Three types of non-pharmacological interventions used to enhance relaxation and decrease pain during childbirth - T3.3
What is effleurage, counterpressure, & water therapy?
Pg. 310 BOX 14.2
Mary is a 27-year-old, G1 P1, who gave birth vaginally 2 hours ago to a term female infant weighing 8 lb 12 oz (3970 g) after a 13-hour labor. She had a second-degree perineal tear that was repaired. Mary is now on the Mother-Baby Unit. Her vital signs on admission are: Temp 99 (37.2 C), Pulse 94, Respirations 20, B/P 120/80. The nurse performs a postpartum assessment. The fundus is boggy, located 2 fingerbreadths above the umbilicus, and displaced to the right. The lochia flow is heavy with several clots larger than a quarter.
Highlight the signs that would indicate uterine atony and excessive bleeding after birth.
- infant weighing 8 lb 12 oz (3970 g)
- 13-hour labor
- fundus is boggy, located 2 fingerbreadths above the umbilicus, and displaced to the right
- lochia flow is heavy with several clots larger than a quarter
Pg. 462
Which vitamin is not present in breast milk?
What is Vitamin D
Indication for all three newborn meds (Hep B, Erythromycin, & Vitamin K)
Hep B: Prevent liver hepatitis
Erythromycin: Prevent bacterial eye infections (STD's)
Vitamin K: Provide clotting factors for infant
The connective tissue that surrounds the umbilical cord & protects the veins and arteries
What is Wharton's Jelly?
pg. 152
This emergency occurs when the fetus passes meconium prior to delivery. May or may not cause fetal distress.
What is Meconium-Stained Amniotic Fluid?
Correct nursing interventions during the first stage of labor include which of the following?
A. Encourage patient to take a warm shower or bath.
B. Restrict activity to lying in bed for safety reasons.
C. Encourage Holly to change position every 2 h.
D. Encourage Holly to void every 4 h.
E. Give Holly sips of water and ice chips.
F. Encourage use of birthing balls.
What is:
A, C, E, F
T3.2
Describe what kind of patient education could be provided to help relieve perineal pain T5.1
Apply ice packs in the first 24 h.
Apply witch hazel compresses.
Encourage use of soft pillows and donuts when sitting.
Encourage prescribed perineal creams, sprays, or ointments.
Pg. 462
Which type of infants are at risk for hypoglycemia?
Preterm or late preterm; SGA or LGA; low birth weight; infants of mothers with diabetes; and infants who experienced perinatal stress such as asphyxia, cold stress, or respiratory distress
Pg. 559
A patient arrives to OB Triage with a B/P of 176/100, +3 DTR's, a constant headache, and +2 pitting edema of her lower extremities. Which medication should be administered and what nursing assessments should take place?
What is: Magnesium Sulfate
Assessment: DTR's, lung sounds, vision changes, blood pressure, clonus, seizure precautions
Difference between oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios
What is:
Oligo - too little amniotic fluid (less than 300mL's)
Poly - too much amniotic fluid (more than 2L's)
pg. 152
This emergency is characterized by the anterior shoulder of the infant getting stuck under the public bone.
What is a Shoulder Dystocia?
Describe the difference between the first, second, third, and fourth stages of labor T3.1
1st stage: from labor onset to cervix being 10cm dilated
2nd stage: from cervix being 10cm dilated to delivery of infant
3rd stage: from delivery of infant to delivery of the placenta
4th stage: from delivery of placenta until pt is stable (about 1 hour postpartum)
pg. 328
Describe normal versus abnormal lochia presentation T5.2
Normal:
Rubra (dark red), Serosa (brownish-red or pink), Alba (yellowish white) scant to moderate amount, Few clots, Fleshy odor
Abnormal:
Large amount of lochia, large clots: uterine atony, vaginal or cervical laceration, Foul odor: infection Pg. 463 Table 19.1
Differentiate between physiologic jaundice and pathologic jaundice
Physiologic jaundice: occurs after 24 hours of life
Pathologic jaundice: occurs within 24 hours of life
Pg. 557
Hemorrhage medication that is held for hypertension.
