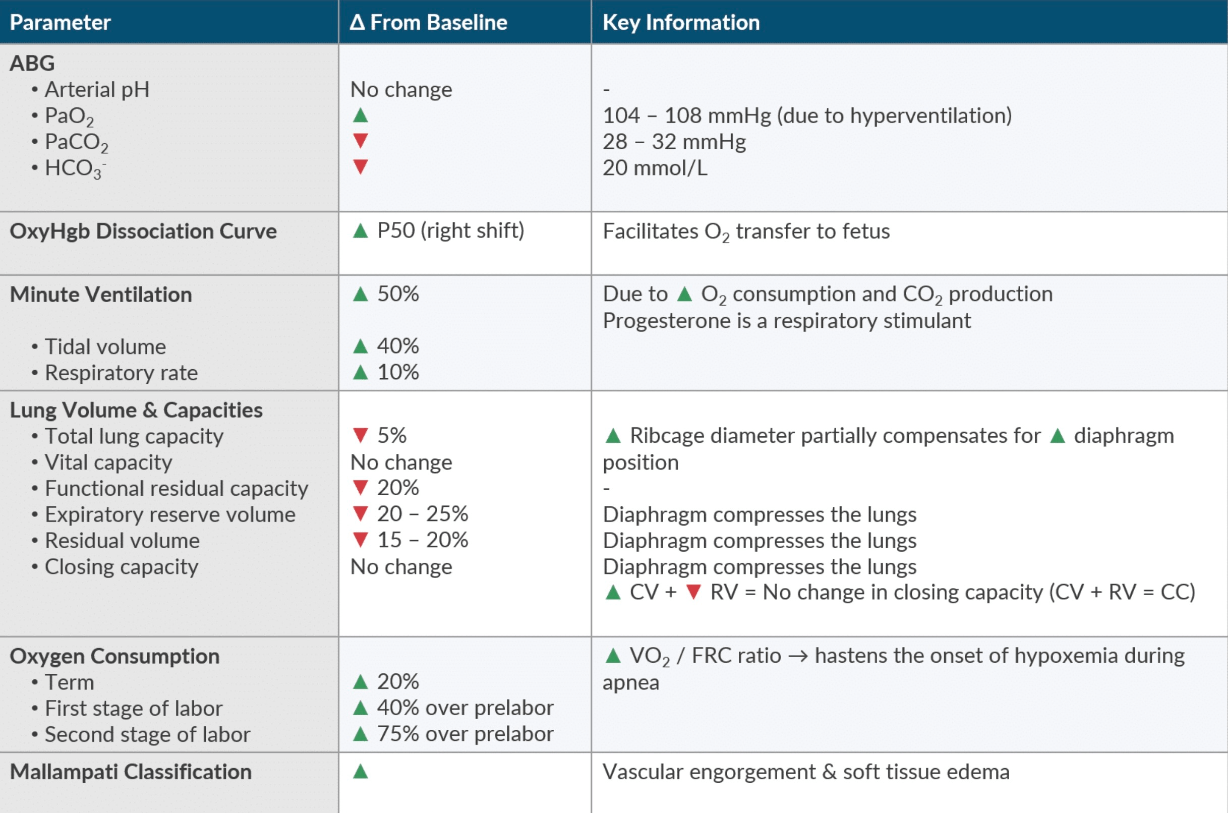
In the parturient patient, vascular engorgement and and soft tissue edema causes the Mallampati Classification to ___.
✦ Increase
✦ The glottic opening is narrowed: downsized (6.0-7.0) EET should be used.
✦ Additionally, the tissue in the nasopharynx is particularly friable because of the number of hormonal changes and local edema. Hence why nasal intubation should be avoided in full term mothers.
Which hemodynamic variables increase during pregnancy? (Select Two)
a. Heart Rate
b. Stroke Volume
c. SVR
d. PAOP
a. Heart Rate
b. Stroke Volume
✦ Stroke volume is increased as a function of increased intravascular volume, while the HR is increased to satisfy higher metabolic demand.
✦ In the vascular smooth, increase progesterone stimulates nitric oxide release. This reduces SVR.
✦ Additionally, dilutional anemia also contributes to the reduction in SVR.
✦ PAOP is unchanged.
