Your patient went for a femoral cath, you are watching for these complications (at least three).
What are hematoma, pseudoaneurism, limb ischemia, retroperitoneal bleed, infection, sepsis?

Appropriate actions
What is Ventricular-Fibrillation or V-Fib?
Beta blockers are the 1st line agent in the treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome, name at least two benefits it offers these patients.
What are reduces infarct size, decreases rate of complications, reduces rate of re-infarction, decreases rate of life threatening dysrhythmias, and reduce early and late mortality rate in acute MI?
Your patient is taking warfarin sodium, (a) lab values that should be checked and (b) a therapeutic range for this patient.
(a) What is International Normalized Ratio (INR) and (b) 2.0-3.0.
Medical term for generalized edema.
What is anasarca?
(a) Category for Enalapril, captopril, and ramipril.
(b) Common side of effect.
What are ACE (Angiotensin I converting enzyme) inhibitors? What is a dry cough?

Appropriate actions
What is atrial fibrillation? What is correct the heart rate?
The change on ECG alerts me to the fact that my patient is having a STEMI
What is ST elevation in at least two contiguous leads?
Thrombocytopenia meaning.
What is low platelets?
Name Heart Failure (HF) Nursing Diagnosis (at least three).
fluid volume excess
decreased cardiac output
impaired gas exchange
altered tissue perfusion
potential for alteration in skin integrity
fear/knowledge deficit
fatigue
Because of it's vaso/veno dilation and resultant preload reduction, nitroglycerin (NTG) is commonly used in combination with other drugs, to treat an exacerbation of this condition.
What is heart failure or HF?
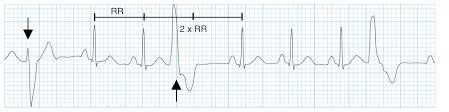
What is a premature ventricular contraction or PVC?
Statins are often prescribed to lower serum cholesterol. They are prescribed for Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) for the following three additional reasons:
What are enhances plaque stability in arteries and reduces progression of atherosclerosis, has anti-inflammatory effects, and reduces platelet aggregation?
Blood test to determine acute myocardial infarction.
What is troponin?
Goals of Heart Failure Management (at least three)
What are:
1. Promote rest to decrease workload of heart
2. Increase force of efficiency of cardiac contractions
3. Eliminate edema & congestion
4. Assess hemodynamic status?
Early signs of toxicity with this drug are: anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. Other signs include: dysrhythmias, bradycardia, tachycardia, PVCs, PAT, blurred vision, double vision, yellow vision, green halos around objects.
What is digitalis?

What is ventricular tachycardia or V-Tach?
Categories of medication options for atrial fibrillation or A-Fib. Give an example of a drug in each category.
What are beta blockers (lol), (atenolol [Tenormin], labetalol [Trandate], metoprolol [Lopressor], propranolol [Inderal]
What are calcium channel blocker (amlodipine [Norvasc], nifedipine [Procardia], dilitiazem [Cardizem], verapamil)
What are sodium channel blockers (flecainide [Tambocor], propafenone [Rythmol], quinidine)
What are potassium channel blockers (amiodarone [Cordarone or Pacerone], sotalol [Betapace], dofetilide)
Hold this medication if heart rate (HR) is less than 60.
What is a beta-blocker?
Nursing interventions for Cardiac Failure (CF) (at least five)
• encourage rest (organize care to ↓02 demand)
• positioning high Fowler's (legs dependent decrease venous return to the heart to decrease preload, pulmonary congestion)
• 02
• STRICT I & O
• daily weights
• promote tissue perfusion (position changes, TEDS, deep breathing & leg exercises)
• pharmacological management (diuretics, vasodilator, digitalis)
(a) A patient with Atrial fibrillation is admitted to begin treatment with a heparin Infusion the HCP orders Heparin 18 units /kg/hr. prior to an elective Cardioversion. The patient’s weight =58 kgs. Available Heparin 25,000 units in 500 ml D5W. If a bolus of Heparin 3500 units is ordered and there is Heparin 5000units/ml available how much will the RN draw up to administer IVP?
(b) HCP orders infusion of Heparin 18 units/kg/hr. The Heparin preparation is 25,000 units in 500 ml. The RN will set the IV infusion pump at _____________ml/hr
(a) Desired: 3500 units = X/mls Have: 5000 units = 1 ml. 3500/5000 (units cancel out) = 0.7 ml.
(b) Desired: 18 units/kg/hr 18 units X 58 kg = 1044 units/hr
Have 25,000 units/500 mls. = 1044 units/hr /X (ml/hr)
Cross multiply: 25,000 (X ml/hr)=522,000
X ml/hr=675,000/25,000
X = 20.88 or 21 ml/hr
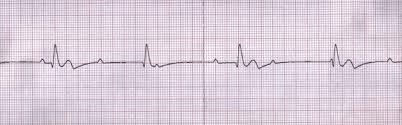
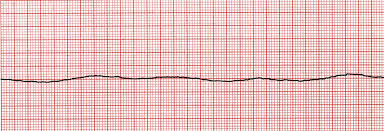
(a) Identify both strips. (b) Identify necessary actions. (c) Identify potential causes.
(a) What is pulseless electrical activity or PEA (#1) and what is asystole?
(b) What is start CPR?
(c) What are the H's & T's?
H: hypoglycemia, hypothermia, hypovolemia, hypoxia, hyper/hypokalemia, hydrogen ion (acidosis);
T: toxins, tamponade, tension pneumothorax, thrombosis, trauma
An electrode catheter is inserted into a vein and guided to the diseased area of the heart. Radio-frequency energy or freezing temperature is applied to the abnormal area of heart tissue. This interrupts the path of the abnormal electrical impulse thus curing the arrhythmia - one of the major causes of sudden cardiac death..
What is a cardiac ablation?
(a) Your patient suddenly appears restless, cold, clammy, grey, cyanotic nailbeds, weak pulse and thready, neck veins distended, and tachypneic. May become breathless. List the diagnostics.
(b) You call Rapid Response Team and they suspect acute pulmonary edema (APE). List probable treatments (at least three).
(a) vitals, ABG, ECG, CXR, cardiac enzymes, electrolytes or BMP (basil metabolic profile), CBC, creatinine
(b) Medications: Dopamine/dobutamine (to increase CO without increasing cardiac oxygen demands).
Morphine IVP in small doses to decrease peripheral resistance
Diuretics: IV Lasix Digoxin.
Aminophylline.
Vasodilators: NTG
Treatments: Oxygen, high Fowler's position, strict I&O, arterial line, emotional support
(a) A diabetes drug that has been approved to reduce risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization in adults with heart failure even if they are not diabetic. Reduces sodium re-absorption, which results in decreased preload and after-load.
(b) Nursing interventions for patients on this medication.
(c) List of potential adverse effects.
(a) What is empagliflozin (Jardiance)?
(b) What is monitoring for dehydration before and after administration?
(c) What are UTI, urosepsis, pyelonephritis, ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia?