L.P., EEG, CT Scan, MRI
What are neurological diagnostic procedures
Fractures occurring at the growth plate, rapidity healing related to age, periosteum thicker than adults
What are the characteristics of children's bones
DELAYED GROSS MOTOR DEVELOPMENT
ABNORMAL MOTOR PERFORMANCE
ALTERATIONS IN MUSCLE TONE
REFLEX ABNORMALITIES
What are the clinical signs of cerebral palsy
Check the pulse for one full minute and hold if a child's HR is less than 90 or an adult is less than 60
What is digoxin?
1 Week old neonate on ventilator
ABG: PH 7.32, PCO2 68, PO2 82, HCO3 21
What is respiratory acidosis?
The period after a seizure
What is the post-ictal phase.
Most common intervention for anxiety-driven respiratory alkalosis
What is breath into a paper bag?
Name a leukotriene modifier
What is zafirlukast, montelukast
The reason why children under the age of 1 should never be given honey
What is infantile botulism?
Tense Bulging Fontanel, High pitched cry, Setting-Sun sign, irritability
What are the signs of increased intracranial pressure in infants (most often with hydrocephalus)
Hixtory of major trauma or surgery, prolonged immobilization, sudden development of chest pain/dyspnea
What are the signs of a pulmonary embolism
Spina bifida occulta
Meningocele
Myelomeningocele
What are neural tube defects?
#1 antibiotic for group B Strep.
What is PCN/Amoxil
Medication given to close a PDA
What is indomethacin
Abnormalities of the myocardium that interfere with its ability to contract effectively. Can lead to heart failure.
What is cardiomyopathy
Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system and inadequate compensatory response by the parasympathetic nervous system most commonly associated with lesions at T6 and above
What is Autonomic dysreflexia?
A nurse is planning care for a child who has asthma.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse
include in the plan of care? (Select all that apply.)
A. Perform chest percussion.
B. Place the child in an upright position.
C. Monitor oxygen saturation.
D. Administer bronchodilators.
E. Administer dornase alfa daily.
What is B, C, D?
What age of children should display Industry vs Inferiority?
What is school-age children or 6-12 yrs
Headache, diplopia, blurred vision, forceful vomiting
What are the signs of increased intracranial pressure in children
Chest Pain, Dyspnea, Pain and Swelling in the Lower Extremity
What are the signs of deep vein thrombosis
Group of permanent disorders of the development of movement and posture, causing activity limitations
What is cerebral palsy
#1 asthma rescue drug
What is albuterol?
This can result in permanent damage including dystonia and athetosis, upward gaze, hearing loss, and cognitive impairments. Bilirubin in excess of 25mg/dL
What is acute bilirubin encephalopathy?
A high cortisol level indicates that a client may be suffering from what chronic disease?
What is Cushing's disease?
This assessment finding consists of an involuntary rhythmic side-to-side, up and down, or circular motion of the eyes
What is nystagmus?
A nurse is caring for a client who is taking propylthiouracil. Which of the following findings should the nurse monitor for as an adverse effect of this medication?
A. Bradycardia
B. Insomnia
C. Heat intolerance
D. Weight loss
What is Bradycardia?
Flexion of the extremities occurring with deliberate flexion of the child's neck
What is Bredzinski's sign?
Sudden fixed and dilated pupils after a fall
What is a neurosurgical emergency
Most common sports injury, damage to the soft tissue, edema and pain, ruptured blood vessels
What is a contusion
Lack of bowel control, flaccid paralysis, varying degrees of sensory deficits including heat or cold
What are the clinical manifestations of spina bifida?
#1 treatment for persistent diaper rash, oral thrush, Candida albicans
What is nystatin?
Cyanotic heart defect characterized by a ventricular septal defect, the aorta positioned over the ventricular septal defect, stenosis of the pulmonary valve, and hypertrophy of the right ventricle
What is Tetralogy of Fallot
Systolic murmur at the apex, S3 sounds, Fatigue and weakness, Atrial fibrillation, Dyspnea on exertion, Orthopnea, Atypical chest pain, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
What are the S/S of mitral valve insufficiency?
Severe dysfunction at the level of the midbrain. Demonstrates a backward arching of the legs and arms, flexed wrists and fingers, extended neck, clenched jaw, and possibly an arched back.
What is Extension posturing?
Known to form crystalline aggregates in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, causing irritation and obstruction that causes acute kidney injury if fluid intake is inhibited.
What is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Most common form of leukemia in children
What is acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL)
When should the Moro Reflex resolve?
