What is the differential for abnormal uterine bleeding?
What is PALM-COEIN?
Structural vs Non-Structural
Polyps, Adenomyosis, Leiomyomas, Malignancy, Hyperplasia
Coagulopathy, Ovulatory Dysfunction, Endometrial, Iatrogenic, Not otherwise classified
A history of cesarian delivery followed by fever, uterine tenderness, and foul-smelling lochia
Bonus: what kind of bacterial infection is this and what antibiotics should be started?
What is endometritis?
Polymicrobial infection both gram-positive (Staphylococcus epidermidis and group B streptococci) and gram-negative (Gardnerella vaginalis) bacteria.
Treat with clindamycin and gentamicin
You have a high suspicion that your patient has a primary ovarian malignancy, what is your next step in diagnosis, biopsy vs surgical excision?
Fine-needle aspiration is absolutely contraindicated in potentially resectable ovarian tumors because it can directly spread tumor cells to the peritoneum.
- Surgical biopsy
- Recommended for definitive diagnosis of ovarian cancer
- Should be performed in patients with clinical, radiographic, and/or laboratory findings that suggest ovarian cancer
- Laparoscopic removal is the preferred surgical procedure.
A 29 yo F is post partum day 1 and desires contraception. What can you offer her?
What is
Progestin only pills
IUD (progestin or copper)
Depot shots
Nexplanon implant
Triad of
- Cardiac defect: most common defect (e.g., patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis)
- Cataracts: Other eye manifestations may also occur later in life, including glaucoma and salt and pepper retinopathy (abnormal retinal pigmentation)
- Cochlear defect: bilateral sensorineural hearing loss
What is congenital rubella syndrome?
Additional buzzwords blueberry muffin rash, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, microcephaly
Name the type of incontinence:
1. detrusor overactivity which results in involuntary leakage of urine
2. impaired detrusor contractility leading frequent involuntary loss of urine
3. loss of urine with physical stress such as coughing, sneezing, and laughing caused by urethral hypermobility
1. Urge incontinence
2. Overflow incontinence
3. Stress incontinence
The criteria for preeclampsia:
What is new onset gestational hypertension with proteinuria or end organ dysfunction
*three primary features of PREeclampsia are Proteinuria, Rising blood pressure (hypertension), and End-organ dysfunction*
itchy, erythematous, scaly rash on the areola
What is Paget disease of the breast?
What are contraindications to combined oral contraceptive pills?
age >35 years old and smoking >/equal to 15 cigarettes a day
high risk of VTE with our without a history
migraines with aura
history of hypertension
The single most accurate method of estimating the gestational age in the first trimester
What is ultrasonographic measurement of crown-rump length (CRL)?
Define ectopic pregnancy and its risk factors.
Ectopic pregnancy is characterized by implantation of the fertilized ovum outside the uterus.
Symptoms: amenorrhea, enlarged uterus, and lower abdominal pain, with or without vaginal bleeding. Ectopic pregnancies have the potential to rupture and cause hemorrhagic shock.
Risk factors include: prior ectopic pregnancy, hx of infertility, PID, acute appendicitis, prior tubal surgery, smoking, and advanced maternal age.
Incidence: 1 in 100 pregnancies
What is the criteria for a reactive Nonstress Test (NST)?
≥ 2 fetal heart rate accelerations that last for at least 15 seconds and are > 15 bpm above the baseline within a 20-minute period
A nulliparous patient with a history of late-onset menopause presents with a tender, enlarged, and erythematous breast, nipple flattening, blood-tinged nipple discharge, and axillary lymphadenopathy
What is inflammatory breast cancer?
What options are there for emergency contraception?
1. IUD
- General principles
- The IUD is the most effective method of emergency contraception
- Efficacy is unaffected by obesity and/or body weight.
- Can provide long-lasting (up to 12 years) contraception
- Timing: within 5 days of unprotected intercourse
- Mechanism of action: prevents fertilization and may affect the oocyte and endometrial lining
- Types of IUDs: copper IUD and progestin IUD
2. Emergency contraceptive pills
- General principles
- Significantly less effective in individuals with a BMI ≥ 25 or above a specified weight cut-off
- Timing after unprotected intercourse [8]
- Levonorgestrel: most effective when taken within 3 days
- Ulipristal acetate and the Yuzpe regimen can be used within 5 days
- Types of ECPs
- Ulipristal acetate (prescription only)
- Levonorgestrel (emergency contraceptive)
- Yuzpe regimen (prescription only) [26][71]
- Contraindications
- Established pregnancy is the only contraindication.
A prodrome of flu-like symptoms (e.g., fever, headache, nausea, vomiting), an erythematous macular rash that involves the palms, soles, and inner thighs, and mucosal inflammation
What is Toxic Shock Syndrome?
Episodic lower abdominal pain shortly before menstruation in an adolescent with a normal physical exam
What is primary dysmenorrhea?
The most common gynecological complaint among adolescent females. The condition is most likely caused by an increased production of endometrial prostaglandin (PG) F2α. PGF2α causes dysrhythmic uterine contractions and consequently abdominal pain and uterine ischemia. The accompanying symptoms of primary dysmenorrhea (e.g., headache, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea) are also believed to be mediated by PGF2α.
1st line treatment: NSAIDs
2nd line: OCPs (MOA --> suppress ovulation)
The sudden increase in labor pains, hemodynamic instability, loss of fetal station, fetal distress, and a decreased amplitude of uterine contractions.
Which feature is most specific for this diagnosis?
What is uterine rupture and loss of fetal station?
Patient presents with adnexal mass and pelvic pain, you are concerned for ovarian cancer, what tumor marker(s) should you order?
- CA-125 levels are elevated in ∼ 80% of malignant epithelial ovarian tumors (and in certain germ cell tumors).
- Premenopausal women: Elevated CA-125 may indicate a benign process (e.g., endometriosis, pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease).
- Postmenopausal women: Elevated CA-125 (> 35 U/mL) raises concern for malignancy.
- Additional tumor markers:
- Germ cell tumor markers:
- βhCG, AFP, LDH
- Granulosa cell tumor: inhibin
- Also can consider CEA and CA 19-9
- Germ cell tumor markers:
What is the incidence of pregnancy for patients using long acting reversible contraception (LARC)?

