This type of ocean current is driven by the wind?
a. Deep ocean current
b. Surface ocean current
c. Both A and B
What is b. Surface ocean current?
In what zone does approximately 90% of all ocean life live?
a. sunlight
b. twilight
c. midnight
What is a. sulight?
Which ocean floor feature is labeled "F"?
a. Continental shelf
b. Abyssal Plain
c. Ocean trench
d. Continental slope
What is a. Continental Shelf?
90% of sunlight is absorbed at the surface of the ocean, keeping the surface ___________ in temperature.
a. Cold
b. cold and warm
c. warm
What is c. warm?
This is the regular rise and fall of sea levels due to the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun.
a. currents
b. waves
c. tides
d. hurricanes
What is c. tides?
This ocean current is driven by differences in water temperature and salinity, aka differences in density.
a. Deep ocean current
b. Surface ocean current
c. Neither
What is a. Deep Ocean current?
As oceans become deeper, the water pressure ___________________.
a. decreases
b. increases
c. stays the same
What s b. increases?
"D" on the diagram labels the...
a. Trench
b. Mid-ocean ridge
c. seamount
d. Volcanic Island
What is b. mid-ocean ridge?
Where do hurricanes form?
a. Near the poles
b. Near the equator
What is b. near the equator?
The process of deep, nutrient-rich water moving upward to replace surface water that has blown farther offshore is called ___.
a. downwelling
b. upwelling
c. rip current
d. longshore current
What is b. upwelling?
Which two things factor into density differences of ocean water?
a. Temperature and light
b. Temperature and Salinity
c. Color and pollution
d. Depth and Temperature
What is b. Temperature and Salinity?
The ocean layers are divided by the amount of __________________ in each layer.
a. animals
b. salt
c. light
d. people
What is c. light?
One of the main pollutants threatening the Chesapeake Bay is
a. Oil spills from ships
b. Fertilizer runoff from farms
c. Heavy metals from old sunken ships
d. Litter such as paper and bottle caps
What is b. Fertilizer runoff?
How are hurricanes categorized?
a. based on their destination
b. based on their wind speed
c. based on where they form
What is b. based on their wind speed?
A place where freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the ocean (ex. Chesapeake Bay); biodiverse ecosystem
a. Marsh
b. Swamp
c. Estuary
d. Lake
What is c. estuary?
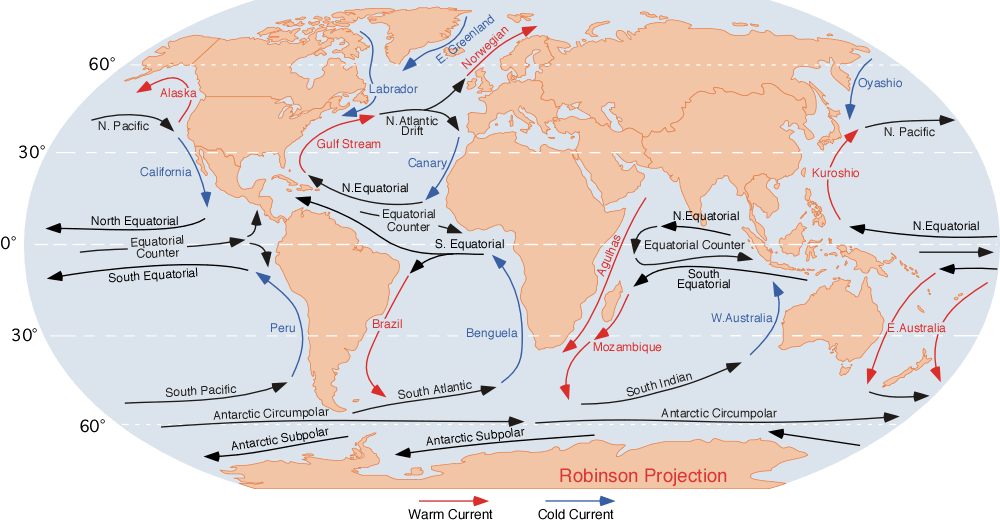
The Gulf Stream currents is a warm ocean current that travel from the Equator up the East Coast of N. America. What influence does this current have on East Coast cities?
a. Provides a cooler climate
b. Provides a warmer climate
c. Has no effect on climate
What is b. provides a warmer climate?
