A maneuver used to enhance hypoactive deep tendon reflexes in a leg.
A) Clenching fists together
B) Elevate an arm
C) Stare at a distant object
D) Think of moving the limb
E) Sensory stimulation of the opposite limb
What is A (clenching fists together)?
To achieve full relaxation of a joint, patient may need to be distracted. This can be accomplished by asking them to clench their jaw or asking them to hook their fingers together and forcefully pull their arms apart (Jendrassik maneuver)
A 37 year-old patient is evaluated for progressive spastic paraplegia. He also reports new onset visual loss. MRI of spine is notable for a longitudinal lesion in the cervical spinal cord, and MRI of the brain shows enhancement in the optic nerve. Antibodies to the following agent is associated with the disorder:
A) Lyme
B) Ganglioside
C) Aquaporin-4
D) Acetylcholine receptor
E) Glutamic acid decarboxylase
What is C (aquaporin-4)?
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: antibody selectively binds aquaporin-4 (AQP4)
NMOSD is characterized by episodic myelitis and optic neuritis. AQP4 is a channel protein in the cell membrane that allows water to pass through and is predominantly found in astrocytes in the spinal cord & optic nerve. Several new preventative treatments have been approved since 2019: eculizumab, inebilizumab, satralizumab, ravulizumab.

This is an optimal time to conduct amniocentesis for chromosome analysis of genetic disorders.
A) 8 weeks gestation
B) 12 weeks gestation
C) 18 weeks gestation
D) 28 weeks gestation
E) 34 weeks gestation
What is C (18 weeks gestation)?
The sleep of a healthy 70 yo individual is most likely to show a decrease or absence of this finding.
A) REM sleep
B) Slow waves
C) K complexes
D) Alpha waves
E) Sleep spindles
What is B (slow waves)?
With aging, these are changes associated with aging:
Decreased total sleep time
Decreased sleep efficiency
Decreased deep sleep (N3 slow wave sleep)
Increased number of nocturnal awakenings
Increased time spent awake during the night
This leads to formation of the neural tube.
A) Somites
B) Ectoderm
C) Notochord
D) Mesoderm
E) Endoderm
What is B (ectoderm)?
The formation of a neural tube in embryonic chordates occurs via the process of neurulation
- Cells located in the outer germ layer (ectoderm) differentiate to form a neural plate
- The neural plate then bends dorsally folding inwards to form a groove flanked by a neural crest