What is Methergine?
Indicators that your patient will be at high risk for nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy T2.4
What is poverty, alcohol/drugs, weight at conception under or over normal weight, low hemoglobin and/or hematocrit values, poor dietary habits with resistance to change, etc.
Pg. 214 BOX 9.2
This emergency is characterized by the cord slipping in front of the fetal head when the membranes are ruptured.
What is a Prolapsed Cord?
A 19-year-old G1 P0 at 40 weeks' gestation presents to labor and delivery triage stating, “I think I am in labor!” Initial assessment findings include the following:
A. Review provider orders.
B. Discuss patient’s preferences for labor and birth.
C. Prepare for general anesthesia.
D. Administer Pitocin IM.
E. Provide labor support.
F. Perform fundal massage.
What is:
A, B, E
Pg. 328 T7.1
What is:
Maintaining good uterine tone & preventing bladder distention
Which is the most significant cause of heat loss for the infant during first few days of life?
A. Convection B. Radiation C. Evaporation
D. Conduction
C. Evaporation
In the newborn, heat loss by evaporation occurs as a result of moisture vaporization from the skin. This heat loss is intensified by failing to completely dry the newborn after birth or with bathing.
Pg. 514 T6.1
In relation to the contractions, when is the appropriate time to give IV pain meds during labor? T3.4
What is: during a contraction (pg. 353)
Describe the fetal lie, presentation, presenting part, and attitude of this baby. 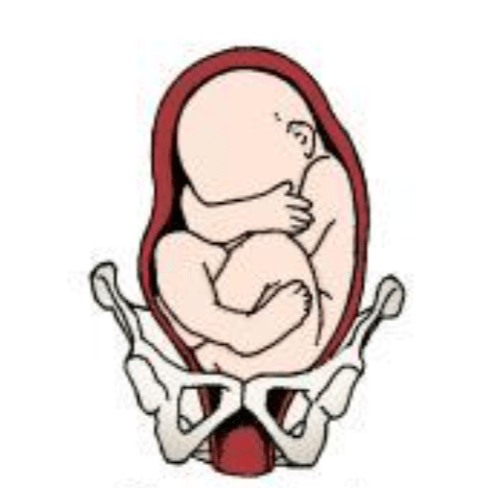
Lie: Longitudinal or vertical
Presentation: Breech
Presenting Part: Sacrum
Attitude: General Flexion
pg. 319 FIGURE 13.2
This emergency is characterized by a loss of fetal station, sharp abdominal pain, change in FHT category, & bright red bleeding.
What is Uterine Rupture?
Identify signs and symptoms that a laboring patient has developed an infection.
Maternal fever (>100.4 *F), fetal tachycardia, uterine tenderness upon palpation, maternal chills, foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
Pg. 435
If a postpartum woman complains of extreme perineal pain, especially after having received pain medication, the first action by the nurse should be to... T5.2
Assess the perineum.
There may be a hematoma or perineal infection that is causing the pain. Although rare, an unusual degree of pain can be a sign of serious complications, including perineal cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, or angioedema.
Pg. 465
Identify at least 3 physiological adaptations the newborn must make to survive extrauterine life. T6.1
(1) establishing and maintaining respirations; (2) adjusting to circulatory changes; (3) regulating temperature; (4) ingesting, retaining, and digesting nutrients; (5) eliminating waste; and (6) regulating weight
Pg. 511
Medication that can be used for high blood pressure and preterm labor.
What is Nifedipine?
Type of pelvis shape most likely associated with an OP (Occiput Posterior) presentation of the fetus.
Anthropoid
(Platypelloid is most commonly found in transverse presentations)
Pg. 325 Table 13.2
This emergency is called an anaphylactoid syndrome. It is characterized by a sudden, acute onset of hypoxia. hypotension, and hemorrhage caused by coagulopathy.
What is an Amniotic Fluid Embolus?