In a trauma situation this type of survey is done to identify & manage any life-threatening injuries.
What is a PRIMARY SURVEY?
Causes of this kidney disorder are severe drop in blood pressure, cardiovascular injury, infection, and kidney stones.
What is ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI)?
This atrial dysrhythmia is characterized by no discernable P wave and is irregular causing dizziness & difficulty breathing. Complications include a PE or stroke.
What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (A-Fib)?
This medical emergency presents with elevated T3 & T4 levels, tachycardia, fever and changes in LOC.
What is a THYROID STORM?
The earliest indication of respiratory deterioration for this disorder is decreasing vital capacity.
What is MYASTHENIA GRAVIS?
This type of shock is caused by bacterial toxins that lead to vasodilation.
What is SEPTIC SHOCK?
The assessments for this oncological emergency caused by a tumor(s) near the spinal cord include:
Assessing for back pain, weakness, numbness and tingling, unsteady gait, loss of ability to distinguish hot and cold, and constipation or incontinence.
What is SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION?
This phase of the disaster cycle includes disaster drills, evacuation plans, and fire drills.
What is PREPAREDNESS?
Clinical manifestations of this respiratory disorder include dyspnea, reduced lung compliance & SEVERE hypoxemia despite administration of 100% O2.
What is ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS)?
The client presents with one of the four cardiac arrest rhythms (pVT, VF, PEA or Asystole). After assessing the client this is done next.
What is BEGIN HIGH-QUALITY CPR?
This disorder is caused by the excessive release of ADH resulting in fluid retention, decreased UO & increased urine osmolality.
What is SYNDOME of INAPPROPRIATE SECRETION of ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE (SIADH)?
Evidence of a intracranial hemorrhage (on a CT scan), last known well time > 3 hours, & major surgery or other serious trauma in the preceding 14 days.
What are EXCLUSION CRITERIA for TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR (rt-PA) for an ischemic stroke?
This type of shock can be cause by a MI, severe valvular dysfunction and is characterized by decreased cardiac output, increased CVP, hypotension and tachycardia.
What is CARDIOGENIC SHOCK?
Clinical manifestations of this oncological emergency include: hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, tachypnea, heart block, elevated BUN, elevated creatinine and decreased urine output.
What is TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME (TLS)?
The management for this environmental injury includes cleaning the site with soap and water and keeping the affected extremity immobilized in a functional position BELOW the level of the heart.
What is a SNAKE BITE?
Causes of this respiratory complication include blunt or penetrating trauma, mechanical ventilation and medical procedures (i.e., central line placement).
What is a TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX?
This cardiac disorder is characterized by muffled heart sounds and may be caused by chest trauma, infections, and/or hemorrhage.
What is CARDIAC TAMPONADE?
This disorder is a complication of DMII characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperosmolality & dehydration. Treatment priorities include standard care for dehydration with IV fluids.
What is HYPEROSMOLAR HYPERGLYCEMIC STATE (HHS)?
What is the GLASCOW COMA SCALE?
The clinical manifestations of this complication include prolonged capillary refill, cyanosis of the fingertips and a petechial rash due to clots obstructing the small blood vessels.
What is DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION (DIC)?
This oncological emergency is found in cancers that metastasize to bone. Clinical manifestations include: delirium, somnolence, muscle weakness, polyuria, bradycardia, nausea, and constipation. Treatment includes Biphosphonates & hydration with normal saline.
What is HYPERCALCEMIA?
This is a complication of displaced fractures of the right hip, femur, tibia and fibula resulting in shortness of breath.
What is a DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) or a FAT EMBOLISM?
This complication of the liver requires administering lactulose to reduce ammonia levels, improve mental status and avoiding protein overload.
What is HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY?
This is a component of Stroke Volume (SV) that is measured through central venous pressure (CVP) and can be increased with a fluid bolus/resuscitation.
What is PRELOAD?
This disorder is a complication of DMI characterized by hypotension, tachycardia, hyperkalemia, Kussmaul respirations & ketone smelling breath. Treatment includes hydration, insulin & electrolyte replacement.
What is DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA)?
Clinical manifestations for this client are: anorexia (early), delirium (middle/late), dyspnea (late), increased secretions (late), Cheyne-Stokes breathing (late), respirations sound loud & wet (late), and the client will lose the ability to swallow (late).
What is a DYING CLIENT?
The PRIORITY assessments/interventions for this integumentary disorder include TBSA, depth, location, presence of other injuries, involvement of the respiratory system and fluid resuscitation.
What is a BURN INJURY?
This oncological emergency is found in tumors of the chest, lung cancer and lymphoma. Clinical manifestations include: dyspnea, visual disturbances, headache, altered mental status, prominent jugular veins, brachial veins, and chest vessels.
What is SUPERIOR VENA CAVA (SVC) SYNDROME?
This designation in the SALT Disaster Triage model is characterized by a client who follows commands, has stable vital signs, has a significant injury and CANNOT walk.
What is a YELLOW (DELAYED) designation?
The client's ABGs are: pH of 7.25, PaCO2 of 30 mm Hg, HCO3- of 20.
What is PARTIALLY COMPENSATED METABOLIC ACIDOSIS?
The assessments/interventions for this rhythm are vital signs, oxygen, nitro, aspirin, morphine and a trip to the Cath Lab.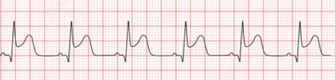
What is a ST ELEVATED MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (STEMI)?
Complications of this posterior pituitary disorder are hypovolemia and hypernatremia resulting in confusion, neuromuscular excitability, seizures, or coma.
What is DIABETES INSIPIDUS (DI)?
This type of care is after death and includes retaining catheters & tubes in the body, answering the family's questions, allowing the family to spend time and/or pray with the client, and applying ID tags according to policy.
What is POSTMORTEM care?
This complication of septic shock affects the respiratory system (ARDS), renal system (increased BUN & Creatinine) and the hepatic systems (increased LFTs).
What is MULTIPLE ORGAN DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME (MODS)?
This oncological emergency is found in client's with acute myelocytic leukemia (AML) with high WBC count. Management includes IV fluids to reduce blood viscosity.
What is LEUKOSTASIS?