- The infolded groove closes off and separates from the neural crest to form the neural tube
- The neural tube will elongate as the embryo develops and form the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
- The cells of the neural crest will differentiate to form the components of the peripheral nervous system
Overview of Neurulation
This gait pattern is characteristic of a patient with left hemispheric stroke resulting in right sided hemiparesis.
A) Ataxia
B) Shuffling
C) Scissoring
D) Paraparetic
E) Circumduction
What is E (circumduction)?
Hemiparetic gait: during the swing phase, the paretic leg performs a lateral movement (circumduction)
Ataxic gait: broad-based, unsteady, caused by cerebellar syndrome (alcohol, phenytoin, stroke, tumor, degenerative, inflammatory)
Scissoring/paraparetic gait: caused by prolonged neonatal hypoxia during birth
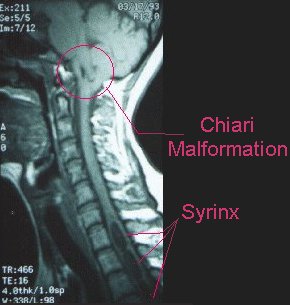
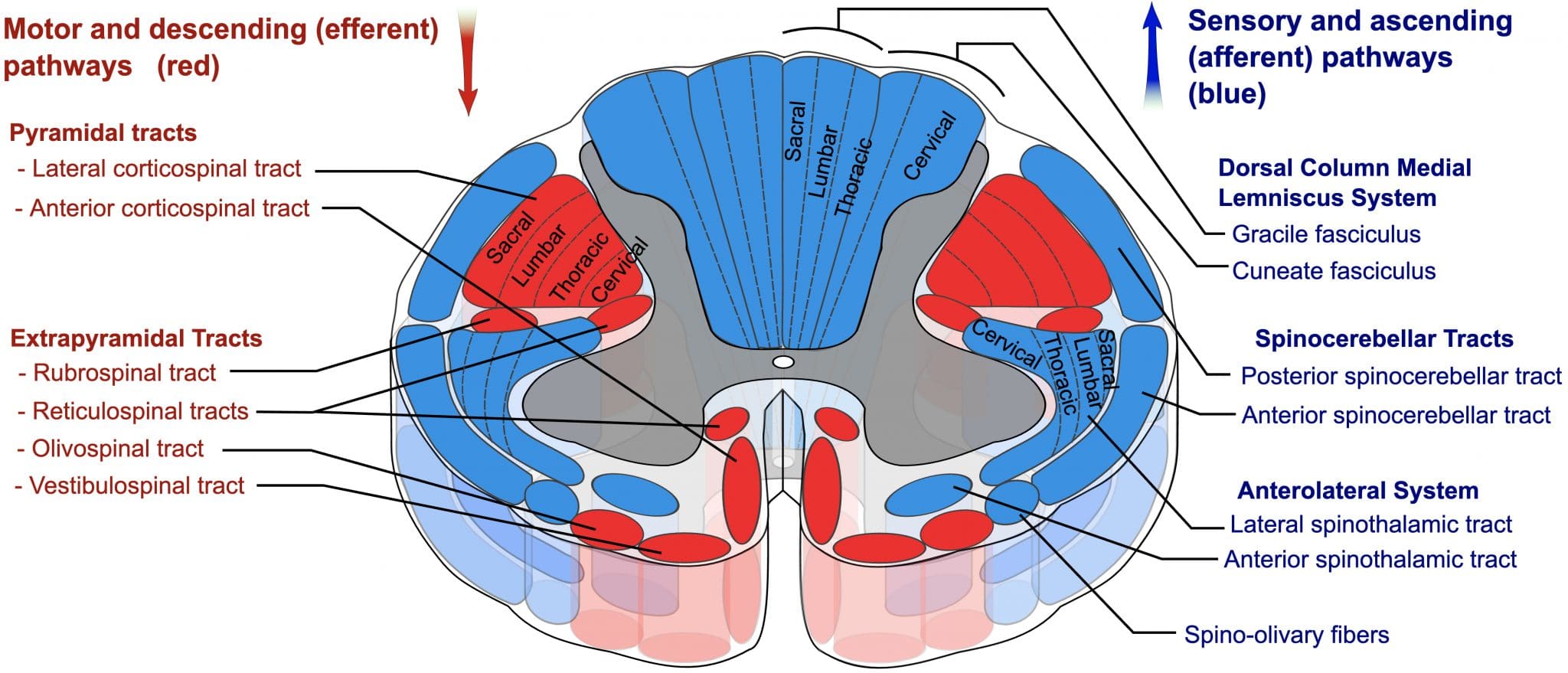
This capacity is most significantly affected when syringomyelia first presents.
A) Propioception
B) Pain perception
C) Auditory perception
D) Vibratory perception
E) Light touch perception
What is B (pain perception)?
Syringomyelia is caused by cyst (syrinx) formation in the spinal cord that first leads to cape-like bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation (spinothalamic tract) in upper chest and arms. It spares the dorsal column/medial lemniscus of the spinal cord, leaving pressure, vibration, touch and proprioception intact in the upper extremities. It is commonly associated with Chiari malformations.
A 25-year old with history of developmental delays presents for evaluation of anger outbursts. Prior karyotyping demonstrated a microdeletion of genetic material, consistent with this disorder.
A) Phenylketonuria
B) Down Syndrome
C) Tuberous Sclerosis
D) Fragile X Syndrome
E) Prader-Willi Syndrome
What is E (Prader-Willi Syndrome)?
Prader Willi Syndrome is related to an epigenetic phenomenon known as imprinting. Normally, a fetus inherits an imprinted maternal copy of PW genes on chromosome 15q11.2q13 and a functional paternal copy of PW genes. Due to imprinting, the maternally inherited copies of these genes are silent. The fetus relies solely on the expression of the paternal copies of the genes. In PWS, however, there is a microdeletion of the paternal copies of PW genes, leaving the fetus with no functioning PW genes.
