What is the estimated blood volume for a pregnant patients in cc/kg?
Normal range for FHR
What is 110-160 bpm?
A synthetic prostaglandin. It acts by binding to prostaglandin E1 receptors causing myometrial contraction
Misoprostol (cytotec)
Hemabate/carborpost is prostaglandin F2alpha
These are the four categories of HTN in pregnancy.
What are 1) cHTN, 2) gHTN, 3) PEC/eclampsia/HELLP, and 4) Pre-E w/ severe features
A prolonged infusion of oxytocin is most likely to produce a clinically significant decrease in this electrolyte
What is sodium?
What is the second stage of labor?
Fully dilated to delivery of baby
Fibrinogen cutoff for transfusion in pregnancy? How about non-pregnant patients?
Approx. 200 for pregnant patients (normal by third trimester is 300-600mg/dL) . For non-pregnant patients the cutoff is 100-150, unless it is intracranial surgery in which case you want it to be 150-200
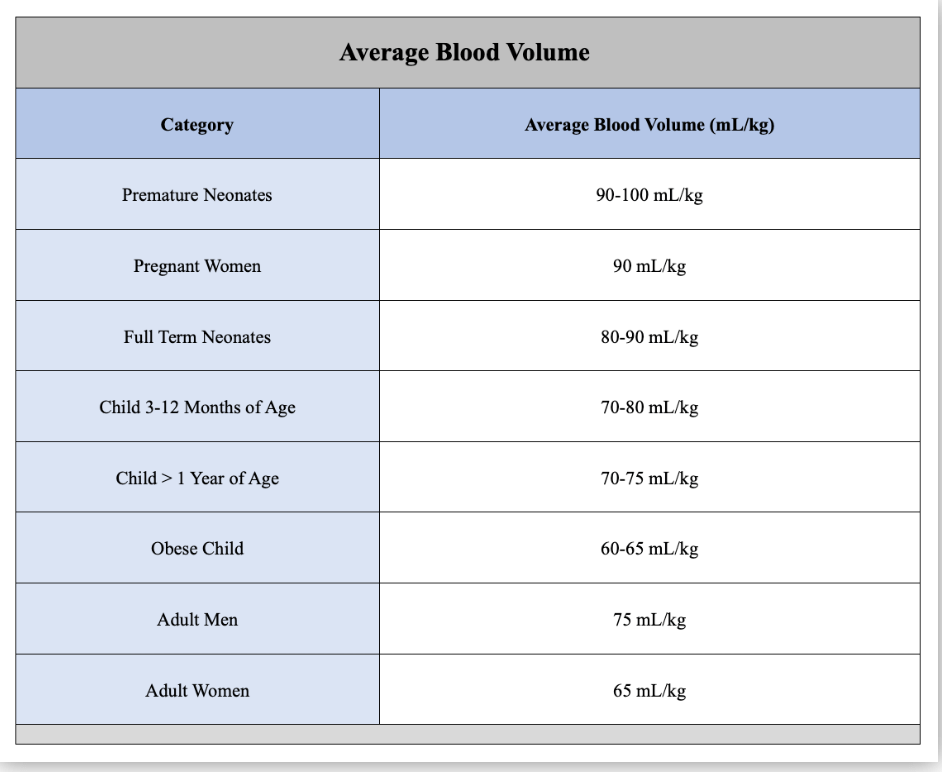
What are early decelerations? What do they indicate?
Early decelerations are caused by fetal head compression during uterine contraction, resulting in vagal stimulation and slowing of the heart rate. This type of deceleration has a uniform shape, with a slow onset that coincides with the start of the contraction and a slow return to the baseline that coincides with the end of the contraction.
This is the antidote for magnesium toxicity
Calcium gluconate 1 g IV push over 3 minutes OR calcium chloride 10% 500 mg over 5-10 min
This is the week gestation that delineates chronic hypertension versus gestational hypertension
What is 20 weeks?
This system is the mechanism for the increase in maternal blood volume during pregnancy
What is sodium retention via renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system?
These are the three prominent changes in the CV system in pregnancy
What are 1) decreased SVR, 2) increased SV/CO, and 3) increased HR?
The normal Cr range in pregnancy
What is 0.4 to 0.8 mg/dL?
The uteroplacental blood flow at term in ml/min
What is 700ml/min?
Clonidine functions as a sympatholytic by this mechanism (name specific receptor, neurotransmitter, and action)
What is stimulating presynaptic α2-receptors leading to decreased release of norepinephrine at both central and peripheral adrenergic terminals
Name the 3 types of placenta accreta spectrum
- Placenta accreta—The placenta grows into a scar in the uterine lining.
- Placenta increta—The placenta grows into the wall of the uterus.
- Placenta percreta—The placenta grows through the uterus wall and possibly into nearby organs.

Where does the spinal cord typically terminate in adults?
L1-L2 (in children it can extend to L3)
What level do you need to achieve for labor analgesia during the first stage of labor?
The first stage of labor includes innervation from the T10-L1
The second stage of labor includes innervation from the sacral nerve roots (S2-S4) as well as T12-L1
Name two clotting factors that decrease in pregnancy?
