This lab value rises when you have acute renal failure.
What is creatinine?
A post-operative patient is experiencing nausea and vomiting (PONV). Which of the following antiemetics would the provider likely choose as the first choice for treatment?
A. Ondansetron (Zofran)
B. Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
C. Promethazine (Phenergan)
D. Scopolamine
Answer: A. Ondansetron
Rationale: While Promethazine (Phenergan) and compazine can be effective for treating PONV, it is often not the first choice due to its higher incidence of extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) including tremors, rigidity, dystonia, and drowsiness. Ondansetron, is generally preferred for its lower risk of EPS and its effectiveness in treating PONV as well as no risk of respiratory depression. Scopolamine is not a first choice.
A patient underwent a laparoscopic cholecystectomy 24 hours ago. The patient is now complaining of severe left shoulder pain. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's pain?
A. Atelectasis from not doing IS
B. Soft tissue injury from the operation
C. Referred pain from insufflation of gas during the surgery.
D. Surgical site infection
Answer: C. Referred pain from the surgical site
Rationale: Shoulder pain is a common complication after laparoscopic surgery, especially abdominal surgery. This is due to the carbon dioxide gas that is used to inflate the abdomen during the procedure. The gas can irritate the diaphragm and nerves in the shoulder, causing pain. To have the pain controlled, getting the patient up and moving will work to disperse and eradicate the gas. Pain medication often will not help the pain as much as walking will. Atelectasis would cause lung pain with inspiration. In normal circumstances, soft tissue injury is not a routine complication from gallbladder surgery. It would be too early to have surgical site infection.
A circulating nurse is assisting with a surgical procedure. Which of the following tasks would be appropriate for the circulating nurse to perform?
A. Assisting the surgeon with suturing the surgical incision
B. Passing sterile instruments to the surgeon
C. Monitoring the patient's vital signs and fluid status
D. Scrubbing in to assist with the surgery
Answer: C. Monitoring the patient's vital signs and fluid status
Rationale: The circulating nurse is responsible for tasks outside of the sterile field. This includes monitoring the patient's vital signs, fluid status, and overall well-being during the surgery. Assisting with suturing and passing sterile instruments are tasks typically performed by the scrub nurse, who remains within the sterile field.
A patient is undergoing a surgical procedure and suddenly develops a rapid heart rate, muscle rigidity, and a high temperature. Which of the following medications would be most appropriate to administer?
A. Dantrolene sodium
B. Succinylcholine
C. Furosemide
D. Morphine
A. Dantrolene sodium because malignant hyperthermia is suspected.
This lab is the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood.
What is hematocrit?
A registered nurse (RN) is caring for a patient who has been stable post-operatively. Which of the following tasks would be appropriate to delegate to an unlicensed nursing assistant (CNA)?
A. Change a sterile dressing
B. Assessing the output from a JP drain
C. Collecting a urine sample
D. Insert an IV
Answer: c. This is within the scope of practice for the CNA.
Rationale: The other tasks listed include assessment skills which require further education above the scope of practice for a CNA.
A patient is postoperative from abdominal surgery and has an incentive spirometer (IS) ordered. Which of the following are appropriate indications for using an IS? (Select all that apply.)
A. To prevent atelectasis
B. To improve lung expansion
C. To monitor oxygen saturation
D. To manage pain
E. To prevent pneumonia
Answer: A, B, E
Rationale:
C. To monitor oxygen saturation: IS is not used to monitor oxygen saturation only improve aeration of the lungs. O2 saturation is measured with a pulse oximeter.
D. To manage pain: While deep breathing relax the patient and indirectly contribute to pain management, IS is not specifically used for this purpose.
A nurse is preparing to enter the restricted zone of the operating room and chooses the following surgical attire. Which of the following would indicate that further education is needed?
- A. Scrubs
- B. Surgical cap
- C. Surgical mask
- D. Street shoes
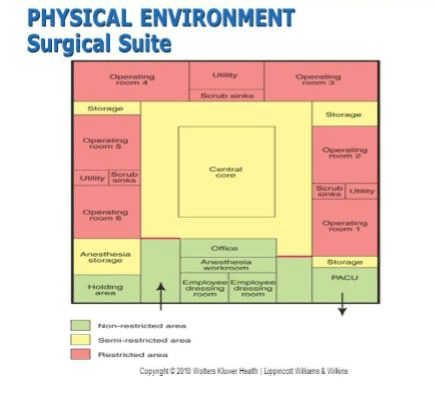
Answer: D. Street shoes
Rationale: Street shoes are not allowed in the restricted zone of the operating room due to the risk of introducing microorganisms. Proper surgical attire in the restricted zone typically includes a scrub suit, surgical cap, and surgical mask.