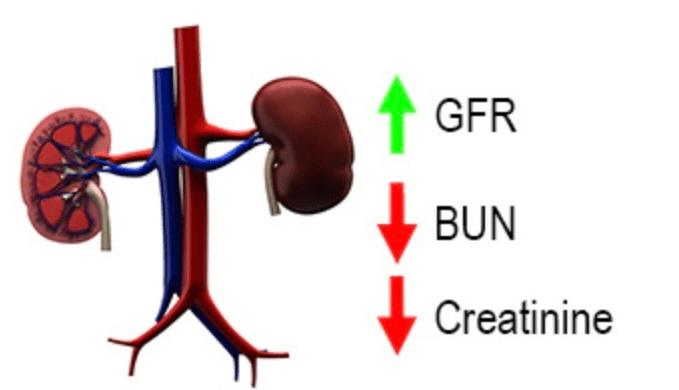
Pregnancy typically produces:
a. An increase in GFR
b. An increase in serum creatinine level
c. An increase in BUN
d. A decrease in renal blood flow
a. An increase in GFR
✦ During pregnancy, the GFR increases from about 140 ml/min to 160 ml/min as a result of an increase
Uterine blood flow is: (Select two)
a. 20% of the cardiac output
b. 700 ml/min
c. Not autoregulated
d. Reduced by phenylephrine (at clinical dosing)
b. 700 ml/min
c. Not Autoregulated
✦ At term, the UBF increases up to 700-900 ml/min
✦ UBF is 10% of CO
✦ UBF is not autoregulated → it dependent on maternal MAP, cardiac output, uterine vascular resistance
✦ UBF is not reduced by phenylephrine (actually can increase if being given for hypotension)
The MAC of volatiles is affected by pregnancy. Is it increased or decreased, and to what extent (%) at term pregnancy?
Extra credit (200): What endogenous hormones or molecules are responsible for this change? (2 total, must mention both)
✦ MAC progressively decreases during pregnancy, at term, by as much as 40%.
✦ MAC returns to normal by the third day after delivery.
✦ Extra credit: Progesterone, β-endorphins
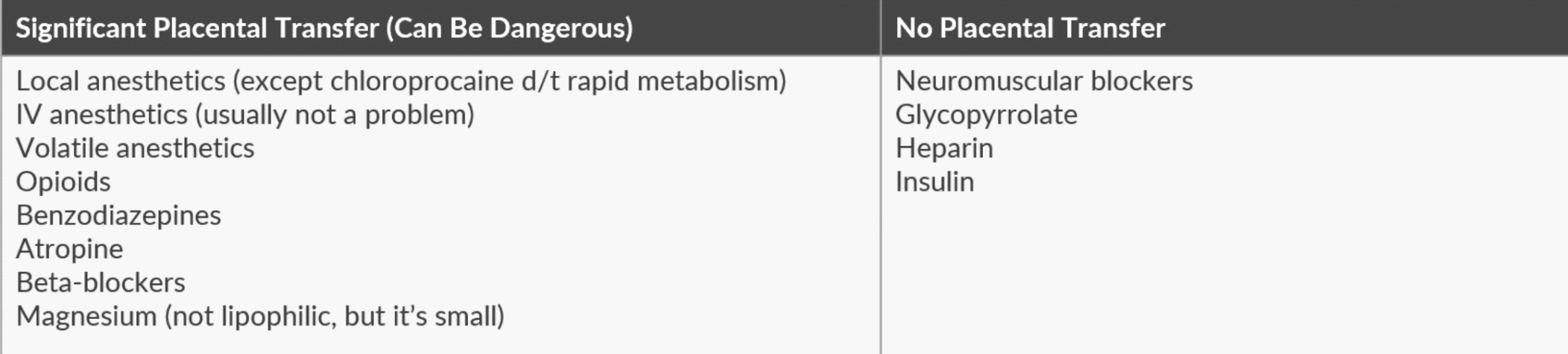
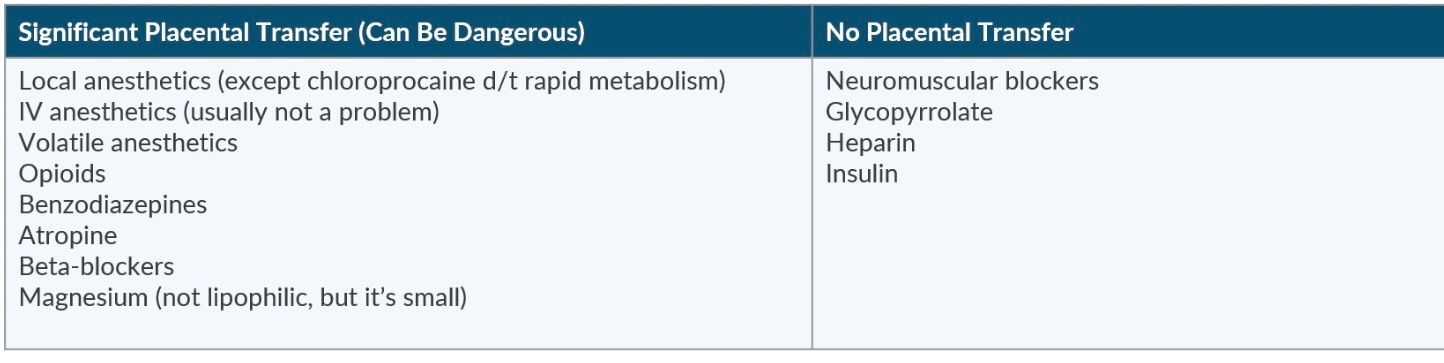
Name 3 drugs that do not cross the placenta
✦ Heparin (Highly charged)
✦ Insulin
✦ Glycopyrrolate (Hydrophilic – Quaternary amine structure)
✦ Non-depolarizing NMBA (ionized, high molecular weight, poor lipid solubility)
✦ Succinylcholine (highly ionized)
"He Is Going Nowhere Soon"
The greatest increase in maternal cardiac output occurs ___.
a. During the first stage of labor
