Math
Which condition is the most likely cause of bright red blood in the stool and rectal itching?
A. Anal fissure
B. Rectal prolapse
C. Upper GI bleed
D. Hemorrhoids
D. Hemorrhoids
Rationale:
-Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the rectum, which is a common (abnormal) problem. They typically cause bright red blood in the rectum and may cause rectal pain or itching.
-Anal fissures are extremely painful and may cause bleeding but are not likely to cause itching.
-Rectal prolapse is the protrusion of the rectal tissue through the anus.
-An upper GI bleed is more likely to be associated with black, tarry stool. Bright red blood indicates a bleed in the colon/rectum, whereas dark blood indicates a bleed higher up in the GI tract.
Which of the following breast findings is expected?
A. Breast tenderness 1 week before menstrual cycle
B. Red, hot rash
C. New or sudden nipple inversion
D. Dimpling
A. Breast tenderness 1 week before menstrual cycle
Rationale:
-Breast tenderness before and during menstrual cycle is a normal, expected finding. Breasts have the least amount of tenderness about 7-9 days after the menstrual cycle, which is why self-breast exams are recommended at that time.
-Signs of inflammation, rashes, lumps, dimpling, nipple discharge, or new changes in the nipples are unexpected, abnormal findings and may be concerning for breast cancer.
A single painless genital chancre sore is a manifestation of which STI?
A. Genital herpes
B. Syphilis
C. Chlamydia
D. Gonorrhea
B. Syphilis
Rationale:
-In the primary (early) stage of syphilis, a painless sore ("chancre") may be found on the genitals where syphilis was contracted.
-Genital herpes causes PAINFUL red vesicles.
-Chlamydia & gonorrhea may cause dysuria and/or genital discharge.
Which of the following is an abnormal finding in the older adult?
A. Smaller liver borders
B. Accumulation of fat around the abdomen
C. Increased saliva & peristalsis
D. Weak abdominal muscles
C. Increased saliva & peristalsis
Rationale:
Older adults have an increased amount of subcutaneous fat around the abdomen, but a decreased amount of overall body fat. Other physiological changes that occur as we age include weaker muscles, smaller liver borders, decreased peristalsis, and decreased production of digestive enzymes, saliva, and tears.
Which of the following findings occur as a result of muscle weakness?
A. Muscle hypertrophy
B. Increased motility
C. Increased coordination
D. Muscle atrophy
D. Muscle atrophy
Rationale:
Muscle atrophy, or muscle wasting, may occur as a result of muscle weakness or decreased muscle use. The muscle mass decreases or shrinks, which you can visibly see.
Muscle hypertrophy (growth) would not be seen in the older adult.
Motility and coordination would decrease as a result of muscle weakness.
How long should bowel sounds be auscultated before they are confirmed to be absent?
A. 30 seconds
B. 1 minute
C. 2 minutes
D. 3-5 minutes
D. 3-5 minutes
Rationale:
Bowel sounds cannot be deemed "absent" unless you auscultate for 3-5 minutes and do not hear any sounds within that time period.
What is this finding called?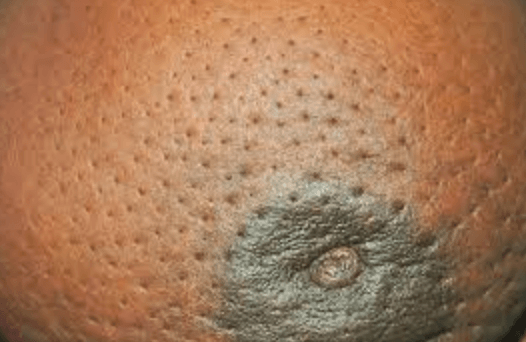
Peau D'Orange
Rationale:
This is referred to as P'eau D'Orange because the breast has an "orange peel" appearance. This is very concerning because it may be a sign of breast cancer.
Which of the following is true regarding this rash?
