Fill in the missing word: "Organic Chemistry is the field of chemistry that studies (______)-based compounds"
Organic Chemistry is the field of chemistry that studies carbon-based compounds
 Name the compound identified by these structures
Name the compound identified by these structures
butane
A compound ending in -OH is classified as what?
An Alcohol
What are the three stages of free-radical substitution?
Initiation, Propagation, Termination
Define "Alkene"
an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
A _________ Hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon where all c-c bonds are single bonds
A Saturated Hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon where all c-c bonds are single bonds
Fill in the missing compound in the pattern: "Methane, Ethane, ____ane, Butane, Pentane, Hexane"
"Methane, Ethane, Propane, Butane, Pentane, Hexane"
What functional group is this?:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/carboxylgroup-56a129e15f9b58b7d0bca5e9.jpg)
A carboxyl group
Why are Alkanes unable to undergo addition polymerization?
Monomers with only single C-C bonds do not contain enough electrons to link up into a polymer. Addition Polymerization requires C=C double bonds.
Fill in the blank!
"Any chemical reaction in which a material gives up electrons is called _________"
Oxidation
Compounds with the same chemical formula but different structural formulas are called what?
Isomers or Structural Isomers
Draw the structure of and name, according to IUPAC standards, the following: CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)CH2CH3
3-methylhexane
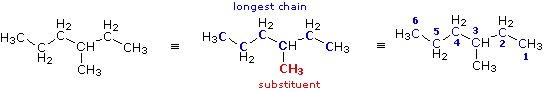
What's the difference between an amine and an amide?
An amino group has a nitrogen connected to three other atoms and has a lone pair. Can connect to 2 hydrogens and 1 carbon, 1 hydrogen and 2 carbons, or 3 carbons.

An amido group is RCONH2, where the C is double bonded to the O, like this:

To test for unsaturation in alkenes, bromine water is used. The color of the solution turns from brown to clear. Why would this test work to identify alkenes but not alkanes?
Br cannot connect to the hydrocarbon unless that hydrocarbon has a double bond, allowing (in this example) the two electrons in Br- to create a bond to each CH2.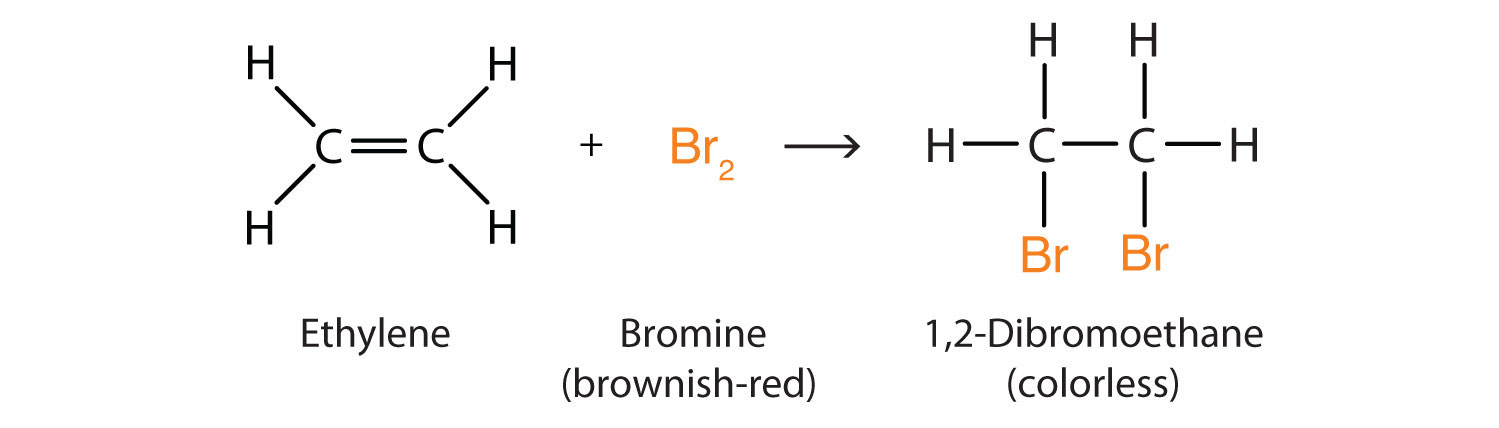
What is an electron-poor species capable of accepting an electron pair called?
An electrophile
Substances whose energy is derived from carbon fixation in plants are called what?
Biofuels

Name according to IUPAC standards
4-methylpent-2-ene

Name all the functional groups of Aspirin.
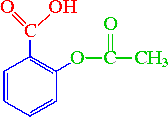
carboxylic acid (R-COOH)
ester (R-O-CO-R')
aromatic (benzene ring)
Fill in the blanks:
"Oxidation of a primary alcohol is a two-stage process that first produces a(n) ________ followed by a(n) __________ ____"
Oxidation of a primary alcohol is a two-stage process that first produces an aldehyde followed by a carboxylic acid.
If, during the process of oxidation of a primary alcohol, the carboxylic acid is the desired product, the aldehyde must remain in the mixture with the oxidizing agent for a longer period of time. To do this, a process called "refluxing" is used. Describe the technique of refluxing.
Cyclic evaporation and condensation of a volatile reaction mixture, preserving the solvent as it does not evaporate.
 Name this process, which is used to separate mixtures by boiling point.
Name this process, which is used to separate mixtures by boiling point.
Fractional distilation

Name according to IUPAC standards.
Chloroacetic acid or Chloroethanoic acid
Name the Functional Group OR Class:
R-C≡N
Functional Group: Cyano
Class: Nitrile
Esterification is a reversible reaction that occurs when a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are heated in the presence of a catalyst, normally concentrated sulfiric acid. Complete the following reaction
CH3CH2COOH(l) + CH3OH (l) ----> H20(l) + ???
CH3CH2COOH(l) + CH3OH (l) ----> H20(l) + CH3CH2COOCH3
Name the difference between Homolytic and Heterolytic Fission
Homolytic seperates a covalent bond equally, leaving two free-radicals that each have a single electron from the previously broken bond.
Heterolytic Fission splits the bond unevenly, leaving one atom with both of the bond's electrons (the negative anion) and one with neither of the bond's electrons (the positive cation)