This term describes the act of washing hands before and after patient contact.
What is hand hygiene?
This common non-invasive procedure measures the oxygen saturation of a patient's blood.
What is pulse oximetry?
This common childhood vaccination is given to protect against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
What is the DTaP vaccine?
This term refers to the first milk, rich in antibodies, produced after giving birth.
What is colostrum?
This class of drugs, including medications like lisinopril, is commonly used to treat hypertension.
What are ACE inhibitors?
It's the position used for patients during most physical examinations.
What is the supine position?
Administered to prevent blood clots, this medication is often given subcutaneously in the abdominal area.
What is heparin?
This developmental milestone is typically achieved by a child at around 12 months of age.
What is taking first steps or walking?
The APGAR score is assessed at 1 minute and 5 minutes post-birth to evaluate these five criteria.
What are 1) Appearance, 2) Pulse, 3) Grimace, 4) Activity, and 5) Respiration?
This 'rescue' medication is commonly used to treat acute asthma attacks.
What is albuterol?
This level of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs includes food, water, warmth, and rest.
What are physiological needs?

This condition, often a complication of long-term diabetes, involves nerve damage causing numbness and pain.
What is diabetic neuropathy?
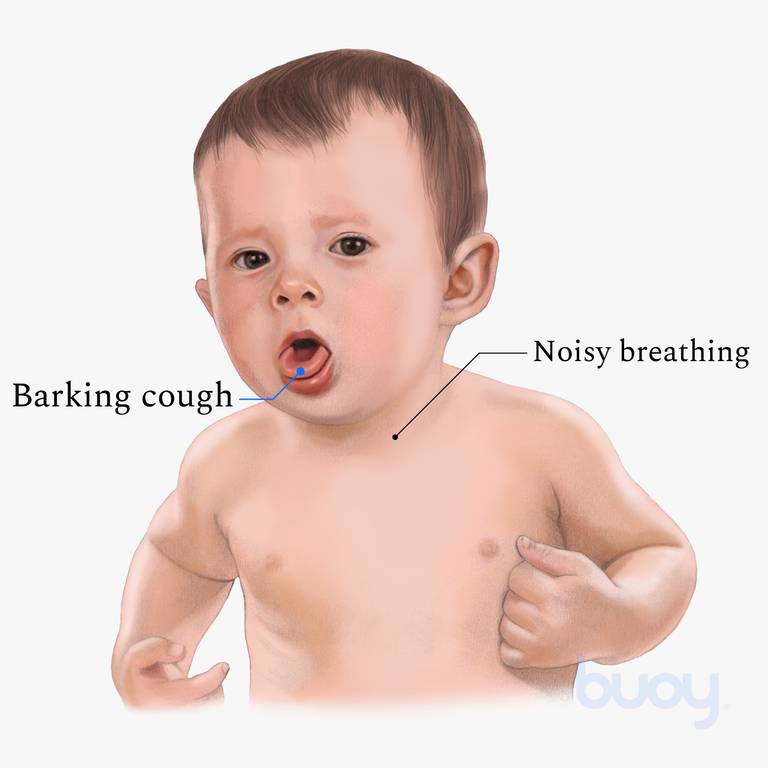
This condition is characterized by barking cough and stridor, often worse at night.
What is croup?
This condition, characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, can occur during pregnancy.
What is preeclampsia?
This anticoagulant drug requires regular blood testing to monitor the INR level.
What is warfarin?
This documentation method focuses on the patient's status from admission through discharge.
What is the SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan) method?
Known as 'silent killer,' this condition presents with no symptoms but can lead to heart attack or stroke.
What is hypertension?
A common genetic disorder, it causes intellectual disability and a characteristic facial appearance, more common in boys.
What is Down syndrome?
This type of delivery involves a surgical incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus.
What is a cesarean section?
This category of medications is used to manage bipolar disorder and includes drugs like lithium.
What are mood stabilizers?

Known as the first nurse researcher, her environmental theory emphasized the importance of patient nutrition and hygiene.
Who is Florence Nightingale?
This term refers to a high-output renal condition, often seen in acute kidney injury, where urine output exceeds 3 liters per day.
What is polyuria?
This severe, chronic respiratory disease in children is characterized by recurrent attacks of breathlessness and wheezing.
What is asthma?
This rare, serious condition occurs when fetal blood cells enter the mother's circulation, leading to sensitization and potential complications in future pregnancies.
What is Rh incompatibility or Rh disease?
This widely used anticoagulant medication, derived from salicylates, can cause Reye's syndrome in children and young adults, especially after viral infections.
What is aspirin?