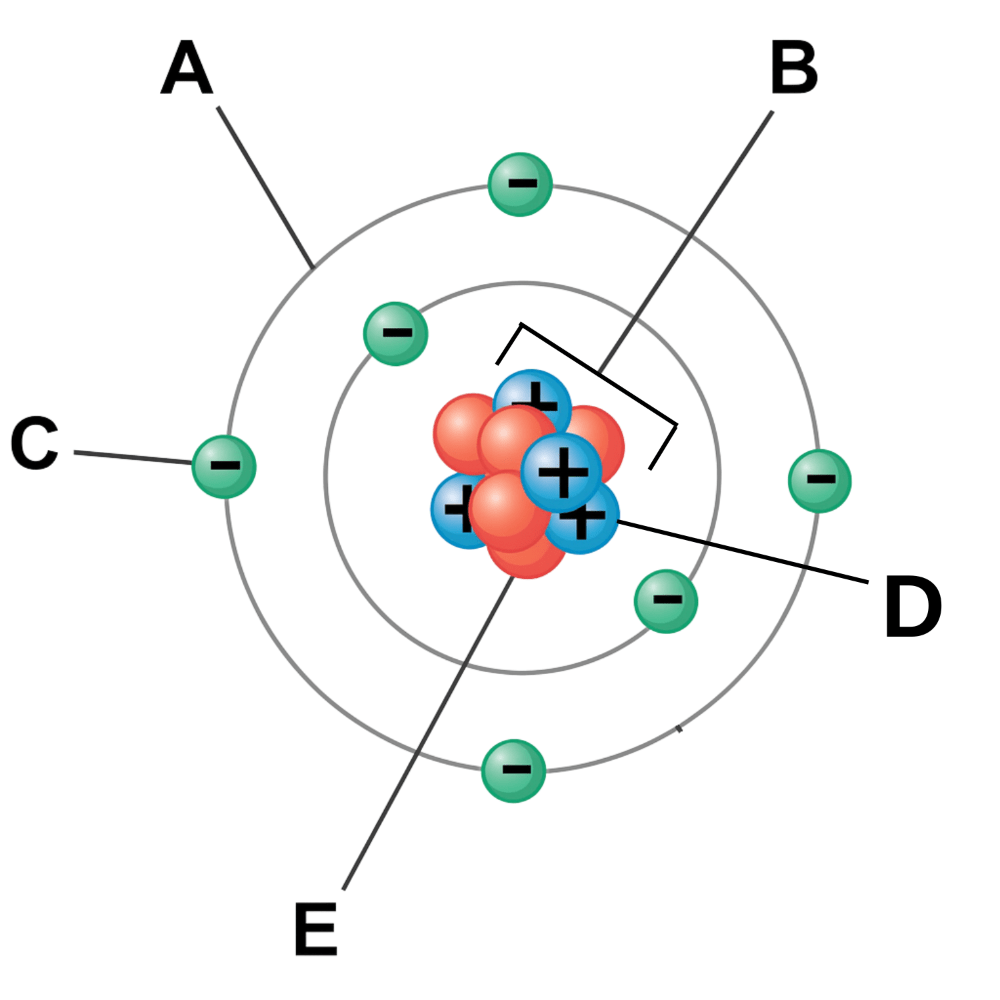 Which particle has no charge? (Labeled E)
Which particle has no charge? (Labeled E)
Neutron
Which is the coldest layer?
Mesosphere
What do we call the rigid top layer of Earth (crust + upper mantle)?
Lithosphere.
Which type of heat transfer occurs when particles in a solid bump into each other, passing energy along?
Conduction
Which nuclear reaction requires extremely high temperatures and pressures to occur?
Nuclear Fusion
Which type of decay involves releasing high-energy electromagnetic radiation?
Gamma decay
Which particle is much smaller than protons and neutrons?
Electron
Which layer fades into space?
Exosphere
What is the rigid rock layer above the asthenosphere called?
Lithosphere
Materials that allow heat to pass through easily are called what? And what are materials that do not allow heat to pass through called?
Conductors and insulators