b. During the second stage of labor
c. Immediately after delivery
d. During the first trimester
c. Immediately after delivery
✦ By term, the cardiac output will increase up to 40% above baseline.
✦ During labor the cardiac output can be be as high as high as 12 to 14L/min.
✦ It reaches its peak (80% above baseline) immediately after delivery.
✦ It is during this time that patients with pre-existing cardiac issues have an increased risk for decompensation.
✦ The cardiac output gradually returns to normal in a timespan of about two weeks.
In the obstetric population, RSI should be implemented at __th week of gestation.
✦ 20th Week
✦ At the 20th week:
1. Lower esophageal sphincter pressure is decreased
2. Gastric volume exceeds 25mL
3. Gastric pH is below 2.5 (Gastrin is secreted by the placenta → increases gastric H+ secretion)
✦ Increasing the risk of aspiration and adverse events.
Which local anesthetic will cross the placenta the least?
a. Chloroprocaine
b. Ropivacaine
c. Lidocaine
a. Chloroprocaine
✦ Due to its rapid metabolism
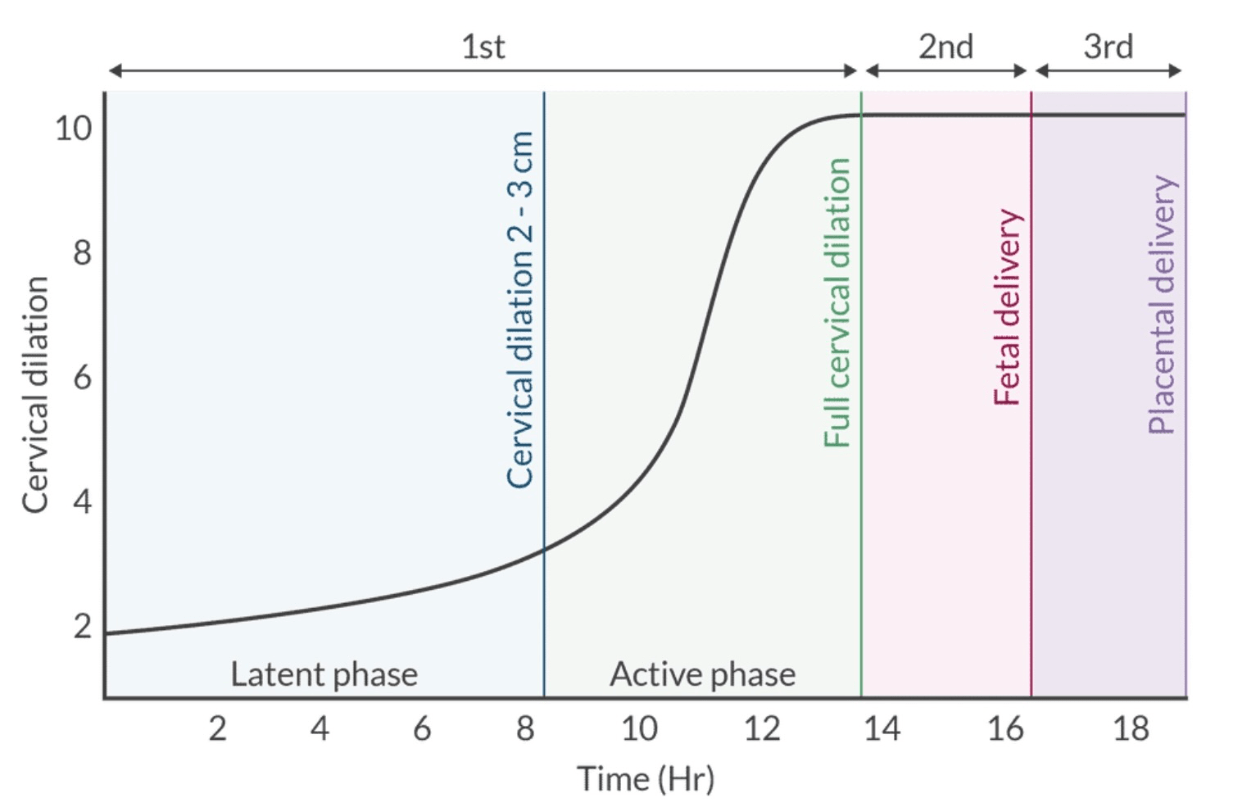
Which stage of labor begins with the onset of perineal pain?
✦ Second Stage
✦ First stage begins with cervical dilation with regular uterine contraction and ends with full cervical (10cm). It is divided into the latent phase and active phase of labor.
✦ The second stage begins with full cervical dilation and ends with the delivery of the newborn.
✦ The third stage begins with the delivery of the newborn and ends with the delivery of the placenta.
The leading cause of death of parturients receiving general anesthesia is due to ___.
✦ Difficult and failed intubation