XI, XIII, and Protein S decline. Protein C is constant. You also get dilutional thrombocytopenia
This is the associated cause of this fetal heart tracing

What is (utero)placental insufficiency?
This drug causes smooth muscle relaxation in the uterus via release of nitric oxide
What is nitroglycerin?
Treatment for eclampsia
What is magnesium sulfate 4-6 g IV loading dose over 15-20 min followed by a 2 g/hr maintenance?

In the setting of LAST, this is the dose of Intralipid 20% emulsion administration
100cc IV over 2-3 min (if <70kg, 1.5 cc/kg bolus)
250cc over 15-20 min (if <70kg, 0.25cc/kg/min)
What happens if you accidentally give TXA intrathecally?
Potent Neurotoxin:TXA is a potent neurotoxin when administered intrathecally.
Serious Complications:Intrathecal TXA can cause:
- Refractory seizures
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Paraplegia
- Neurological injury
- Death
- High Mortality Rate:Some reports indicate a mortality rate of 36% or even 50% in cases of intrathecal TXA toxicity.
How does FEV1, FEV1/FVC, flow volume loops, and closing capacity change during pregnancy?
They are unchanged. (FRC decreases, oxygen consumption increases, minute ventilation increases- mostly due to an increase in tidal volume). Remember, closing capacity does not change with obesity or position, but it does increase with age.
Fetal blood flow is characterized by these three anatomic communications between the left and right circulations
What are the ductus venosus, the foramen ovale, and ductus arteriosus
This drug causes uterine relaxation by beta-2 receptor stimulation
What is terbutaline?
Name 4 of the possible criteria for pre-eclampsia with severe features

How long should you hold low dose prophylactic lovenox prior to neuraxial anesthesia?
12 hrs
What is it called when increased abdominal pressure (such as during pregnancy) leads to entrapment of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, causing pain in this distribution
What is meralgia parasthetica
This system is the last to return to its pre-pregnancy state
What is the renal or GU system?
Fetal hemoglobin has a greater O2 affinity than adult hemoglobin owing to a decreased interaction between hemoglobin F and this molecule
What is 2,3-DPG?
This is the site of action for opioids administered in the intrathecal space (name receptor and location)
What is mu receptors in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, in the substantia gelatinosa?
This is the beginning stages in the pathophysiology of PEC
What is abnormal remodeling of the spiral arteries?
The structure labeled #2
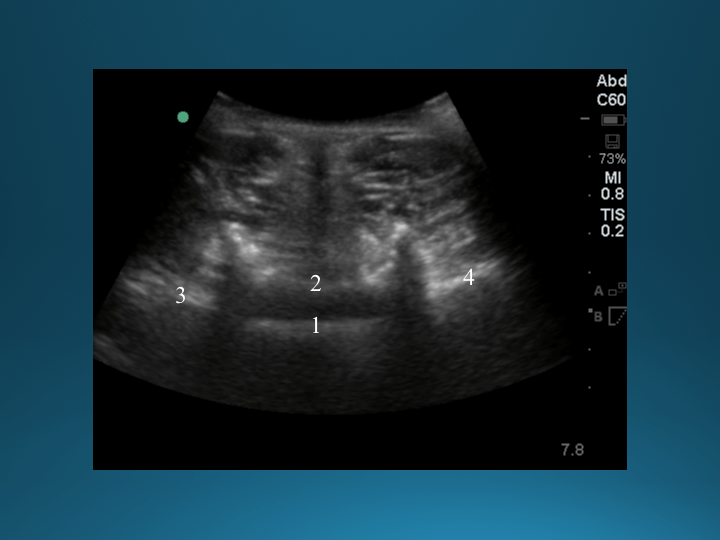
What is the ligamentum flavum?
This nerve block can be used for pain relief in the 1st stage of labor
What is a paracervical block?