A. This is a priority finding that must be treated immediately
B. This is a manifestation of an STI
C. This is a normal finding
D. The patient should be assessed for related symptoms & onset of rash
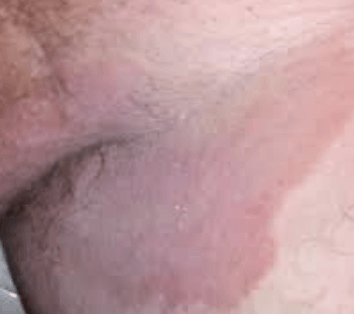
D. The patient should be assessed for related symptoms & onset of rash.
Rationale:
This is tinea cruris ("jock itch"). Tinea cruris is a common skin rash found near the groin in males. It is not a normal finding, so it should be assessed further using OLDCARTS. It is not an STI. It does not need to be treated immediately; the priority action given this information is to assess further.
Which of the following findings in the older adult would be unexpected?
A. Difficulty hearing high-frequency sounds
B. Decreased visual acuity, including peripheral vision
C. Decreased sense of taste
D. Increased expansion & vital capacity of the lungs
D. Increased expansion & vital capacity of the lungs
As we age, our sensory function decreases.
Our muscles become weaker and our thorax becomes less mobile. Our lungs become rigid and harder to inflate, and the vital capacity decreases. This may lead to pneumonia.
You are taking care of a 75 y/o patient who just had a stroke and now has limited mobility. Which of the following complications of immobility should you monitor for when taking care of a 75 y/o post-stroke patient?
A. Unilateral upper extremity weakness
B. Non-blanchable redness on sacrum
C. Difficulty speaking
D. Unilateral facial droop
B. Non-blanchable redness on sacrum
Rationale:
-Unilateral upper extremity weakness, difficulty speaking, and unilateral facial droop are symptoms of the stroke itself.
-Complications of immobility may include pneumonia, muscle weakness, contractures, DVT, pressure injuries, etc. Non-blanchable redness on the sacrum is a stage 1 pressure injury, which is a complication of immobility.
Which abnormal abdominal finding is depicted in this photo?
A. Obesity
B. Ascites
C. Diastasis recti
D. Scaphoid contour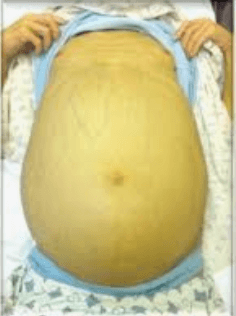
B. Ascites
Rationale:
-Ascites is a manifestation of liver disease, characterized by abdominal distention due to buildup of fluid. It may be accompanied by jaundice as seen in the picture.
-A scaphoid contour is concave (often seen when a patient is malnourished).
-Obesity would not cause jaundice, & subcutaneous fat would be noted in the chest as well.
Which of the following techniques should NOT be used when assessing the breast?
A. Inspecting the breasts while standing in front of a mirror
B. Palpating the breast with the palm of your hand
C. Gently squeezing the nipple
D. Using three finger pads to palpate with light, medium, & firm pressure
B. Palpating the breast with the palm of your hand
Rationale:
For both clinical breast exams and self breast-exams, the breasts should be inspected while standing in different positions, and the entire breast tissue (including the axillae) should be palpated using three finger pads, alternating between light, medium, and firm pressure. This will help identify any abnormal tissue, lumps, or masses. You will not be able to identify very many masses if you use the palm of your hand, so the palm should not be used. The nipple should be gently squeezed to assess for discharge.
Which organ is the red arrow pointing to?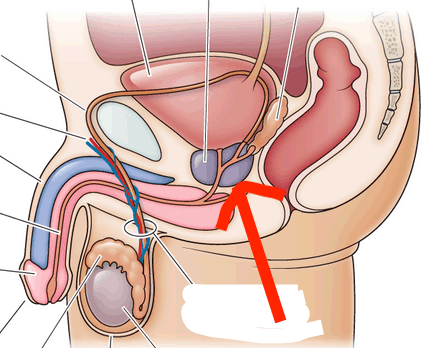
Prostate
Rationale:
The prostate is a walnut-shaped organ that wraps around the urethra in males. An enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hypertrophy/BPH) is a very common condition in older men and causes urinary symptoms such as urinary retention or nocturia (increased urinary frequency at night).