✦ In fact, difficult and failed intubation is 8x higher in the full-term patient.
✦ Side Note → Due to the anatomical changes that occur during pregnancy, a short handled laryngoscope (Datta handle) should be considered. This can be especially useful in women with large breasts.
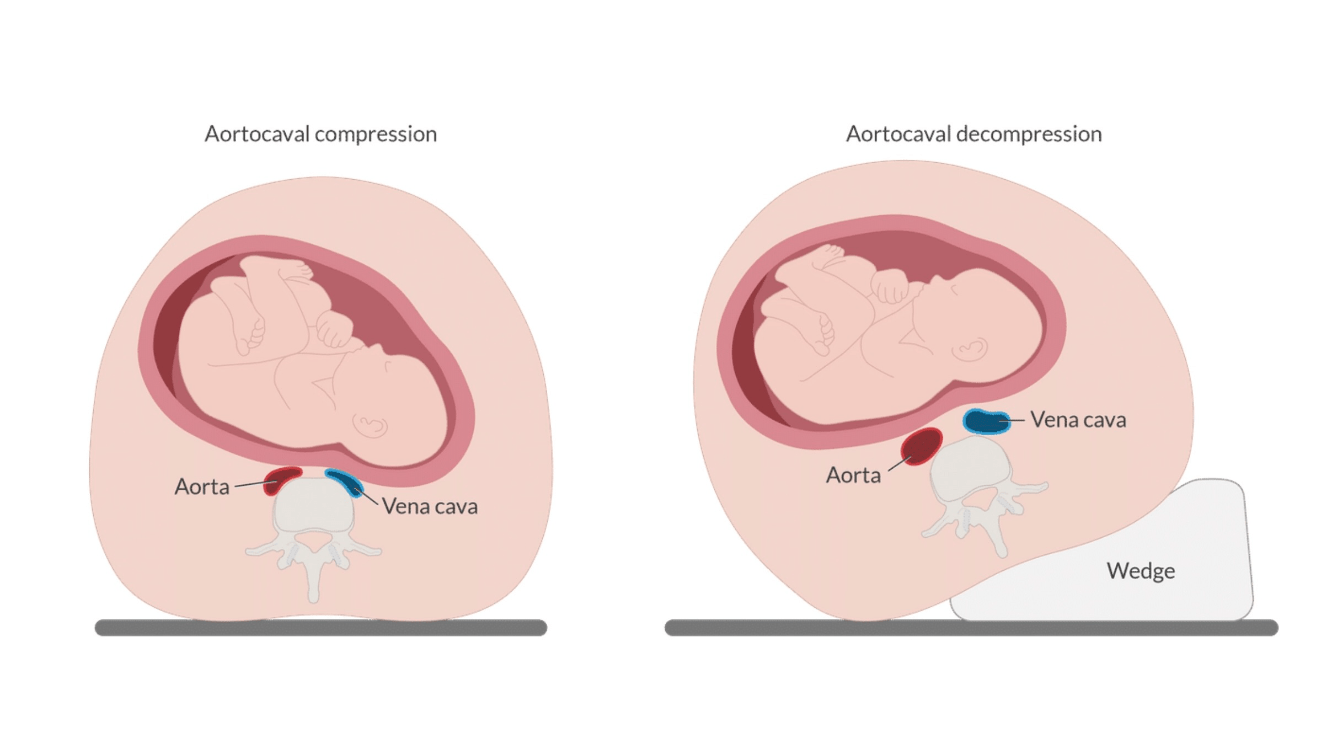
True or False: Left uterine displacement can be accomplished by tilting the mothers right torso by 5- to 10 degrees.
✦ False! Should be a tilt of about 15- to 30 degrees.
✦ Aortocaval Compression or "syndrome of supine hypotension" occurs when the maternal patient is in the supine position → the gravid uterus begin to compress both the vena cava and the aorta.
✦ In turn:
1. This decreases venous return to the heart as well as arterial flow to the uterus and lower extremities
2. Decreased cardiac output compromises fetal perfusion and can also cause the mother to lose consciousness.
✦ By displacing the uterus away from the vena cava & aorta, we can reduce its compressive effect.
✦ It should be implemented during the second and third trimester.
Pseudocholinesterase level __ throughout pregnancy.
✦ Decreases
✦ It decreases by 30% during the first two trimesters
✦ However, proongation of the DOA of drugs that depend on cholinesterase for metabolism and elimination such as succinylcholine & Ester LA's are uncommon.
Drug characteristics that favor placental transfer include:
✦ ___ molecular weight
✦ ___ lipid solubility
✦ Ionized or unionized?
✦ Polar or non-polar?
✦ Low molecular weight: < 500 Daltons readily cross the placenta
drugs > 1,000 Da (eg, heparin, protamine, insulin) do not readily cross the placenta