DAILY DOUBLE
In a preoxygenated 80 kg woman – this is the time to desaturation if you assume O2 consumption is 10ml/kg/min (hint: the FRC in pregnancy is 20 ml/kg)
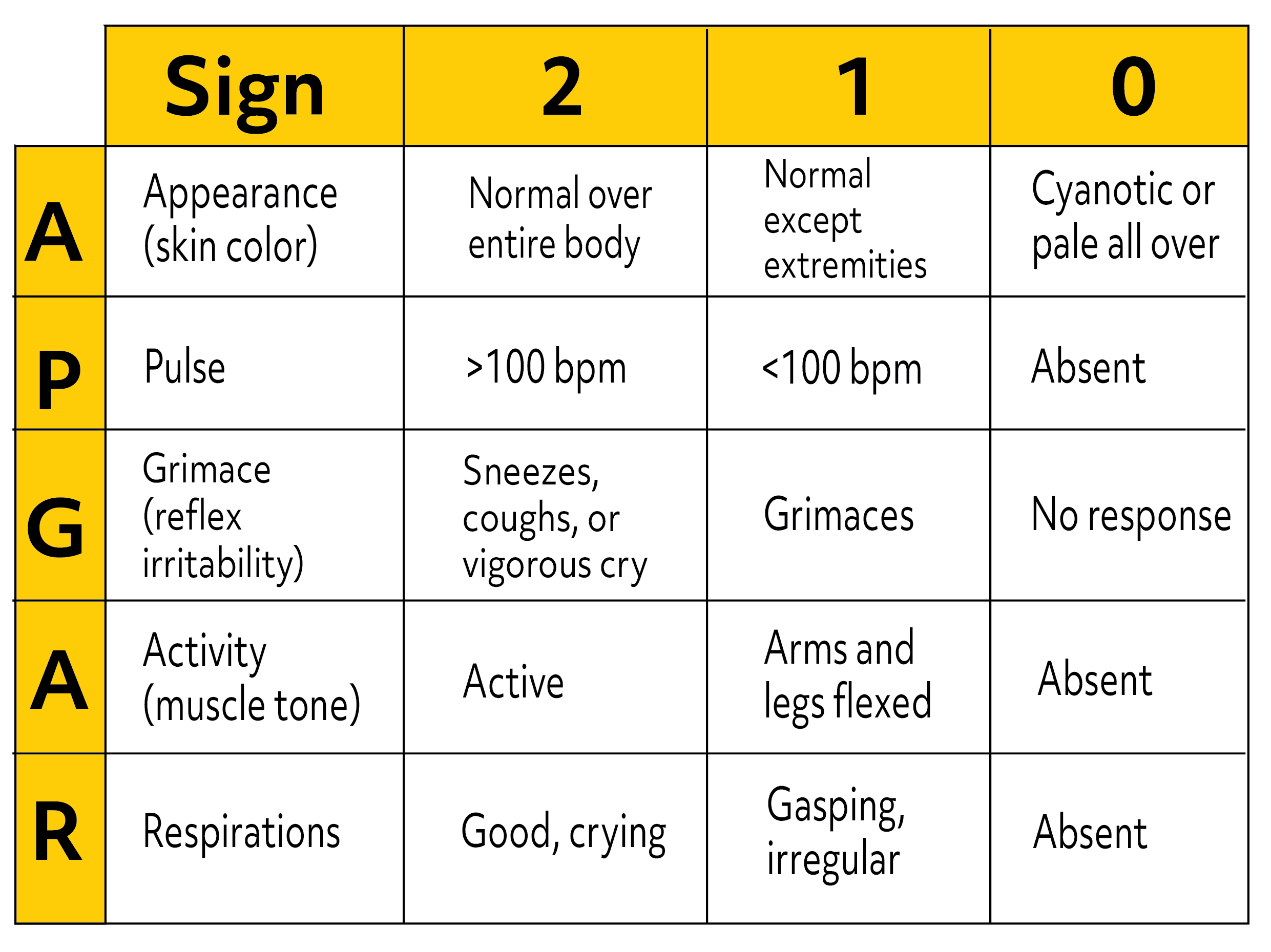
The APGAR score for the following newborn: some flexion of the arms/legs, weak cry after suctioning, slow and irregular respirations, HR 110, pallor all over body and extremities
What is APGAR 5?
Frequency that methergine can be given? What about hemabate
Methergine: every 2-4 hrs
Hemabate: every 13-90 minutes up to 8 doses (not to exceed 2mg)
Diagnostic Criteria for HELLP? (Tennessee Classification system)
- Hemolysis:
- Abnormal peripheral smear: Look for schistocytes, helmet cells, and burr cells.
- Increased bilirubin: Bilirubin levels may be elevated due to hemolysis.
- Elevated LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels should be > 600 U/L.
- Abnormal peripheral smear: Look for schistocytes, helmet cells, and burr cells.
- Elevated Liver Enzymes:
- AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) or ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase):AST or ALT levels should be > 70 U/L or twice the upper limit of normal.
- AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) or ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase):AST or ALT levels should be > 70 U/L or twice the upper limit of normal.
- Low Platelet Count:
- Platelet count: Platelet count should be < 100,000/mm3.
- Platelet count: Platelet count should be < 100,000/mm3.
For rotem, what is prolonged if you have a deficiency of factor VII?
Clotting time in the Extem
Ideal blood volume for an epidural blood patch
Approximately 20cc
A multicenter study of over 500 patients reported >95% relief of PDPH when using epidural blood patch volumes of 15 mL or greater. It was noted, however, that injection volume greater than 20 mL showed no advantage.
Normal blood gas parameters in a parturient
pH, PaCO2, PaO2, bicarbonate
7.40-7.45/30/100-107/18-20
During labor, a normal fetal scalp blood pH is considered to be greater than ...
> 7.25 is normal
7.20-7.25 is borderline
<7.20 suggests fetal distress or hypoxia
Toxic dose of chloroprocaine?
12 mg/kg
For pregnant patient's with type 1 von willebrand disease, what percentage factor VIII levels do you want? What is the treatment if below this?
>50% factor VIII levels. Treatment is desmopressin
What are the 4 nerves blocked by the TAP block?
Intercostal, Subcostal, Iliohypogastric, and Ilioinguinal
This is the year of the first reported use of neuraxial anesthesia in obstetrics by Dr. Oskar Kriese in Germany.
What is 1900?