This is the name of a condition caused by an imbalance in the production and aborption of CSF in the ventricuar system
hydrocephalus
This test - and the result - that would indicate a NTD
Elevated MSAFP
SATA: Risk factors for OM
Being formula fed
Secondhand smoke
Bottle propping
Home schooling
Cleft palateSecondhand smoke
Bottle propping
Cleft palate
These are causes of increased ICP in children:
Vomiting
Bleeding
Tumor
HTN
Edema
Bleeding
Tumor
Edema
This is the name for when parts of the cerebellum and brain stem protrude into the spinal canal
Chiari malformation
This is done to ensure consistency in daily head circumference measurements
This type of midline deformity consists of a sac containing nerves.
Myelomeningocele
Ear infections are caused by a dysfunctional _______
Eustachian tube
These are early s/s of increased ICP in children:
Bounding energy
Irritability
Nausea
Sunken fontanelles
High pitched cry
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Irritability
Nausea
High pitched cry
This is the age when the child's sutures are fused
12 y/o
These are the two biggest complications for a VP shunt
Infection and malfunction
This device is used to support a more comfortable latch while an infant is feeding in a non-typical position
Nipple shield
A child that has had 4 ear infections in 12 months should be considered for this
Tube placement
Bacterial causes of OM:
S. pneumoniae
S. aureus
C. diff
M. catarrhalis
N. gonorrhoeae
H. influenzae
S. pneumoniae
M. catarrhalis
H. influenzaeThis is the name of downward herniation of the brain into the brainstem
Chiari malformation
SATA: Signs of increased ICP:
Mania
Irritability
HA
N/V
Sunken fontanels
Changed LOC
Irritability
HA
N/V
Changed LOC
SB patients are especially at risk for these two types of tissue injury
Pressure and thermal
This often precedes otitis media
Viral respiratory infection
Post-surgical care s/p VP shunt placement:
Straight cath
Keep flat
Monitor V/S
Keep prone
Neuro checks
Monitor V/S
Keep flat
Neuro checks
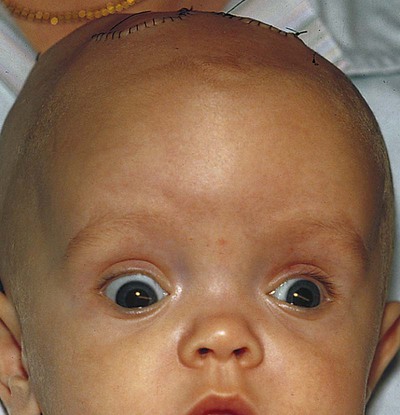
Setting sun sign
This is why shunt patients are kept flat following surgery
Allow time for the brain and CSF pathways to adjust. (Prevents too much or too little CSF fluid from draining at one time)
This is the name of the surgical placement of ventilation tubes in the ear
Findings that would prompt you to notify HCP:
Acrocyanosis
Central cyanosis
Diffuse petechiae
+ Moro reflex at 5 months- Babinski reflex at 9 months
12 hour fetal kick count of 20
Bulging fontanels
Sunken fontanels
Central cyanosis
Diffuse petechiae
- Babinski reflex at 9 months
Bulging fontanels
Sunken fontanels