What is the stability of an element determined by?
The neutron-to-proton ratio
What is a rule of transmutations that always must hold true?
Matter must be conserved. The same amount of matter must be on each side.
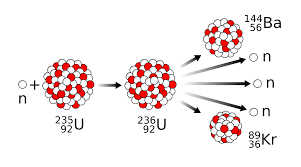
The splitting apart of breaking up of U-235 is defined as what?
Nuclear Fission
Describe what a half-life is.
The time it takes for one-half of an isotope to transmute (decay) into some other isotope.
What is a radioisotope?
What are the n/p ratios that fall within the band of stability?
1:1 and 1.5:1
When does a radioisotope stop decaying?
When it is stable
Two atoms that combine together and release a ton of energy in the process is defined as what?
Nuclear Fusion
What is the mass number of Uranium-235 after it undergoes decay?
231
List the types of decay in order of penetrating power (greatest to least).
Gamma, beta, alpha
How do atoms become stable when too many neutrons or protons are present?
They undergo radioactive decay
What is the charge of an alpha particle?
+2
Both Fission and Fusion reactions release massive amounts of what in addition to their respective atomic nuclei?
Energy
What two things are produced if carbon-14 undergoes beta decay?
Nitrogen-14 and an electron
What device is used to detect radiation?
A Geiger counter
List the 6 kinds of radiation and their symbols.
Alpha particle α
beta particle β-
gamma radiation 𝛾
neutron n
proton p
positron β+
What happens to the mass number in positron radiation? What happens to the atomic number in positron radiation?
Stays the same. Decreases by one.
What subatomic particle is primarily responsible for causing chain reactions involved in fission?
Neutrons!
What percentage of a 600g sample of 37Ca after 2 half-lives?
25%
In chemical reactions, electrons are responsible for the new products. What subatomic particles are at play in nuclear reactions?
All of them. Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Describe what changes are made to an element’s atom when it undergoes alpha decay vs beta decay.
When alpha decay occurs two protons and two neutrons are lost from the original element’s atom.
when beta decay occurs the atomic number increases by 1 (proton is added)
Determine the decay mode and detail the transmutation equation for 198Au
Beta decay
198Au
What is one advantage that fusion has over fission?
Fusion releases a greater amount of energy.
A scientist found a giant sloth frozen and measures that it contained 1/8 of the radioactive C-14 present than normal. How long ago did this organism die?
17,145 years ago
Describe a real-world example/application of radioisotopes and their usage.
Can include in the medical field, warfare, evolution, etc.
Thyroids and I-131
Cancer: Co-60 and Tc-99
Carbon Dating C-14
Uranium Decay - Radon gas production or lead production
Nuclear Weapons
Dirty Bombs
MRems radiation amounts
Radiation Poisoning