Fragile X results from a mutation in the Fragile X Messenger Ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) gene, which is on the X chromosome. People with Fragile X have exhibit intellectual problems, physical features unique to this syndrome (broad forehead, large ears, hyperextensible joints), behavioral challenges, speech and language problems, and sensory issues. Anxiety, ADHD, and ASD are common.
Down syndrome is caused by having three copies of all the genes on chromosome 21.
Tuberous Sclerosis (autosomal dominant) is caused by a mutation of either of two genes, TSC1 and TSC2, which code for the proteins hamartin and tuberin, respectively.
Phenylketonuria is caused by an inborn error of metabolism related to a mutated gene for the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), which converts the amino acid phenylalanine to other essential compounds in the body, in particular tyrosine. PKU is included in the newborn screening panel and is treated with a phenylalanine-restricted diet.
The strongest risk factor for development of chronic daily headache in adults.
1) Obesity
2) Depression
3) Medication overuse
4) Low socioeconomic status
5) Older age of onset of headaches
What is C (medication overuse)?
- CDH defined as 15 or more headache days per month for at least 3 months.
- Prevalence of 1-4% of adults worldwide (F>M)
- Modifiable risk factors for progression to chronic migraine include obesity, medication overuse, stressful life events, snoring, caffeine overuse, and other causes of chronic pain
- Usage of any abortive medications 10 or more times per month increased the risk CDH
A 60-year-old man with subacute cognitive symptoms is found to have periodic sharp wave complexes at a frequency of about once per second without evolution. This EEG pattern is most characteristic of:
A) Alzheimer’s disease
B) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
C) Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
D) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
E) Nonconvulsive status epilepticus
What is B (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease)?
Periodic sharp wave complexes at ~1 Hz on EEG are characteristic of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, especially in the setting of rapidly progressive dementia. Alzheimer’s and normal aging cause only diffuse slowing, SSPE shows slower periodic discharges (every 4–10 sec), and metabolic encephalopathies produce triphasic waves rather than sharp complexes.
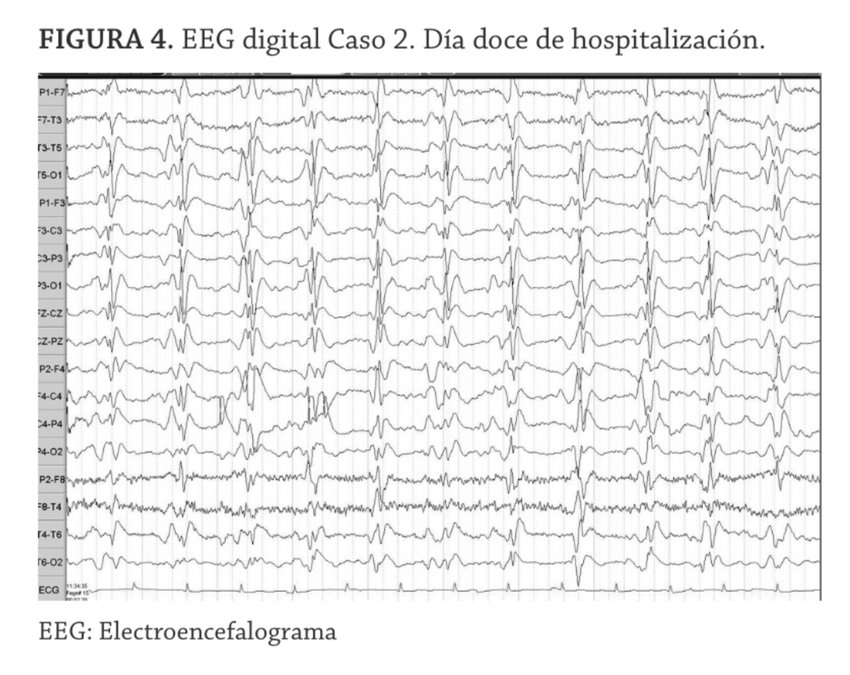
An elderly patient with memory impairment and gait disturbance is being evaluated in neurology clinic. After a large volume LP, his gait is noted to improve. Thus a ventriculoperitoneal shunt is scheduled. He likely had this gait prior to the LP.
A) Scissoring
B) Spastic
C) Shuffling
D) Magnetic
E) Propulsive
What is D (magnetic)?