Dry mucous membranes, skin tenting, and cracked lips may be a sign of what condition?
A. Thrush
B. Dehydration
C. Anemia
D. These are normal findings
B. Dehydration
Older adults are at an increased risk for dehydration for several reasons. Signs of dehydration may include dry mucous membranes, skin tenting, and dry, cracked lips or skin overall. These are not normal findings. Thrush may cause white patches or irritation in the mouth or on the tongue. Anemia may cause pallor, fatigue, shortness of breath, and/or lightheadedness.
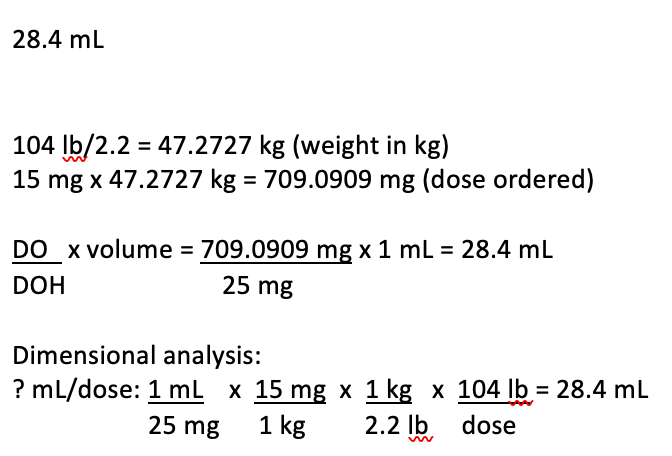
The health care provider orders levofloxacin 15 mg/kg IV once daily for a client who weighs 104 lbs. Levofloxacin is available in 25 mg/mL. How many mL's should the nurse administer per dose? Round the answer to the nearest tenth.
Which region is the uterus located?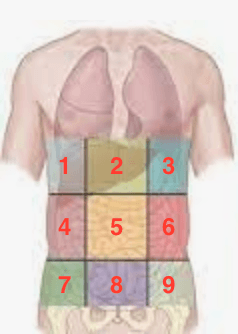
#8 (Hypogastric/Suprapubic)
The bladder is also found in this region.
Which of the following findings is abnormal? (Assume all are chronic unless stated otherwise)
A. Nipple elasticity
B. Asymmetrical breasts
C. Inverted nipples
D. Lump under areola
D. Lump under areola
Rationale:
Nipple elasticity, asymmetrical breasts, and inverted nipples are all normal findings as long as they are not NEW. A lump found anywhere in the breast or axilla is abnormal and concerning.
Costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness may indicate inflammation of which organ?
A. Kidney
B. Bladder
C. Liver
D. Prostate
A. Kidney
Rationale:
CVA tenderness is assessed by placing your non-dominant hand on the patient's back at the costovertebral angle and striking it with your dominant hand. This is indirect percussion directly over the kidneys, so pain or tenderness may indicate inflammation of the kidneys.
Which of the following is most accurate regarding osteoporosis?
A. Osteoporosis is a spinal deformity.
B. Osteoporosis occurs due to formation of new, weaker bones.
C. Osteoporosis is an increase in the bone matrix.
D. Osteoporosis occurs due to gradual bone density loss.
D. Osteoporosis occurs due to gradual bone density loss.
Rationale:
Osteoporosis occurs due to a gradual loss of bone density, and older adults are at increased risk for this. Loss of bone density in the vertebrae leads to loss of height, which is a normal age-related finding.
Osteoporosis is not a spinal deformity, but people with osteoporosis are more likely to have kyphosis (exaggerated curvature of the thoracic spine).
A client consumes the following during your shift: Breakfast: 4 oz orange juice, 3 oz water, 8 oz coffee
Mid-afternoon: 6 oz bone broth, 5 oz tea
Lunch: 2 oz cream, 8 oz soda
How many milliliters (mL) should you document for the client's total fluid intake during the shift?