✦ High lipid solubility
✦ Non-ionized
✦ Non-polar (No Charge)
Drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins are less likely to cross the placenta. Unbound fractions may still cross. Mom has 50% more plasma proteins vs fetus and thus maintains a higher concentration of protein-bound drugs (eg, bupivacaine and ropivacaine)
Describe the 3 stages of labor.
✦ Stage I: Onset of true labor (regular contractions) → complete cervical dilation (10cm). 2 phases.
-- Latent phase: regular, painful contractions without much cervical dilation. Cervix may efface. Duration can be extensive ( ~ 20h for primigravida, < 14h for multiparous).
-- Active phase: Rate of cervical dilation increases (nulliparous: ~ 1.2 cm/h, multiparous: ~ 1.5 cm/h)
✦ Stage II: Complete cervical dilation → delivery
✦ Stage III: Delivery of baby → delivery of placenta
Minute ventilation will progressively __(increase/decrease)__ by up to ____% by term pregnancy
This is primarily due to an increase in what hormone?
Extra 100 points: What contributes more to the increased MV--- TV or RR?
✦ Increase → Minute Ventilation will increase by up to 50% to meet metabolic demands
✦ Progesterone is a respiratory stimulant, and also causes a leftward shift of the CO2-ventilatory response curve.
✦ Decrease in FRC coupled with an increase in Minute Ventilation accelerates the uptake of inhaled anesthetics!
✦ Extra: Increased MV is primarily due to increased TV (450 → 600). Small contribution from increased RR (↑ 1-2 breaths/min). Respiratory alkalosis occurs as the PaCO2 is decreased by ~ 10 mm Hg (40 → 30 mm Hg) by the end of the 1st trimester.