Magnetic gait: broad based gait with outward rotated feet and a diminished height of the steps.
Scissoring/paraparetic gait: caused by prolonged neonatal hypoxia during birth
Shuffling gait: narrow based gait with flexed knees and short steps
Propulsive gait: a stooped, stiff posture with the head and neck bent forward
A 22-year-old man with myotonic dystrophy undergoes evaluation for routine monitoring. This diagnostic test would best detect the most common cardiac complications associated with this condition.
A) Angiogram
B) TTE
C) EKG
D) Cardiac MRI
E) Cardiac SPECT
What is C (EKG)?
Myotonic dystrophy is caused by microsatellite expansions in either the DMPK gene (DM Type 1) or the CNBP gene causes type 2 (DM Type 2). The condition is associated with progressive muscle atrophy, cataracts, intellectual disability and cardiac conduction problems (commonly prolongation of the PR interval and QRS duration). These abnormalities can be detected with EKG.
Tuberous Sclerosis is transmitted by this inheritance pattern:
A) Mitochondrial
B) X-linked dominant
C) X-linked recessive
D) Autosomal dominant
E) Autosomal recessive
What is D (Autosomal dominant)?
Tuberous Sclerosis (autosomal dominant) is caused by a mutation of either of two genes, TSC1 and TSC2, which code for the proteins hamartin and tuberin, respectively. TS is associated with tumors in brain, kidneys, heart, skin, etc. and is associated with epilepsy, intellectual disability, skin abnormalities, and kidney disease. Intracranial manifestations of TSC include subependymal nodules and cortical/subcortical tubers.

Facial Angiofibromas (hamartoma) in butterfly pattern

Aggressive behavior in patients with Alzheimer's disease is most often associated with this risk factor.
A) Word-finding difficulty
B) Concurrent psychosis
C) Premorbid anxiety disorder
D) Late stage of Alzheimer disease
E) Earlier onset of Alzheimer disease
What is B (concurrent psychosis)?
Delusions are a risk factor for physical aggression in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease who have moderate to severe cognitive impairment
This is an expected side-effect for patients prescribed rivastigmine for Alzheimer's disease or Lewy body disease.
A) Nocturia
B) Bradycardia
C) Weight gain
D) Constipation
E) Decreased REM sleep
What is B (bradycardia)?
AChE inhibitors are chiefly used to target cholinergic receptors in the central nervous system but also affect other organs, including the heart. Increased ACh levels can augment parasympathetic tone in the sinoatrial node, slowing heart rate. Bradycardia, a noted adverse effect of AchE inhibitors that may cause or contribute to syncope, has also been reported, particularly when administered in excessive doses.
Your patient with multiple sclerosis has frequent episodes of inappropriate and uncontrollable laughter. This medicine is mostly likely to help.
A) Buproprion
B) Propranolol
C) Risperidone
D) Amitriptyline
E) Carbamazepine
What is D (amitriptyline)?
Pseudobulbar affect (also called emotional lability or emotional incontinence) is a term that describes sudden uncontrollable outbursts of laughter or tearfulness in patients with neurological disorders. Etiology is unclear, but theory is that bilateral lesions in the descending corticobulbar tract causes failure of voluntary control of emotion, which leads to the disinhibition, or release, of laughing/crying centers in the brainstem. Treatment options include SSRIs, TCAs, and Nuedexta (dextromethorphan + quinidine).
This is the most specific test to identify heavy alcohol consumption.
A) Lipase
B) Bilirubin
C) Prothrombin Time
D) Aspartate transaminase
E) Carbohydrate deficient transferrin
What is E (Carbohydrate deficient transferrin)?
Carbohydrate deficient transferrin (CDT) is the most specific serum biomarker of heavy alcohol consumption, defined as ≥ 350–420 g alcohol/week.
A CDT level above 0.12 suggest chronic excessive alcohol use. CDT is fairly specific for excessive use though can be elevated by rarer liver diseases, such as primary biliary cirrhosis. This is more useful than a GGT, but not routinely available and used mostly by specialists.
Broad face, flat midface, progressively coarsening facial features, short broad hands, small toes, and hoarse, deep voice are physical features associated with the chromosomal deletion of:
A) 2q9.12
B) 5p15.2
C) 7q11-23
D) 17p11.2
E) 22q11
What is D (17p11.2)?