A patient is undergoing a surgical procedure and has been administered benzodiazepines for sedation. After the procedure, the patient is having difficulty waking up and is still heavily sedated. Which of the following medications would be most appropriate to administer?
A. Flumazenil
B. Naloxone
C. Atropine
D. Neostigmine
Answer: A. Flumazenil
Rationale: Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist used to reverse the effects of benzodiazepines. In this scenario, the patient is experiencing prolonged sedation due to the benzodiazepines. Administering flumazenil can help to reverse this sedation and allow the patient to wake up.
A nurse is caring for a patient who was admitted to the hospital 24 hours ago for severe dehydration. The patient's current vital signs are: BP 100/60 mmHg, HR 120 beats/min, RR 20 breaths/min, and T 98.6°F. The patient's laboratory results show a BUN of 40 mg/dL, creatinine of 2.5 mg/dL, and potassium of 5.2 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's elevated creatinine level?
A. Chronic kidney disease
B. Acute kidney injury
C. Heart failure
D. Liver disease
Answer: B. Acute kidney injury?
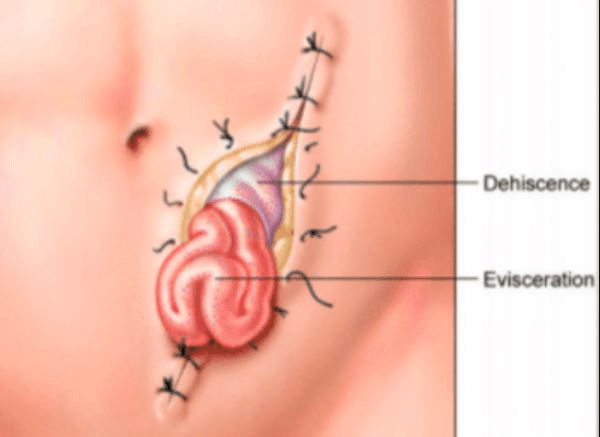
Tom is 2 days post operative from open hernia repair. He reports coughing hard and feeling a "tearing/ripping" sensation at the incision site. Upon assessment, you see that the incision site is separated and a portion of small bowel is protruding from the site. What is this called and what is the first thing that the nurse does before calling the physician?
Answer: What is eviseration. Cover the bowel with sterile moistened gauze.
Rationale: Dehiscence is the separation of the incision site and evisceration is the protrusion of the small bowel from the site. Both are surgical emergencies! Moistened gauze will help to protect the exposed organs from further fluid loss and loss of heat leading to hypothermia.
Additionally, the gauze will provide a protective barrier to reduce risk of bacterial contamination and infection.
A patient is undergoing a surgical procedure and suddenly develops a rapid heart rate, muscle rigidity, and a high temperature. The patient's vital signs are: BP 80/50 mmHg, HR 150 beats/min, RR 30 breaths/min, and T 104°F. The nurse suspects malignant hyperthermia. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of malignant hyperthermia? (Select all that apply.)
A. Tachycardia
B. Hyperoxia
C. Muscle rigidity
D. Hyperthermia
E. Decreased urine output
F. Bradypnea and Decreased carbon dioxide production
Answer: A, C, D, E
Rationale:
- A. Tachycardia: A rapid heart rate is a common symptom of malignant hyperthermia.
- C. Muscle rigidity: Muscle rigidity, particularly in the jaw and chest, is a hallmark sign of malignant hyperthermia.
- D. Hyperthermia: A rapid rise in body temperature is a key characteristic of malignant hyperthermia but is a later sign.
- E. Oliguria: Decreased urine output (oliguria) can occur due to the increased metabolic demands of malignant hyperthermia.
- B. Hyperoxia:Hypoxia is often seen in MH due to increased oxygen consumption due to increased metabolic rate not elevated o2 sats.
- F. Decreased carbon dioxide production: Increased carbon dioxide production and tachypnea, not decreased, are typically seen in malignant hyperthermia due to the increased metabolism, especially in the muscles due to the rigidity.
A nurse is observing a surgeon during a surgical procedure. Which of the following actions by the surgeon would indicate a break in sterile technique?
- A. Reaching across the sterile field to retrieve a sterile instrument.
- B. Keeping the sterile field within sight and reach.
- C. Maintaining a sterile distance of at least 12 inches from the sterile field.
- D. Wearing sterile gloves and gown while performing the procedure.
Answer A. Reaching across the sterile field to retrieve a sterile instrument.
A patient underwent a 5-hour abdominal surgery and received general anesthesia and postoperative opioids. The patient is now in the recovery room and has the following vital signs: BP 90/60 mmHg, HR 50 beats/min, RR 4 breaths/min, and T 98.6°F. The patient is unresponsive to verbal and tactile stimuli. Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement? (Select all that apply.)
