What is the definition of a postpartum hemorrhage?
>1000 mL blood loss OR blood loss with hemodynamically unstable vital signs
What is the first step in management of a shoulder dystocia?
CALL FOR HELP
What station must the baby be at in order to consider performing VAVD?
What is the definition of chronic vs gestational HTN?
<20 weeks vs >20 weeks onset of SBPs >140 or DBPs >90 on two separate occasions, greater than 4 hours apart
What is the definition of labor
Cervical change and regular contractions
What is the difference between primary versus secondary PPH?
Primary = occurs within 24 hours of delivery
Secondary = occurs 24 hours to 12 weeks postpartum
McRoberts and Suprapubic pressure
What obstetric emergency must you anticipate (what can we cause) if you are to perform a VAVD?
Shoulder Dystocia
What is the definition of pre-eclampsia without severe features
What is the definition of active labor?
What are the 4 etiologies of PPH?
T - Tone (atony)
T - Trauma (lacerations)
T - Tissue (retained placenta)
T - Thrombin (clotting factor loss, DIC)
What position is this fetal head in?
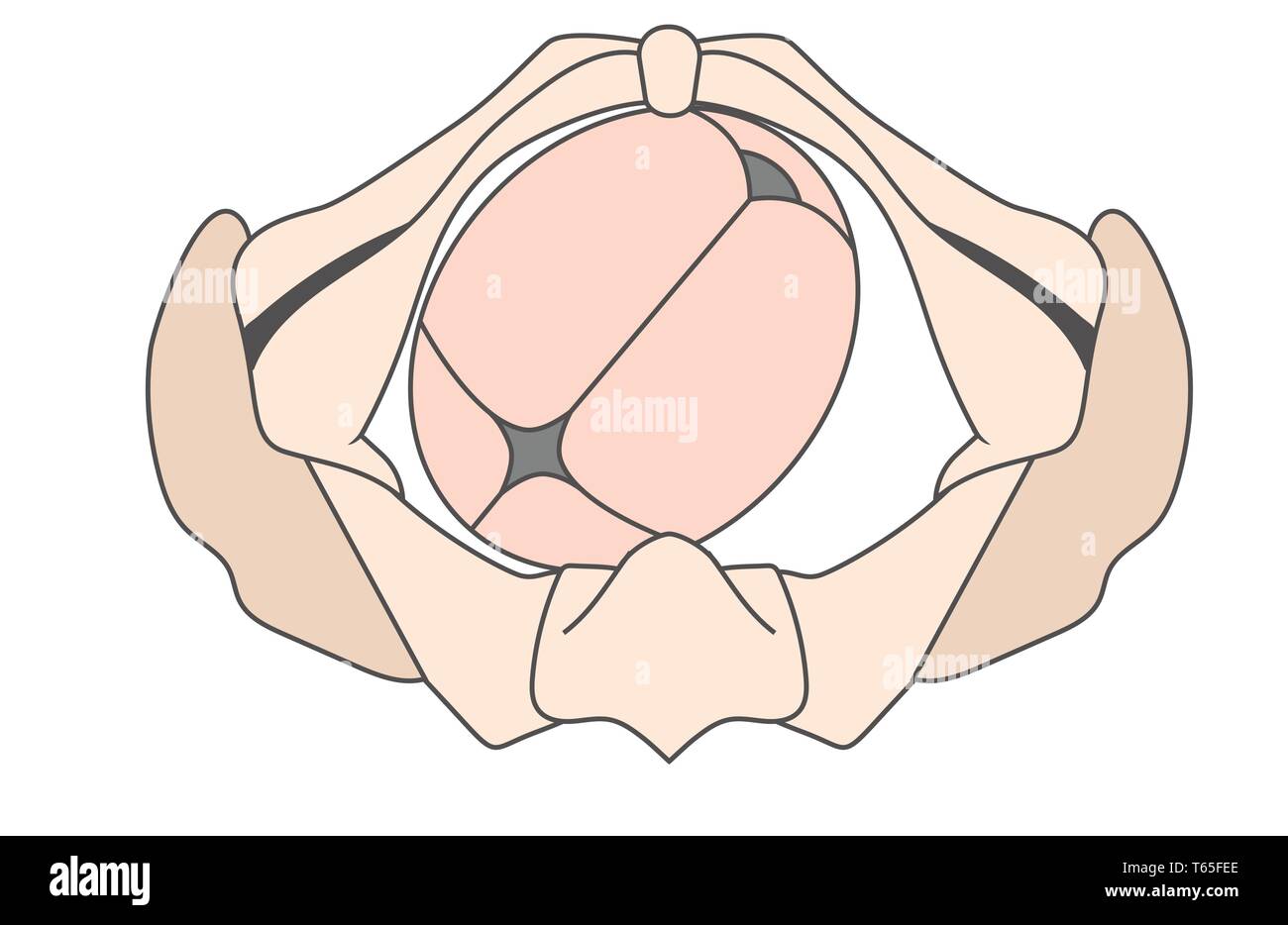
Left Occiput Anterior
Describe where the vacuum is applied, use anatomic markers
3 cm anterior to the posterior fontanelle
MR BPs + presence of a severe feature:
- sustained SR BPs (>160/>110),
On 2 occasions at least 4 hours apart (or once if treatment needed immediately)
- LFTs 2x upper range
- Cr >1.1 or 2x the baseline
- Platelets <100k
- Pulmonary Edema
- Cerebral or Visual Disturbances
What is the definition of a Cat I tracing?
FHR 110-160
Moderate variability
No late or variable decels
+/- accelerations
What are the contraindications to carboprost/hemabate? Methergine?
Asthma, HTN
Define and demonstrate the rotational maneuvers
Remove posterior arm
Rubins
Woods
Reverse
What are the contraindications to performing a VAVD?
Fetal head not engaged
CPD
<34 weeks GA
Known fetal complications affecting bone
Noncephalic or face presentation
What are the delivery timing indications for pre-e w/o SF vs pre-e w/ SF