Smith–Magenis syndrome: 17p11.2 deletions involving RAI1 gene. MS is most commonly characterized by a variable degree of intellectual disability including speech and motor delay, craniofacial and skeletal anomalies, sleep disturbance, self-injurious and attention-seeking behaviors. Craniofacial features include brachycephaly, midface hypoplasia, tented upper lip, and deep-set and hypoteloric eyes.
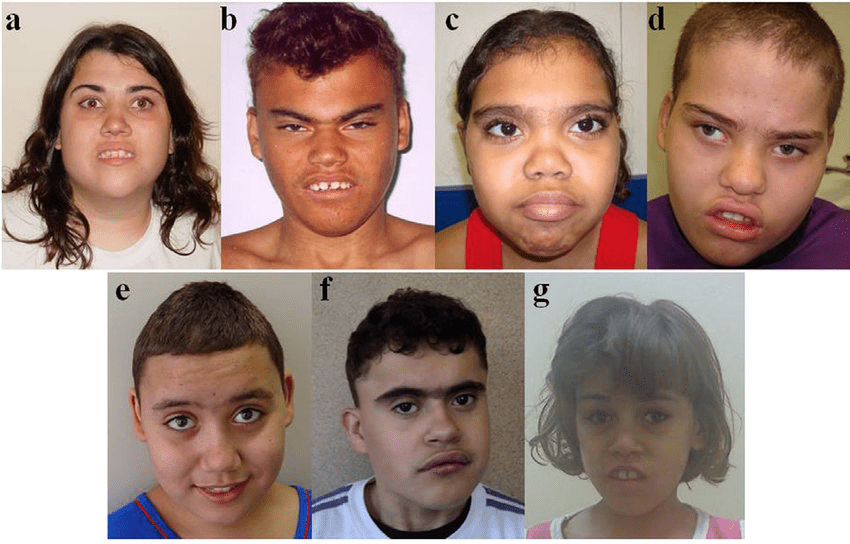
Cri du chat syndrome can be seen with 5p15.2 deletions. Patients present with microcephaly, a round face, hypertelorism, micrognathia, prominent nasal bridge, epicanthic folds, hypotonia, and severe psychomotor retardation. Infants also exhibit a high pitched cry similar to the mewing of a cat.
Williams-Beuren syndrome is caused by a hemizygous contiguous gene microdeletion at 7q11.23. Supravalvular aortic stenosis, mental retardation, overfriendliness, and ocular and renal abnormalities comprise typical symptoms in WBS.
Digeorge Syndrome (CATCH-22): Cardiac abnormality (commonly interrupted aortic arch, truncus arteriosus and tetralogy of Fallot), Abnormal facies, Thymic aplasia or hypoplasia, Cleft palate, Hypocalcemia/hypoparathyroidism early in life
This adverse side-effect related to carbamazepine is more commonly found in people of Asian descent than in other ethnic groups.
A) Agranulocytosis
B) Liver dysfunction
C) Stevens Johnsons Syndrome
D) Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion
E) Dizziness
What is C (Stevens Johnsons Syndrome)?
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome, have been reported during treatment with carbamazepine. Studies in patients of Chinese ancestry have found a strong association between the risk of developing Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN and the presence of HLA-B*1502, an inherited allelic variant of the HLA-B gene. HLA-B*1502 is found almost exclusively in patients with ancestry across broad areas of Asia. Patients with ancestry in genetically at-risk populations should be screened for the presence of HLA-B*1502 prior to initiating treatment with carbamazepine. Patients testing positive for the allele should not be treated with carbamazepine.
Successful global cognitive performance with aging has most consistently been positively associated with the size of this brain structure.
A) Cerebellum
B) Parietal lobe
C) White matter
D) Frontal lobes
E) Hippocampal formation
What is E (hippocampal formation)?
Hippocampus is a critical structure in cognitive aging, playing a role not only in episodic memory, but also processing speed, working memory and executive function.
A 55-year-old woman undergoes gastric bypass surgery and, several weeks later, develops gait imbalance and numbness in the feet. Neurological examination is remarkable for hyperreflexia, spasticity in the legs and absent vibration sensation at the toes. Serum B12 level is normal. This deficiency is most likely to explain her symptoms.
