Name the different types of prompting.
Gestural, visual, verbal, textual/written, auditory or physical
Name 5 ADLs.
Bathing, dressing, self-feeding, functional mobility/transferring, toileting and toilet hygiene, and grooming
Name 5 IADLs
1. Communication management
2. Driving and Community mobility
3. Financial management
4. Home management
5. Meal preparation and clean-up
6. Safety
7. Shopping
8. Medication management
What are the benefits of sensory input?
Self-regulation, achieving optimal level of arousal, enhanced motor planning ability, improved function in school and ability to perform daily activities, etc.
pencil grip, slanted writing board, tactile paper, loop scissors, etc.
Name some areas that OT addresses.
ADLs, IADLs, Fine Motor/Upper extremity function, gross motor skills, leisure, executive functioning, etc.
Name the steps of brushing your teeth.
1. Gather needed items (toothbrush, toothpaste, access sink, etc).
2. Take cap off toothpaste.
3. Get toothbrush.
4. Put toothpaste on toothbrush.
5. Thoroughly brush all areas of mouth.
6. Spit out toothpaste.
7. Thoroughly rinse mouth.
8. Clean toothbrush with water.
9. Put cap on toothpaste.
10. Put toothbrushing supplies away.
Name the steps to making a peanut butter and jelly sandwich.
1. Gather needed items.
2. Put bread on plate
3. Spread peanut butter on a slice of bread.
4. Spread jelly on the other slice of bread.
5. Put bread together.
6. Eat
7. Clean-up
Name 2 types of sensory input.
Visual, auditory, taste, touch, vestibular, and proprioception
What are fine-motor skills? Give an example of a task that requires fine motor skills.
Ability to make movements using the small muscles in our hands and wrists.
Examples: Holding a pencil, writing, holding eating utensils, cutting paper, cutting food, etc.
What are the different levels of assistance?
Minimal (25%), moderate (50%), maximum (75%), supervision, set-up assist, modified independent (independent with task accommodations), and independent (100%)
What is the difference between eating and self-feeding?
Eating is the act of chewing and swallowing food. Self-feeding is the physical act of bringing food from plate to mouth.
Fill in the blank: IADLs are activities that allow an individual to live independently in the _______ .
Community
Name 3 items used to give a student sensory input.
body sock, weighted vest, jumping, spinning, wall push-ups, heavy work-laundry tasks/chores
What are visual-motor skills? Give an example of a task that requires visual-motor skills.
Ability to interpret visual information and respond with a motor action.
Examples: handwriting, copying shapes, catching a ball, using an iPad for communication, tying shoe laces, etc.
Name 3 things that occupational therapy can help improve.
ADLs, IADLs, fine motor skills or upper extremity function, gross motor skills, sensory processing, cognitive skills, visual-perceptual skills, etc.
Name one way an OT could help a student perform ADLs more independently.
-OTs can perform comprehensive ADL assessments with a holistic perspective taking into account physical and cognitive abilities.
-OTs are experts in task analysis.
-OTs can help our student's develop the skills needed to perform the task.
-OTs can provide task or environmental adaptations to increase a student's success with a task.
Name 2 reasons why our students may need assistance for IADL participation.
Impaired physical or cognitive ability, sensory issues, psychological issues, problems with vision, behavioral issues, poor safety awareness
What is the difference between Sensory Seeking vs. Sensory Avoiding?
Most sensory seekers are under-sensitive to input and look for more sensory stimulation.
Most sensory avoiders are oversensitive and may experience sensory input more intensely.
Visual Perception: Which image matches the top?
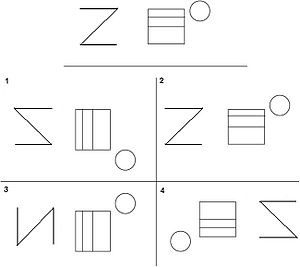
2!
The unique focus of OT is "occupations"; what is an occupation in OT?
Everyday activities that people do as individuals to occupy time and bring meaning and purpose to life.

What are some signs that a student is having difficulty performing ADLs? What should be done?
Wearing the same clothes everyday, needing significantly increased time for tasks, behavioral issues during ADLs, overly sensitive to ADL tasks, difficulty with manipulating zippers, buttons, or shoelaces, etc.
Collaborate with OT!
What makes IADLs different than ADLs?
IADLs require more complex thinking or cognitive ability
True or False: It does not matter what kind of sensory input a student receives as long as the student is happy.
False!
Our sensory systems are complex and any sensory input provided should be specifically individualized to the student. Consult OT!
Name 3 ways an OT could help improve a student's participation in the classroom.
-Improving participation in school routines.
-Specific skill development (fine motor, visual-motor, visual-perception, executive functioning, etc).
-Developing individualized sensory interventions.
-Improve self-care skills.