What is by 6 months?
What does this image portray (answer in order)
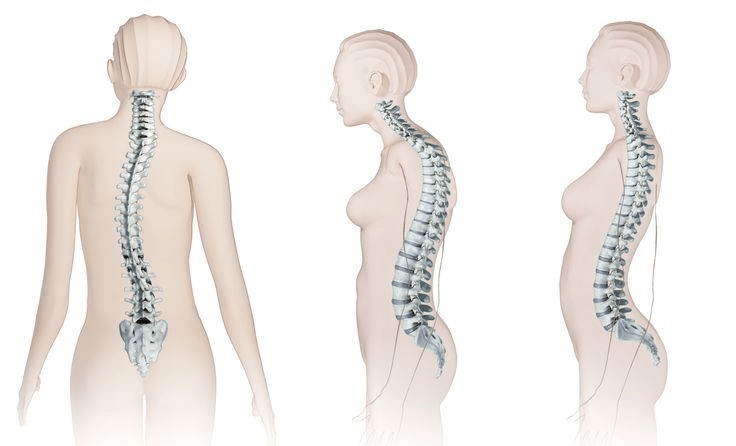
What is Scoliosis, kyphosis and lordosis
Speech problems
Difficulty eating
Difficulty swallowing
Potential for liquids to come out the nose
What are the clinical symptoms of cleft palate?
Drug used to help diagnose myasthenia gravis
What is tensilon?
A nurse is assessing a 12-month-old infant during a well-child visit. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
A. Closed anterior fontanel
B. Eruption of six teeth
C. Birth weight doubled
D. Birth length increased by 50%
What is a C?
By the age of 12 months, the infant’s birth weight should have tripled. Therefore, report this finding to the provider
A congenital disorder where clusters of fluid‑filled cysts develop in the nephrons
What is polycystic kidney disease?
Occurs when tumors are rapidly destroyed, releasing intracellular content into the bloodstream faster than the body can process them
What is Tumor Lysis Syndrome?
Used in benzodiazepine toxicity to counteract sedation and reverse adverse effects
What is flumazenil
This childhood disease is diagnosed on the basis of the modified Jones Criteria
What is Rheumatic Fever
MAJOR CRITERIA
? Carditis ? Subcutaneous nodules
? Polyarthritis ? Rash (erythema marginatum)
? Chorea
MINOR CRITERIA
? Fever ? Arthralgia
Twice as common in females. Uhthoff's sign. Relapsing and remitting. Autoimmune
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
Most common in
Female, fat and over 40 (and Native Americans)
What is Cholecystitis?
Large, frothy, bulky, greasy, foul-smelling stools Deficiency of fat‑soluble vitamins. Decreased insulin production. Increased sodium in sweat
What are the S/S of cystic fibrosis
Ethambutol, rifapentine, isoniazid
What are antimycobacterials?
Term newborn's targeted blood glucose levels
What is between 30 and 60 mg/dL
Used to determine the variations of blood passing through an artery, thus identifying abnormal arterial flow in peripheral vascular diseases.
What is plethysmography?
Inability to speak, Weak ineffective cough, stridor, cyanosis
What are the S/S of choking?
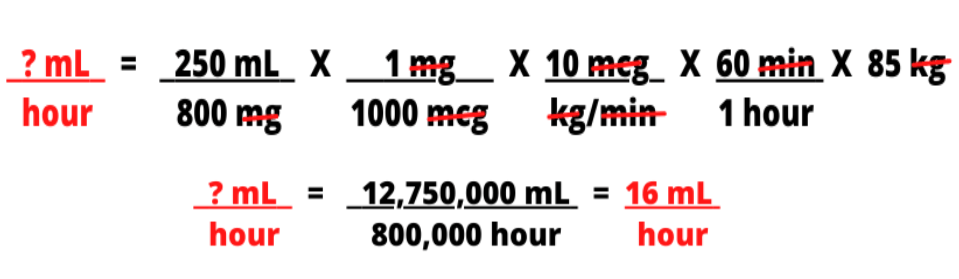
Administer dopamine at 10 mcg/kg/min. The pharmacy provides dopamine 800 mg in 250 mL of D5W. What is the hourly IV pump rate? The patient weighs 85 kilograms.
Infectious skin condition manifested by reddish macules that become vesicular leaving moist erosions with honey-colored crusts. Caused by staphylococcal organisms and spread by direct contact. Typically managed with topical bactericidal ointments
What is Impetigo (contagiosa)