Name the ligaments

What is (in clockwise order)
1. Ovarian ligament
2. Suspensory ligament
3. Broad ligament
4. Round ligament
5. Cardinal ligament
6. Uterosacral ligament
Patient presents complaining of vaginal discharge
Differential for infectious vulvovaginitis:

You have an HIV positive patient on L&D, at what viral load is a c-section indicated and what intrapartum medication should be given?
What is a viral load > 1,000 copies and intrapartum zidovudine is indicated to further reduce the risk of neonatal HIV infection.
You have a high suspicion that your patient has a primary ovarian malignancy, what is your next step in diagnosis, biopsy vs surgical excision?
Fine-needle aspiration is absolutely contraindicated in potentially resectable ovarian tumors because it can directly spread tumor cells to the peritoneum.
What is the incidence of pregnancy for patients using short acting reversible contraception?

Interpret this fetal heart tracing
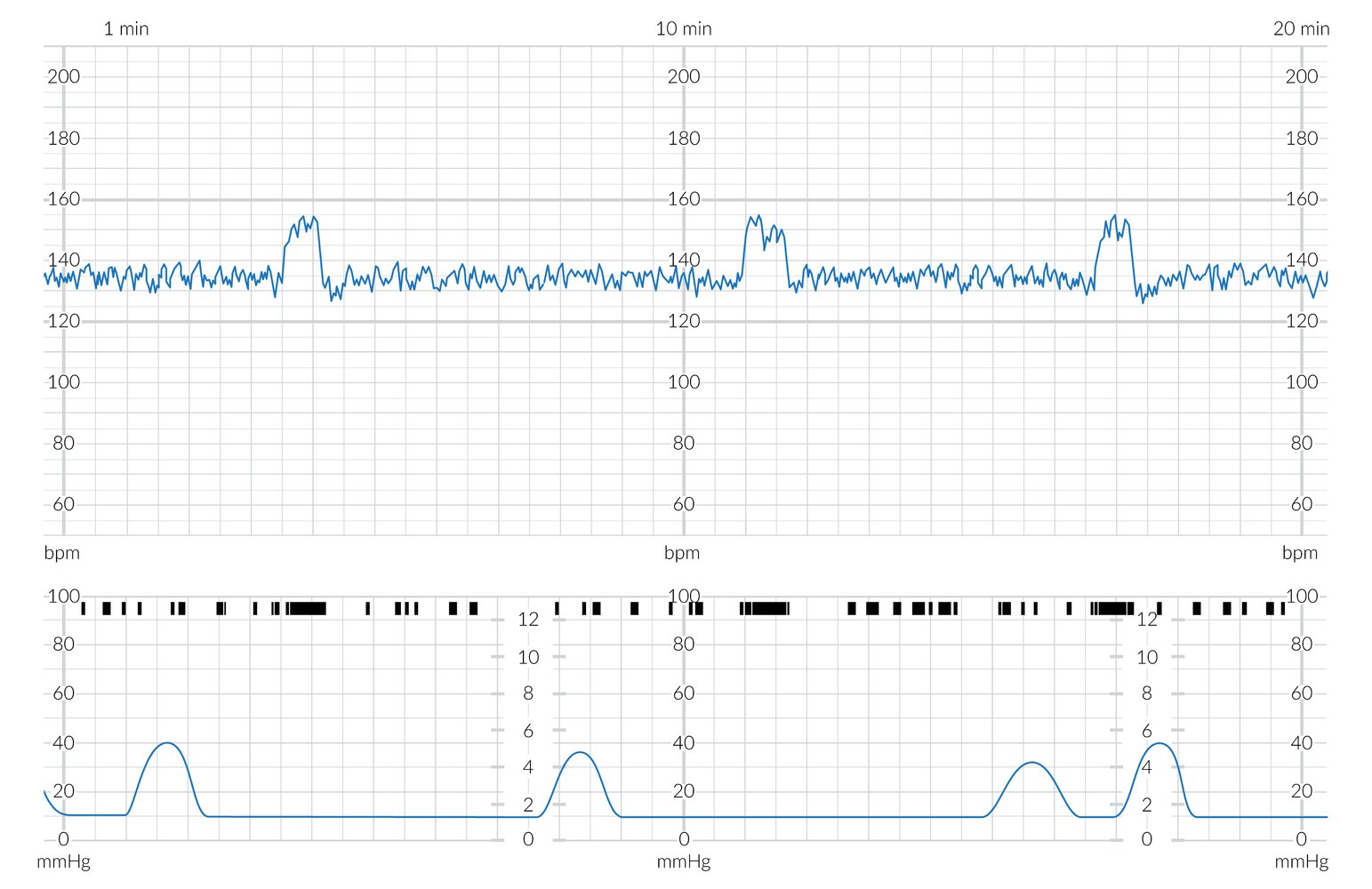
Normal findings

The upper blue tracing shows the fetal heart rate (FHR) in bpm with a baseline of approx 135 bpm which is within the normal range and shows moderate variability (~10 bpm; normal range 6–25 bpm).
The lower blue tracing shows the maternal uterine contractions (in mm Hg). The black markings above this tracing show fetal movements
There are three FHR accelerations which coincide with periods of increased fetal movement.