Due to the systemic alterations that occur in the obstetric population, the MAP ___.
a. Increases by 15%
b. Decreases by 15%
c. Remains unchanged
c. No change
✦ Progesterone causes vascular muscle relaxation. Leading to a decrease in SVR and PVR, which creates an increase in blood flow.
✦ ↑ blood flow + ↓ SVR = Net even effect on MAP

In pregnancy, insulin resistance:
a. Increase due to the effects of epinephrine
b. Decrease due to follicle stimulating hormone
c. Decrease due to the effects of estrogen
d. Increase due to the effects of lactogen
d. Increase due to the effects of lactogen
✦ Maternal insulin requirements increase in the second and third trimesters, but decrease shortly after.
✦ The increase in insulin resistance is due to the increase in lactogen
This phenomenon causes the accumulation of local anesthetics in fetal blood during fetal acidosis
What is ion trapping
✦ Ion trapping occurs when a pH differences across the membrane result in changes in the distribution of a drug.
✦ For example, administering a weak base like lidocaine to a laboring mother with a physiologic pH of 7.4.
✦ In its unionized state, the drug has the ability to cross through the placenta.
✦ With fetal blood being more acidic (pH of 7.25-7.35), the drug will now become ionized, leaving it unable to cross the placental barrier and back into the maternal circulation → Hence, ion trapping.
This local anesthetic is not commonly used for labor analgesia because its known to reduce the efficacy of morphine.
✦ 2- Chloroprocaine → Antagonizes the mu & kappa receptors in the spinal cord.
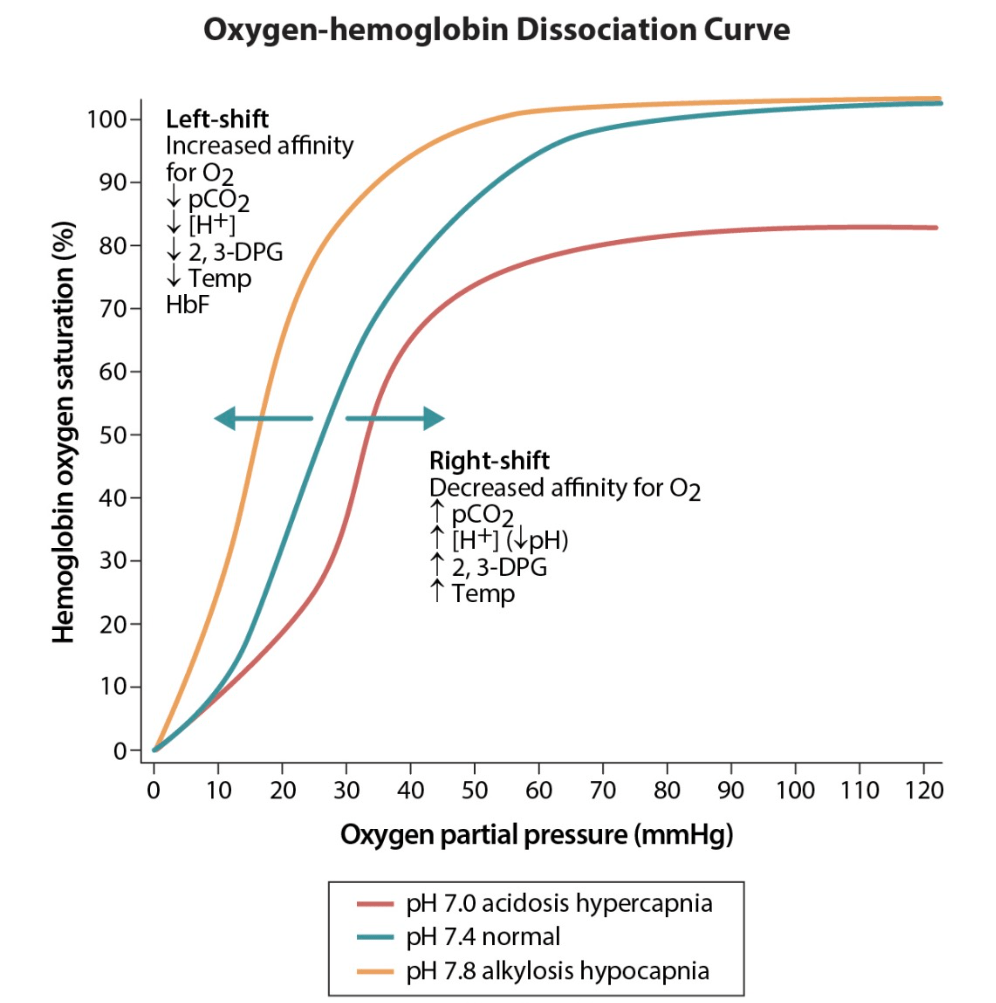
The O2-Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve will shift _____ during pregnancy.