A. Administer naloxone
B. Administer Flumazenil
C. Assess the patient's oxygen saturation
D. Notify the provider immediately
Answer: A, C, D
Rationale:
- A. Administer naloxone: The patient's vital signs and unresponsiveness are consistent with opioid overdose. Naloxone can reverse the effects of the opioid.
- B. Administer Flumazenil: This is given for benzo overdose.
- C. Assess the patient's oxygen saturation: Opioid overdose can lead to respiratory depression, so it is important to monitor the patient's oxygen saturation.
- D. Notify the provider immediately: Opioid overdose is a medical emergency, and it is crucial to notify the provider immediately.
A nurse is caring for a patient who has been on a diuretic for heart failure for the past week. The patient's current vital signs are: BP 100/60 mmHg, HR 110 beats/min, RR 18 breaths/min, and T 98.6°F. Patient has had urine output of 1200 ml in the past 24 hours. The patient's laboratory results show a BUN of 24 mg/dL, creatinine of 1.2 mg/dL, and potassium of 3.0 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing action?
A. Call the physician to get a potassium supplement.
B. Increase the dosage of the diuretic to remove more fluid.
C. Give a thiazide diuretic as it is potassium sparing.
D. Restrict the patient's fluid intake.
Answer: What is A.
Rationale: Notify the physician of the low potassium level in hopes for potassium supplement order. Labs are showing dehydration so diuretic would not be increased as this would worsen dehydration. Thiazide diuretics are not potassium sparing. Restricting fluid intake would worsen renal function.
A patient who underwent an abdominal surgery 8 hours ago is experiencing new-onset hypotension, tachycardia, shortness of breath, dizziness, and nausea. The patient's vital signs are: BP 90/60 mmHg, HR 120 beats/min, RR 14 breaths/min, and T 99.1°F, O2 sats 95% on RA. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's symptoms?
A. Dehydration from nausea
B. Pulmonary embolism
C. Postoperative hemorrhage
D. Infection
Answer: c. Post operative hemorrhage
Rationale: The fact that the patient is hypotensive, tachycardic and dizzy indicates a sudden loss of blood volume suggestive of post operative hemorrhage. The nurse should assess the surgical site immediately before calling the physician with these vital signs to see if there is any increased blood on the dressing. Dehydration could be caused if patient was vomiting, but not usually just from nausea and not present at 8 hours post op. Pulmonary emboli would likely cause tachypnea and lower o2 sat. It would be too early for infection in most cases and temp is not indicative of an infectious process.
A patient is undergoing a surgical procedure and suddenly develops a rapid heart rate, muscle rigidity, and a high temperature. The patient's vital signs are: BP 80/50 mmHg, HR 150 beats/min, RR 30 breaths/min, and T 104°F. The nurse suspects malignant hyperthermia.
Given the patient's presentation, what nursing interventions should be implemented? (Select all that apply)
A. Administer dantrolene sodium
B. Apply ice packs to the patient
C. Decrease the rate of intravenous fluids
D. Monitor the patient's urine output
E. Notify the surgeon immediately
A, B, D, E
- A. Administer dantrolene sodium: Dantrolene sodium is the specific treatment for malignant hyperthermia and helps to relax the muscles and reduce heat production.
- B. Apply ice packs to the patient: Cooling measures, such as applying ice packs, can help to reduce the patient's temperature.
- D. Monitor the patient's urine output: Decreased urine output (oliguria) can be a sign of rhabdomyolysis, a complication of malignant hyperthermia. Monitoring urine output is important to assess kidney function.
- E. Notify the surgeon immediately: Malignant hyperthermia is a medical emergency, and it is crucial to notify the surgeon immediately so that additional interventions can be initiated.
- C. Decrease the rate of intravenous fluids: The patient will likely need increased fluids to help maintain blood pressure and address the metabolic demands of malignant hyperthermia.
A patient is scheduled for a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. During the preoperative assessment, the nurse notes that the patient has a history of hypertension. Which of the following interventions would be most appropriate to implement during the intraoperative period?
A. Administer a beta-blocker.
B. Monitor the patient's blood pressure closely.
C. Restrict the patient's fluid intake.
D. Position the patient in a Trendelenburg position.
Answer: B. Monitor the patient's blood pressure closely.
Rationale: Patients with a history of hypertension are at increased risk for developing intraoperative hypertension. Therefore, it is important to monitor the patient's blood pressure closely during the procedure and be prepared to intervene if necessary. Administering a beta-blocker may be appropriate in some cases, but it would depend on the patient's individual medical history, current blood pressure and the surgeon's orders. Restricting fluid intake and positioning the patient in a Trendelenburg position are not appropriate interventions for managing hypertension during surgery.