A) Iron
B) Folate
C) Copper
D) Thiamine
E) Pyridoxine
What is C (copper)?
Copper deficiency causes myelopathy that closely resembles subacute combined degeneration due to Vitamin B12 deficiency. Risk factors included previous upper gastrointestinal surgery, zinc overload and malabsorption syndromes, all of which impair copper absorption in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Patients typically present with gait difficulties, which arise through sensory ataxia due to dorsal column dysfunction and to a lesser extent through spasticity.
A 59-year old patient develops migraines characterized by a unilateral headache associated with nausea and vomiting. Past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease and renal insufficiency. Which of the following would be the most appropriate abortive treatment?
A) Dihydroergotamine
B) Naproxen
C) Sumatriptan
D) Oxycodone
E) Rimegepant
What is E (rimegepant)?
Rimegepant is a CGRP receptor antagonist that is used for both abortion of acute migraines and prevention of migraines. Unlike triptans/ergots, it does not cause vasoconstriction, so rimegepant is safe in CAD. It is also safer than NSAIDs in patients with renal insufficiency.
A 24-year old is seen on the consult service for worsening disorientation and suspected delirium. The patient's initial presentation was notable for the development of severe headaches after starting a high protein, low carbohydrate diet. There is no prior psychiatric history, but the patient notes slow growth as a child. This test is the most definitive way to establish this patient's diagnosis.
A) Muscle biopsy
B) Chromosome microarray
C) MECP2 gene sequencing
D) Plasma amino acid analysis
E) Ornithine transcarbamylase sequencing
What is E (ornithine transcarbamylase sequencing)?
Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency, a urea cycle disorder, is a rare X-linked genetic disorder characterized by complete or partial lack of OTC. OTC is one of six enzymes that play a role in the breakdown and removal of nitrogen the body. Lack of the OTC enzyme results in hyperammonemia. Symptoms include vomiting, refusal to eat, progressive lethargy, and coma. If left untreated, neuropsychological complications include developmental delay, learning disabilities, intellectual disability, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and executive function deficits.
Urea cycle disorders can be identified through the examination of urine for elevated levels of organic acids and examination for alterations in plasma amino acids and plasma acylcarnitines. Individuals with OTC deficiency usually have both low levels of citrulline and high glutamine in the blood and high levels of orotic acid in the urine. However, most specific diagnostic test is DNA sequencing.
The quadruple screen during pregnancy measures maternal serum quantities of alpha fetoprotein, unconjugated estriol, human chorionic gonadotropin and:
A) Inhibin A
B) Testosterone
C) Progesterone
D) Human placental lactogen
E) Pregnancy associated plasma protein A
What is A (Inhibin A)?
In pregnancies affected by Down Syndrome, the blood levels of AFP and estriol tend to be lower and the levels of inbibin-A and hCG are higher.
In pregnancies affected by trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome), the levels of AFP, uE3, inhibin-A, and ß-hCG tend to be lower than normal.
In pregnancies affected by open neural tube defects, such as open spina bifida or anencephaly, the level of AFP tends to be elevated.
