What is the normal range for potassium?
3.5-5 mEq/L

NG Tube
What angle should you insert an intramuscular injection?
90 degrees
What is the first drug of choice for most people with type 2 diabetes?
Metformin
0.9% NaCl
Isotonic
What is the normal range of sodium?
135-145 mEq/L

Jackson Pratt
What is the correct injection site for heparin?
The abdomen ONLY
The following are signs and symptoms of what acute complication?
- Fruity breath
-Kussmaul respirations
- Thirsty/dehydration
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
5% NaCl
Hypertonic
What is the normal range for calcium?
8.6-10.2 mEq/L
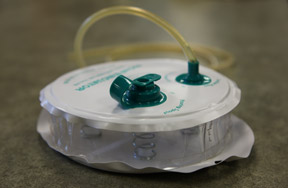
Hemovac
What is the correct needle gauge for a subcutaneous injection?
25-27G
Below what level is a patient considered hypoglyecemic?
Below 70 mg/dL
What fluid would you give to a burn patient?
LR
What is the normal range for magnesium?
1.5-2.5 mEq/L
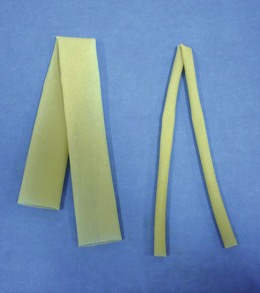
Penrose Drain
What is the correct needle length for subcutaneous injections?
3/8 - 5/8 inch
What test provides a measurement of glycemic control over the period of 2-3 months?
A1C
What nursing indications should you be aware of when administering hypertonic solutions?
- Can cause fluid overload (hypervolemia)
- Can cause pulmonary edema
-Give small amounts and SLOWLY. Diligent monitoring
What is the normal range for phosphorous?
2.4-4.4 mEq/L

Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)
What is the maximum dosage you can inject with a single IM injection?
5 mL (rotate sites if more than that)
Describe the Somogyi Effect
A high dose of insulin produces a decline in blood glucose levels during the night, so the patient becomes hypoglycemic.
What kind of solutions should you NEVER give to patients with increased intracranial pressure, cerebral edema, liver disease, trauma, or burns?
Hypotonic solutions