1,080 mL
4 + 3 + 8 + 6 + 5 + 2 + 8 = 36 oz total
36 x 30 = 1,080 mL
Which of the following are normal findings? Select all that apply.
A. Umbilicus midline
B. Bowel sounds every 60 seconds
C. Rounded contour
D. Hemorrhoids
E. 30 bowel sounds per minute
A. Umbilicus midline
C. Rounded contour
E. 30 bowel sounds per minute
Rationale:
-The umbilicus should be midline with no masses, discoloration, or protrusions. 5-34 bowel sounds should be heard per minute, so bowel sounds that are heard every 60 seconds would be considered hypoactive.
-Normal contours include flat or rounded (scaphoid and protuberant/distended are abnormal).
-Hemorrhoids are not a normal finding.
Which of the following is true regarding post-mastectomy care? Select all that apply.
A. You cannot get breast cancer since you've had a mastectomy
B. Patients still need self-breast exams & clinical breast exams
C. When performing self-breast exams, you should start assessing the post-mastectomy side first
D. We cannot take blood pressures or insert IVs into the right arm if the patient had a right mastectomy
E. The chances of getting breast cancer are reduced after having a mastectomy
B. Patients still need self-breast exams & clinical breast exams
D. We cannot take blood pressures or insert IVs into the right arm if the patient had a right mastectomy
E. The chances of getting breast cancer are reduced after having a mastectomy
Rationale:
-The chances of getting breast cancer are significantly reduced after having a mastectomy, but it is still possible to develop breast cancer. Therefore, patients still need self-breast exams & clinical breast exams.
-We cannot take blood pressures or insert IVs into the arm of the same side as the mastectomy.
-When performing self-breast exams, the patient should start by assessing the unaffected side and then assess the post-mastectomy side.
Which of the following is true regarding testicular self-exams? Select all that apply.
A. They should be performed monthly
B. They should be performed after getting out of a cold shower
C. Testicles should be palpated for lumps using thumb & two fingers
D. They are only necessary if someone has a family history of testicular cancer
E. They should be performed while in a warm shower
A. They should be performed monthly
C. Testicles should be palpated for lumps using thumb & two fingers
E. They should be performed while in a warm shower
Rationale:
-Testicular self-exams should be performed monthly to assess for signs of testicular cancer, regardless of family history. Testicular cancer is common in adolescent men, and the most common sign of testicular cancer is a painless lump in one testicle.
-To perform a testicular self-exam, the thumb and two fingers should be used to palpate for lumps. This should be done in a warm shower.
Which of the following changes are expected in the older adult? Select all that apply.
A. Lungs become rigid and harder to inflate
B. Increased elastin production & subcutaneous fat
C. Wrinkles, liver spots, and thin, dry skin
D. Increased body temperature
E. Increased blood pressure
A. Lungs become rigid and harder to inflate
C. Wrinkles, liver spots, and thin, dry skin
E. Increased blood pressure
Rationale:
As we age, our reflexes (including cough reflex) and sensory functions (sight, hearing, smell, taste, touch) decrease.
All of our muscles become weaker, our organ function decreases, and digestion (peristalsis) slows because we produce less bodily fluids. Our appetite and thirst response decrease.
We lose subcutaneous fat, which decreases our body temperature because we have less insulation. We also produce less elastin, and our skin becomes thin, dry, and wrinkly. We may develop liver spots, which is a normal finding.
Our organs, valves, and vessels become rigid, and less flexible/compliant, which decreases their ability to expand & contract properly. As a result, our blood pressure increases and we are more predisposed to pneumonia.
You are assessing a patient who is having difficulty emptying their bladder. Which of the following should be assessed at this time to gather more data about the chief complaint? Select all that apply.
A. The patient's last bowel movement
B. Burning with urination (dysuria)
C. Frequency of urination
D. Allergies
E. Characteristics of urine
B. Burning with urination (dysuria)
C. Frequency of urination
E. Characteristics of urine
Rationale:
All of the following are relevant symptoms to assess except for last bowel movement and allergies. Although these may be assessed in the health history, they are not components of OLDCARTS so they do not need to be assessed at this time.