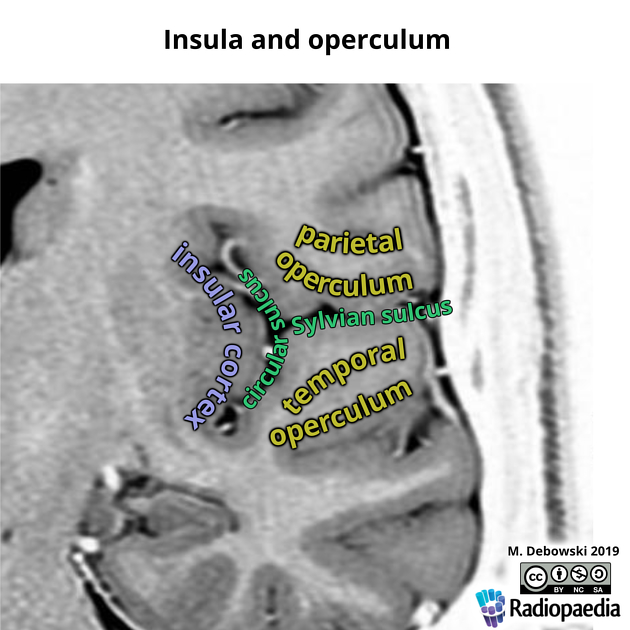
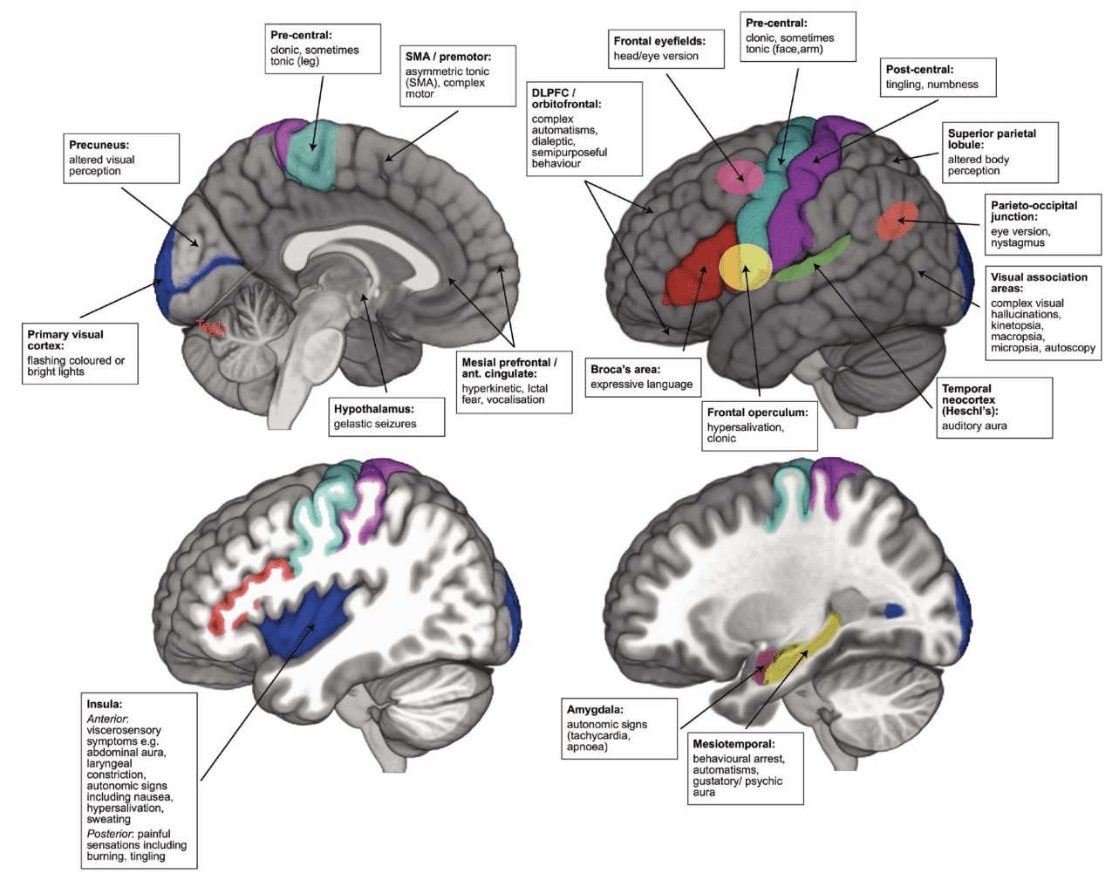
A patient presents with new onset episodes of excessive salivation, chewing and choking sensations. These symptoms may be related to seizures originating in this area.
A) Frontal insula
B) Frontal operculum
C) Mesial temporal lobe singular gyrus
D) Occipital lobe supplementary motor area
E) Dorsolateral frontal lobe entorhinal cortex
What is E (frontal operculum)?
Seizures arising from frontal operculum are characterized by facial clonic movements that may be unilateral, with laryngeal symptoms, hypersalivation and articulation difficulties.
Pure insular epilepsy has a typical ictal sequence beginning with laryngeal discomfort with thoraco-abdominal constriction or dyspnea, followed by unpleasant paresthesias or warmth in the perioral region or involving large somatic areas, dysarthria or dysphonia, and ending with focal motor manifestations.