What is the name of the effect that is taking place within maternal circulation that facilitates O2 unloading?
✦ Rightward. There is a decreased affinity for O2 ("Right = Release"), which facilitates O2 transfer to the fetus.
✦ The Bohr effect: increased release of O2 from Hgb in the presence of higher CO2 levels. Fetal CO2 diffuses across the placenta creating local acidification of maternal blood → Diminishes O2 affinity & causes rightward shift. Conversely, fetal blood becomes more alkalotic (leftward shift) due to the CO2 unloading and therefore increases it's affinity for O2
✦ B.O.H.R (Bohr, Organs, H+, Right Shift)
✦ H.A.L.D. (Haldane, Alveoli, Left shift, Decarboxylation)
✦ Maternal Hyperventilation → Leftward shift of the OxyHgb Curve → Uterine artery constriction → Reducing oxygen delivery to the fetus → Increasing the risk of fetal asphyxia
Pregnancy is considered a hypercoagulable state. Name 3 clotting factors that increase in pregnancy.
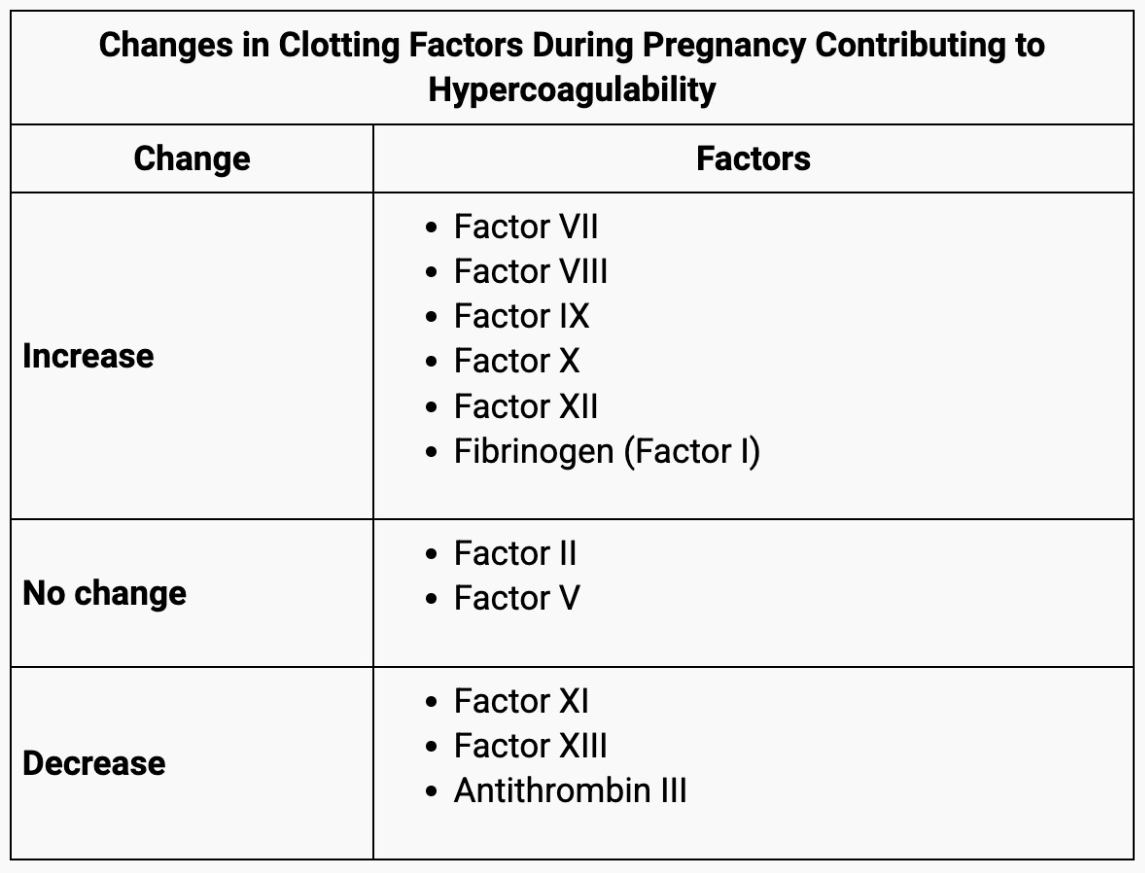
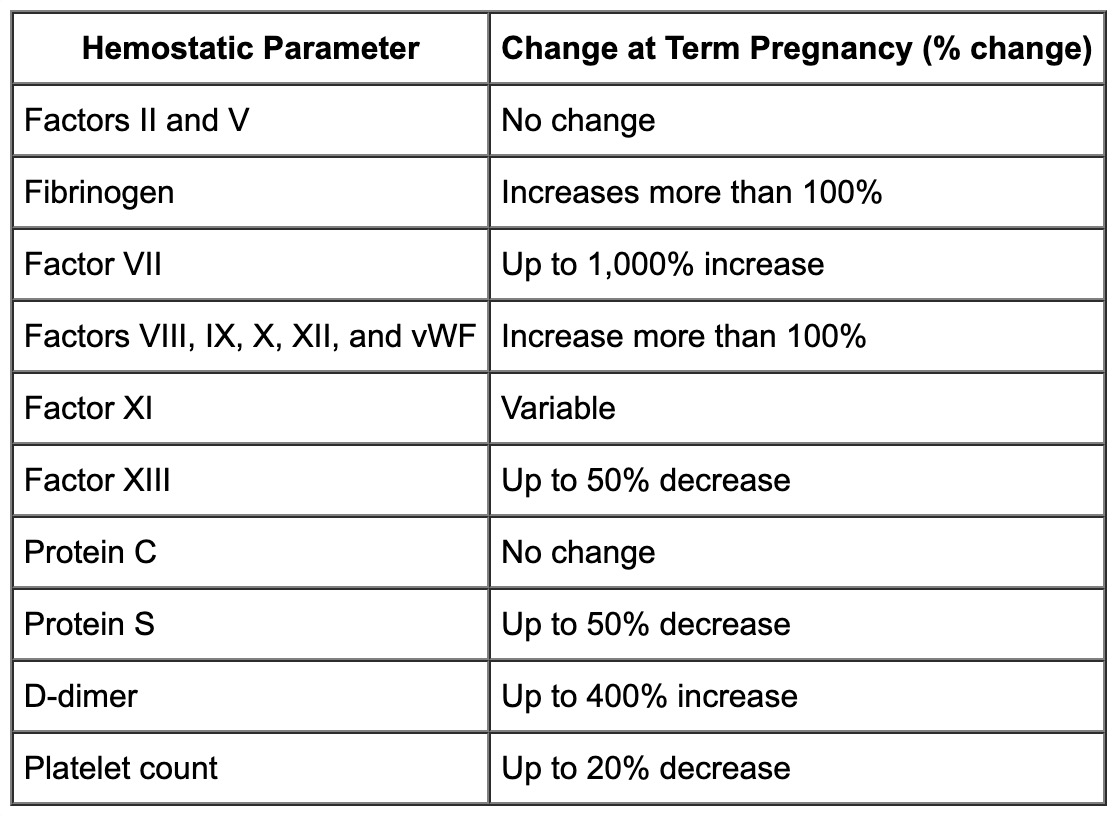
✦ Anticoagulants: ↓ Antithrombin & Protein S, however no change with Protein C.
Which factors are expected to increase during pregnancy (Choose 3)
a. Creatinine Clearance
b. Lower Esophageal Sphincter Tone
c. Sensitivity to LA
d. MAC
e. Gastric pH
h. Urine Glucose
a. Creatinine Clearance
c. Sensitivity to LA
h. Urine Glucose
✦ Creatinine Clearance increases as a function of increased intravascular volume and cardiac output → more creatinine is delivered to the kidney per unit time.
True or False: Due to magnesium's high lipid solubility, it can easily cross the placenta.
✦ False → Magnesium is not lipophilic, however it is has a low molecular weight making it able to cross through the placenta.
Name 2 tocolytic agents
✦ Terbutaline, Ritodrine (β2 agonists)
✦ Magnesium sulfate
✦ Nifedipine
✦ Indomethacin, Keterolac (NSAIDS)