w/o SF = 37 weeks
w/ SF = 34 weeks
What separate internal instruments are used for measuring uterine strength and fetal heart rate
Intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC)
Fetal Scalp Electrode (FSE)
What are the doses of the medications you can use in a postpartum hemorrhage? BONUS points for dosing intervals
0.2 mg methergine IM, can repeat q2-4 hours
0.25 mg carboprost IM, can repeat q15-90 min (max 8 doses)
Oxytocin
- IV infusion: 10–40 units in 500–1000 mL of normal saline or lactated Ringer’s solution, at a rate titrated to uterine tone.
- IM route: 10 u IM one time
1g TXA over 10 min, can repeat 30 min
Recite the entire HELPER pneumonic
H - call for HELP
E - evaluate position, episiotomy
L - Legs in McRoberts
P - SupraPUBIC pressure
E - Enter
R - Remove Posterior Arm
R - Rotational Maneuvers (Rubins, Woods, Reverse)
R - Roll Over
R - Repeat
Recite the Entire A-J pneumonic
Address the patient and discuss risks vs benefits
Ask for help
Assess Anesthesia
Bladder should be emptied
Cervix fully dilated and retracted
Determine fetal head position
Equipment check for adequate suction
Flexion point application of the vacuum (3cm from posterior fontanelle, 6 cm from anterior fontanelle,along sagittal suture)
Gentle traction after applying suction
Halt after 1) 3 pop offs, 2) after 20 minutes, 3) between pushes, 4) after 3 pulls with no progress
Incision (episiotomy) if absolutely necessary
Jaw visible? Remove vaccum
What are the medication names, dosing, and timing intervals for acute HTN management?
LabeTolol = repeat blood pressure in 10 min, administer in 20 mv IV > 40 mg IV > 80 mg IV
Hydral = repeat blood pressure in 20 minute, administer in 5 mg IV > 10 mg IV
Nifedipine = repeat blood pressure in 20 min, 10 to 20 mg PO IR
What is the definition of failure to progress?
Failure of cervix to dilate after 4 hours of adequate contractions in a patient with cervical dilation >6 cm and with ROM OR after 6 hours of inadequate contractions in a patient with cervical dilation > 6 cm and with ROM