A patient is recovering in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) after undergoing a surgical procedure. The patient received isoflurane as the anesthetic agent. The patient's current vital signs are: BP 120/80 mmHg, HR 80 beats/min, RR 10 breaths/min, and T 98.6°F. The patient's oxygen saturation is 88% on supplemental oxygen. Which of the following priority interventions should the nurse implement?
A. Increase the rate of supplemental oxygen
B. Administer a bronchodilator
C. Position the patient in a Trendelenburg position
Answer: A. Increase the rate of supplemental oxygen
Rationale: The patient's low oxygen saturation level indicates hypoxia. Increasing the rate of supplemental oxygen can help to improve the patient's oxygenation.
The other options are not appropriate. A bronchodilator is used to treat bronchoconstriction, which is not likely the cause of the patient's hypoxia in this case. Positioning the patient in a Trendelenburg position would not improve oxygenation.
A patient is scheduled for an elective abdominal surgery. The patient's pre-operative laboratory results are as follows:
WBC: 11,000 cells/μL
Hemoglobin: 12.6 g/dL
Hematocrit: 36%
Platelets: 200,000 cells/μL
BUN: 15 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.2 mg/dL
Glucose: 290 mg/dL
Electrolytes: within normal limits
Given the patient's labs, what is the most concerning in regard to potential post operative complications.
Answer: What is glucose level of 290
Rationale: Elevated glucose levels have the potential to cause delays in wound healing, decreased tissue perfusion and decreased collagen synthesis which can cause wound integrity issues such as delayed wound healing and dehiscence.
The other labs are WNL
A patient who underwent an appendectomy 6 hours ago is experiencing a blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg and a heart rate of 94 beats/min. The patient's rhythm is regular. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's elevated vital signs?
A. Dehydration
B. Infection
C. Pulmonary embolism
D. Pain
Answer: D. Pain
Rationale: Postoperative pain can lead to increased sympathetic nervous system activity, resulting in elevated blood pressure and heart rate. Given the patient's recent surgery and the absence of other clear indications for a rise in vital signs, pain is the most likely cause. Many times they receive a medication like isoflurane that has anesthetic but not analgesic qualities so pain needs to be addressed.
A patient immediately begins to complain of feeling lightheaded and having difficulty breathing with audible wheezing. The patient's vital signs are: BP 80/50 mmHg, HR 120 beats/min, RR 30 breaths/min, and T 98.6°F. Which of the following are priority nursing interventions? (Select all that apply)
A. Administer ordered epinephrine IV Bolus
B. Administer ordered hydrocortisone and diphenhydramine
C. Administer ordered oxygen and give albuterol
D. Notify the provider immediately
Answer: A, B, C, D
Bronchospasm is one of the most common signs in anaphylaxis, along with hypotension, desaturation, angioedema and cardiovascular collapse. Therefore, you would want to maintain patient airway and provide supplemental oxygen. Anticipated treatment includes epinephrine, 100% oxygen and possible intubation if needed, hydrocortisone or methylprednisolone, diphenhydramine, albuterol. Cardiac arrest can occur if not treated immediately!
A patient is scheduled for an elective surgery at 1 PM. The nurse discovers that the patient has eaten a light breakfast at 9:00 AM. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
A. Inform the surgeon.
B. Document the patient's reported intake and continue with the preoperative preparations as planned.
C. Administer a laxative to empty the patient's bowels.
D. Delay the surgery until the patient is NPO for at least 4 hours.
Answer: A. Inform the surgeon immediately and await further instructions.
Rationale: Eating before surgery can increase the risk of aspiration during anesthesia. The nurse should inform the surgeon immediately so that the appropriate course of action can be determined, which may involve delaying the surgery or adjusting the anesthesia plan.
The nurse is preparing for a patient who is returning from the OR to the PACU post laparoscopic appendectomy. The circulating nurse reported that the patient was under general anesthesia with desflurane and denied complaint for her. What might the PACU nurse anticipate that the patient will need early in the recovery period given the above information?
a. Antiemetic medications
b. Wound care consultation
c. Turing the patient every 2 hours
d. Analgesic medication
Answer: A, D
A- Antiemetic medications- nausea and vomiting are common side effects of general anesthesia. Giving an anti emetic early may help the patient avoid post operative nausea and vomiting.
D- Analgesia Medication (Correct)- Dantrolene provides anesthesia but not analgesia so pain medication is anticipated need for the patient upon awakening.
B- Wound care consultation is not indicated for a patient with laparoscopic appendectomy.
C- Patient should be able to turn independently after a noncomplicated appendectomy.