What is the cause of rising surface temperatures of the Pacific Ocean, drought in the western United States, and flooding on the Pacific coast of South America?
a. the Gulf Stream
b. the Jet Stream
c. La Nina
d. El Nino
What is d. El Nino?
Over 50% of oxygen in the atmosphere is produces by.........
a. dolphins
b. algae
c. underwater trees
d. bacteria
What is b. algae?
What happens as a hurricane moves further in-land?
a. it speeds up and gets stronger
b. It turns around and goes back to sea
c. It slows down and gets weaker
What is c. It slows down and gets weaker?
What type of tide is illustrated above?
a. spring tide
b. neap tide
What is b. neap tide?
This phenomenon, driven by the Earth's rotation, causes currents to be deflected to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
What is the Coriolis Effect?
Which of these processes would cause the salinity of seawater to increase?
a. Melting of sea ice
b. Formation of sea ice
c. Runoff from land
d. An increase in ocean temperature
What is b. Formation of sea ice?
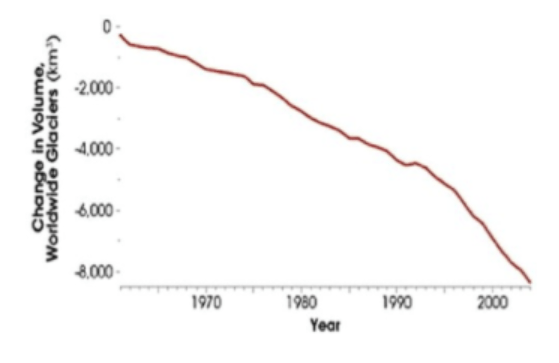 What can be inferred according to this graph?
What can be inferred according to this graph?
a. Sea levels will drop
b. Sea levels will rise
c. Ocean temperatures will get warmer
d. Earth's climate is cooling
What is b. sea levels will rise?
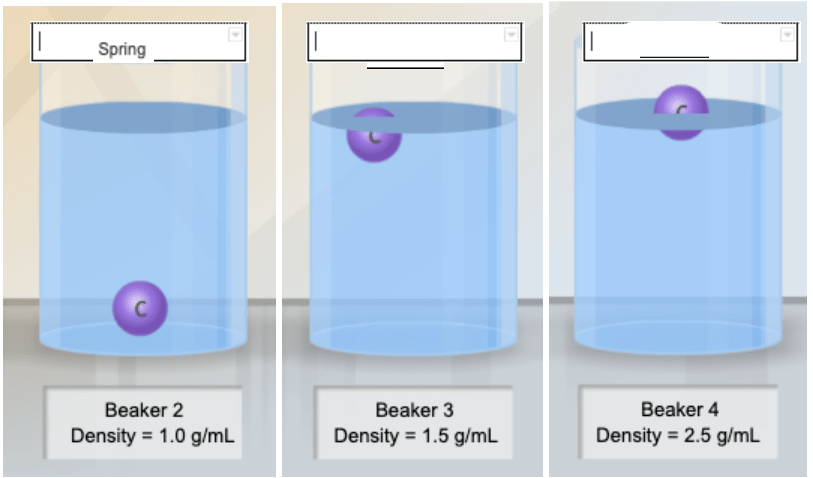
Examine the densities of the 3 beakers. Which beaker would best represent the density of ocean water?
a. Beaker 2
b. Beaker 3
c. Beaker 4
What is c. Beaker 4?
These tidal conditions occur when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are aligned, resulting in higher than normal high tides and lower than normal low tides

What is a Spring tide?



